| ANN | DNA |
|---|---|
 |
- [Os Windows]- Windows 10.
- [Node]- JavaScript run-time environment that executes JavaScript code outside of a browser
- [Language]- JavaScript Es6
- [Web Framework]- Vuejs
- [Graphs]- Google-graphs
- [Jest Test] - Testing and Mocking Framework
homework installation steps you should install nodejs '''sh $ git clone https://github.com/jthoth/AnnsJs.git $ cd AnnsJs $ npm install $ npm run test $ npm run serve '''
This homework is geared for learning or remembering those features about neural Networks. The main idea is build a class which allow us to use basic operations of training an artificial neural network.
Note: The code contains two main parts: Neural Networks classes in the folder /src/anns and all about data loading is in /src/data.
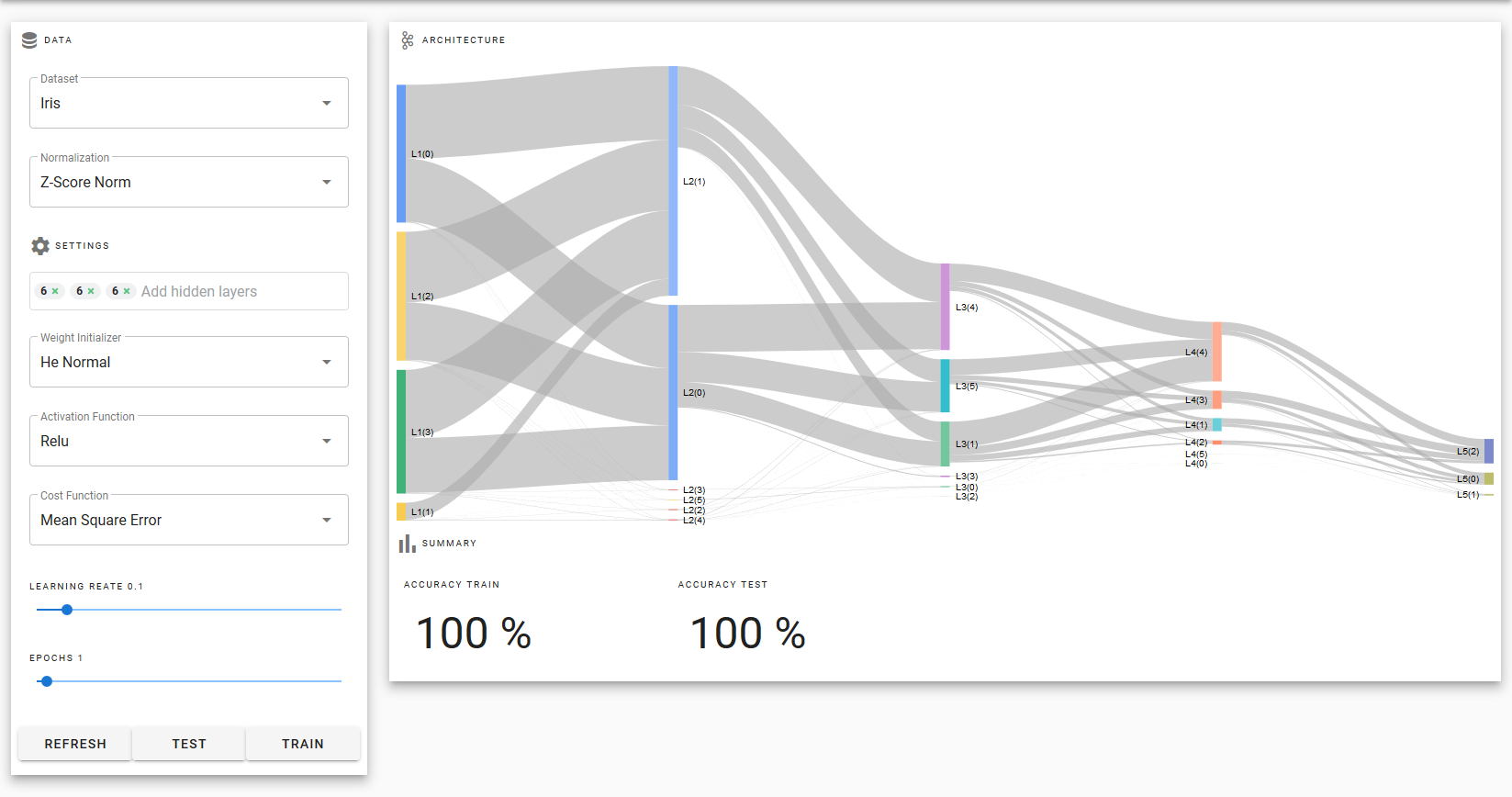
- The neural network only needs 2 to 3 iterations to learn the datasets when the weights are initialized with a normal heuristic distribution and RELU activation function.
