This is a tutorial on how to generate controversial stimuli for ImageNet classifiers using PyTorch. More details on the method of controversial stimuli can be found in our paper:
T. Golan, P. C. Raju, N. Kriegeskorte, Controversial stimuli: Pitting neural networks against each other as models of human cognition. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 117, 29330–29337 (2020). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1912334117
The tutorial is contained in a Jupyter notebook:
Synthesizing_Controversial_Stimuli_Tutorial.ipynb
If you want to run the notebook or the Python code on your own machine (i.e., not on Google Colab), you would have to install the dependencies.
Start with creating a conda environment:
git clone https://github.com/kriegeskorte-lab/controversial_stimuli_tutorial
cd controversial_stimuli_tutorial
conda create -n contro_stim_env python==3.11
conda activate contro_stim_env
Proceed with installing PyTorch according to the instructions on the PyTorch website. This code was tested on PyTorch 1.6 to 2.1.2, and Kornia 0.4.1 to 0.7.1.
Next, install the remaining dependencies:
conda install pytables
pip install -r requirements.txt
If you want to run the notebook, you would also need to install JupyterLab:
conda install -c conda-forge jupyterlab
jupyter lab Synthesizing_Controversial_Stimuli_Tutorial.ipynb
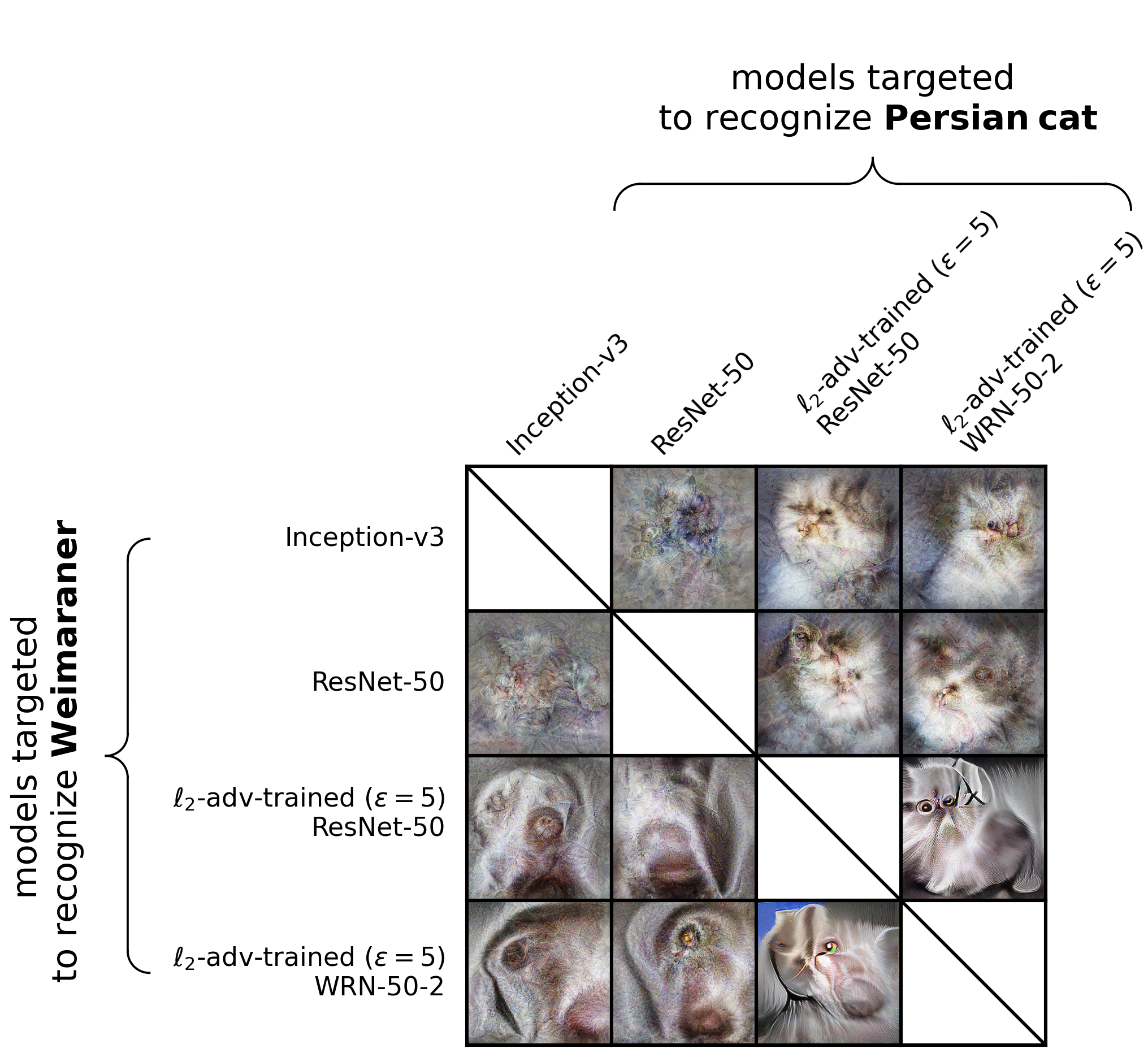
This repository also includes Python code for synthesizing controversial stimuli in a batch. After installing the dependencies, you can synthesize all of the images that appear in the figure above by running:
python batch_optimize.py --experiments cat_vs_dog --optimization_methods CPPN --max_steps=1000
To synthesize all of the images that appear in the tutorial figures, run python batch_optimize.py without arguments (warning: this takes many hours if not done over a GPU cluster). This code is compatible with being run by multiple workers in parallel (it synchronizes tasks through 0-byte file flags). However, let a single worker run alone for a couple of minutes so it can download the necessary DNNs without competition.
Please cite (Golan, Raju, & Kriegeskorte, 2020) if you build upon our method in your research (bibtex link). If want to cite this tutorial directly, you may do so using the following reference:
@software{Golan_2020_Synthesizing,
author = {Tal Golan and
Nikolaus Kriegeskorte},
title = {{Synthesizing Controversial Stimuli (a tutorial with PyTorch)}},
month = nov,
year = 2020,
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {1.0.0},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.4291135},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4291135}
}