fMRI from EEG is only Deep Learning away: the use of interpretable DL to unravel EEG-fMRI relationships
Alexander Kovalev, Ilya Mikheev*, Alex Ossadtchi
BEIRA - domain grounded interpretable convolutional model for predicting subcortical BOLD singals from EEG activity.
The access to activity of subcortical structures offers unique opportunity for building intention dependent brain-computer interfaces, renders abundant options for exploring a broad range of cognitive phenomena in the realm of affective neuroscience including complex decision making processes and the eternal free-will dilemma and facilitates diagnostics of a range of neurological deceases. So far this was possible only using bulky, expensive and immobile fMRI equipment. Here we present an interpretable domain grounded solution to recover the activity of several subcortical regions from the multichannel EEG data and demonstrate up to 60% correlation between the actual subcortical blood oxygenation level dependent sBOLD signal and its EEG-derived twin. Then, using the novel and theoretically justified weight interpretation methodology we recover individual spatial and time-frequency patterns of scalp EEG predictive of the hemodynamic signal in the subcortical nuclei. The described results not only pave the road towards wearable subcortical activity scanners but also showcase an automatic knowledge discovery process facilitated by deep learning technology in combination with an interpretable domain constrained architecture and the appropriate downstream task.
We apply our architecture to a block of raw EEG data. First, the multibranch interpretable feature extraction module estimates physiologically interpretable features that then get compressed by the encoding block to be next unpacked with the decoder into the delayed window of ROI sBOLD activity samples. We use one layer interpretable compact block and several layers for encoder and decoder as outlined in the diagram.CWL EEG/fMRI Dataset. Concurrently recording of EEG and fMRI data - dataset link
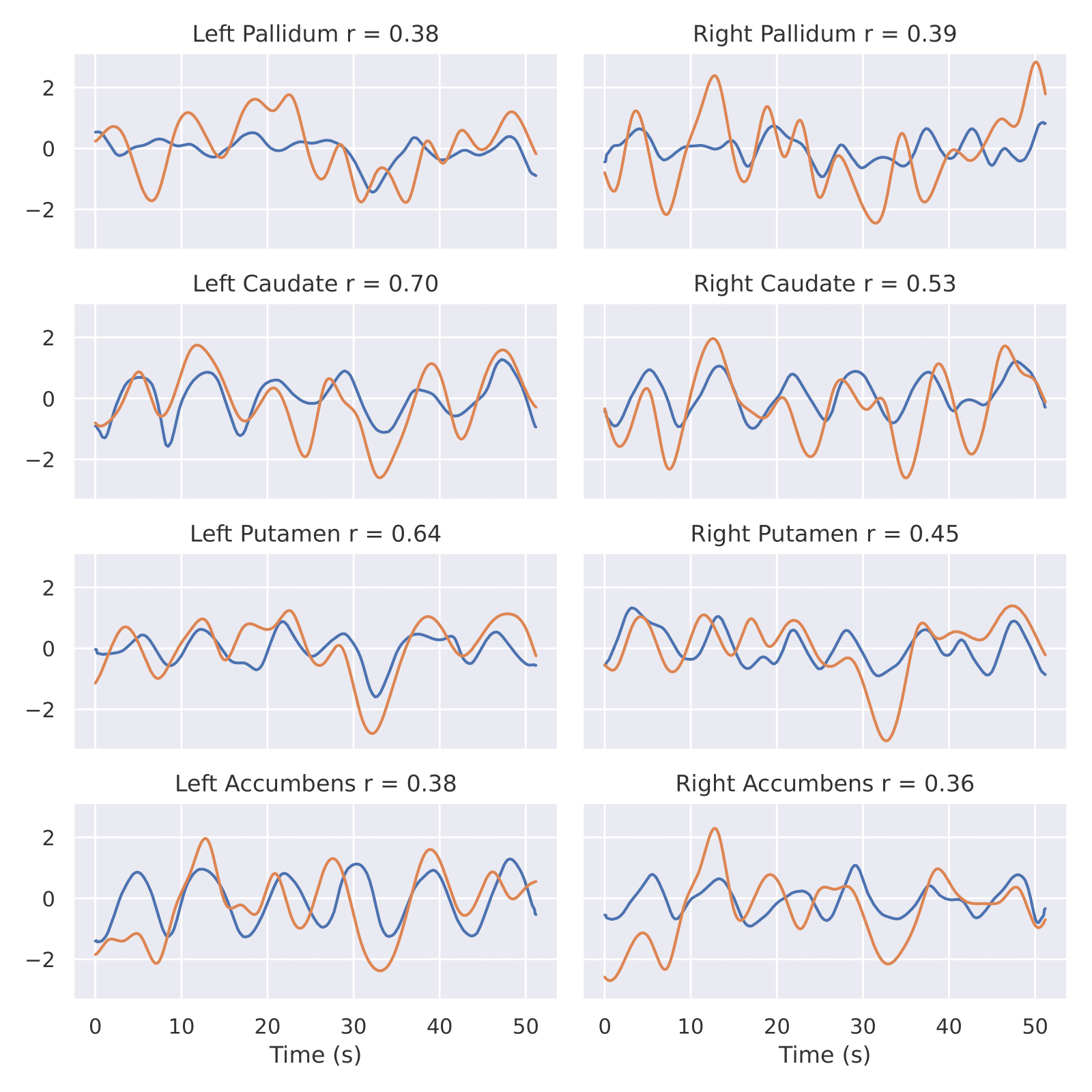
Figure 2. Real and predicted sBOLD time series of different RoI for one patient from CWL dataset: pallidum, caudate, putamen, accumbens. Yellow is real, blue is prediction. x axis - Time seconds. y axis - sBOLD activityFor starting training procees you need to download data from CWL dataset
- Clone repository and create env via env file
- Download data and move to data folder in your repository.
- Run BEIRA_ALL_IN_ONE.ipynb for model training. All result will be logged in wandb.
- Run BEIRA_inference and get the best model in wandb folder and provide interpretation.
Description of the repository. You can modify each step.
├── utils
│ ├── models_arch
│ ├── autoencoder_new_Artur.py - BEIRA architecture.
│ ├── get_datasets.py - build datasets from raw EEG and fMRI data
│ ├── inference.py - scripts for inference of our models. (there are many2one, many2many and many2many window-based).
│ ├── preproc.py - preprocessing functions for raw EEG and fMRI
│ ├── get_datasets.py - build datasets from raw EEG and fMRI data
│ ├── train_utils.py - all functions for model training, loss_functions
└── ...
├── notebook_clean
│ ├── BEIRA_ALL_IN_ONE.ipynb - prepare data and start training.
│ ├── BEIRA_inference.ipynb - provide visualization and interpretation of the trained model.
└── ...
@article{beira2022,
title={fMRI from EEG is only Deep Learning away: the use of interpretable DL to unravel EEG-fMRI relationships},
author={Kovalev, Alexander and Mikheev, Ilia and Ossadtchi, Alexei},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2211.02024},
year={2022}
}