- Vectorized implementation allows the network to converge faster
- The graph of the weights allows seeing when the network is over-adjusted, in addition you can clearly see the exploding or fading of the weights.
- The z-score standardization works best for all 3 datasets as it allows weights to converge faster.
- In conclusion the architecture is robust and dynamic.
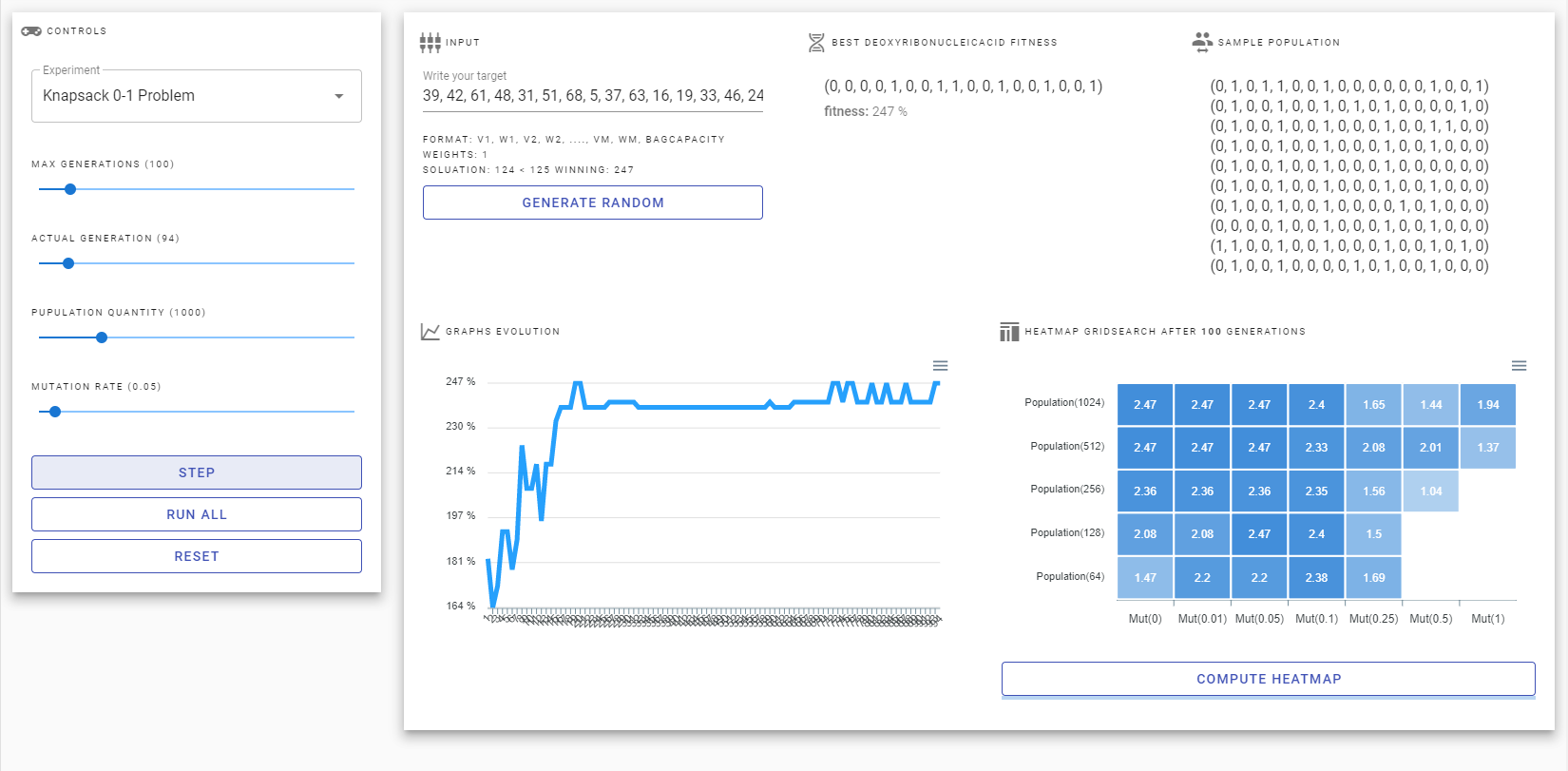
We try to solve the 0-1 Knapsack Problem (KP) using genetic algorithms, this is an optimization problem in which we used a combinatorial approach, this approach tries seeking to maximize the benefit of objects in a knapsack without exceeding its capacity. It was used a simple fitness (adding the weights which was choosing then we constrain to the max capacity, being the fitness score the profit) function due to the fact an implementation with penalties carries to odd results and the computational cost is expensive. Finally, it can be clearly notice that genes determine if something is stored in the bag, and an individual is a list of those choices
The implementation of the core algorithm only depend on of the encoder, I mean the encoder process the input as string and gives to the GA the rules to maximize the score. In addition, we build an interactive tool.
Note: The code contains two main parts: Genetic Algorithms classes in the folder /src/ga and all about using evolution in /src/components/GeneticAlgorithm.vue. In the folder GA there are the encoders this is applied for each problem.
- We found that a big mutation rate don't allow the algorithm convergence.
- The population number has a big impact also the algorithm can find a solution with zero mutation rate.
- The evolution of fitness function for easy problems is stable compared with hard problems
- Commonly for this work there are a good trade-offs between Population and mutation rate, I always mean for each problem for any population number > 64 the best mutation rate was 0.05.
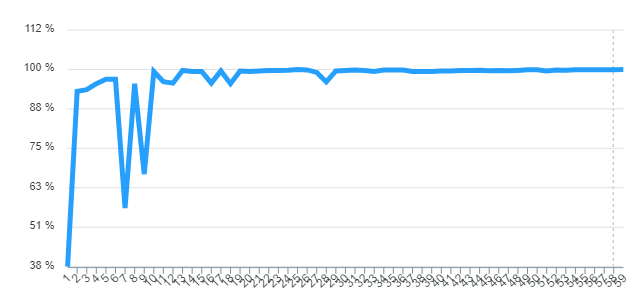
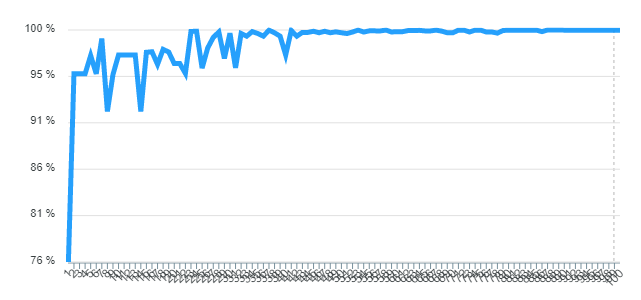
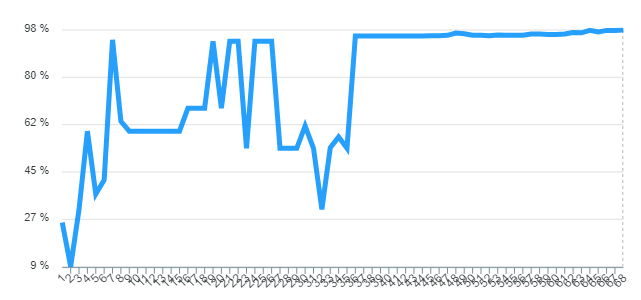
The following lines graph illustrate the score evolution over the n generations of the population. Units are measured in percent. To compute the bellow figures we only change the parameters of the panel.
Overall, the score increased over the generation given. At the start of the generation the score is high; nevertheless, in some cases it fall dramatically. With regards to the maximum score, it was reached approximately in the 33th generation approximately.
The behavior of the graph in this exercise is almost similar to the previous one, with the difference that it converges to a faster approximate score (in average), However, it takes long generations to reached the exact target.
In this case there are more fluctuations than in the previous cases. Additionally it was observed that the tree grew in depth due to the limited options of operations it had.
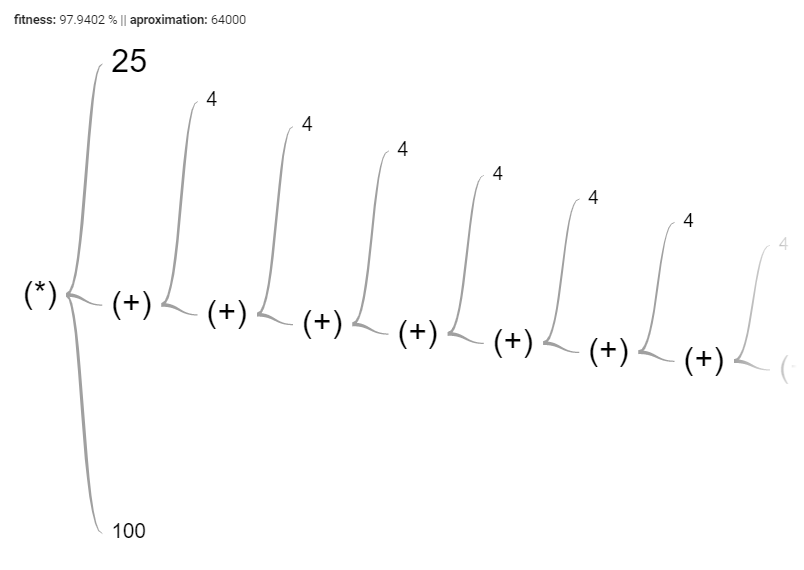
Another interesting thing found in the tree was that prefer addition operation over the rest as we can see in the next image.
To make the library of trees support variable, the only thing that was done was to pass an additional dictionary type parameter to the function that reduces the tree (eval). Additionally, a condition was added to the node terminal that verifies if it is string to retrieve from the dictionary.
class Terminal extends Node{
constructor(value){
super(()=> value)
this.value = value
}
eval(variable={}){
if(isNaN(this.value)){
return variable[this.value] || 0
}
return this.value
}
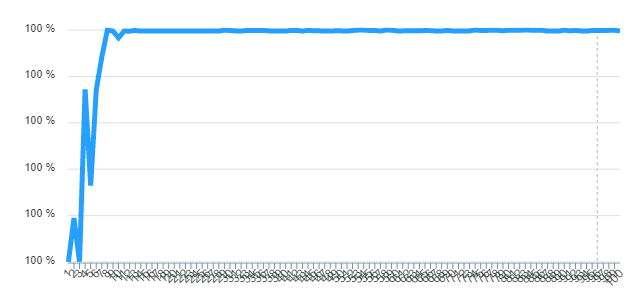
}Since the function to be approximated is not complex, with a considerable amount of population the problem can be easily resolved.
As can be seen in the figure below, the similarity between the functions is almost perfect since starting at 99% similarity, this similarity was calculated with the help of the normalized cosine distance. The idea of the objective function was to maximize the similarity.
In JavaScript does not exist Division Zero Exception, Thus only we need to add a simple characteristic to the fitness function to ignore the Nans values generated for those invalid trees
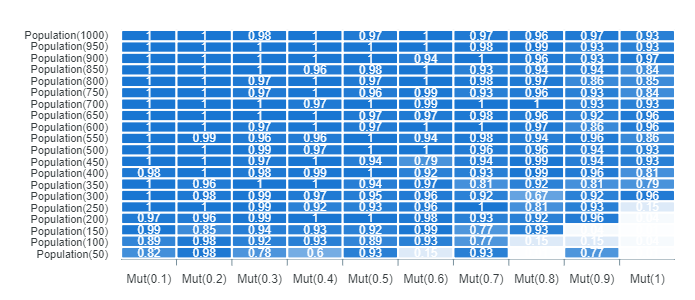
As can be seen in the following figure, a small population with little mutation rate has the worst results. Another important factor to note is that with a high mutation rate the problem does not converge to a solution.
The graph also shows us that for this problem it is advisable to use a small mutation rate with a population of 200 individuals.
MIT