-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 4
EDK II Development Process
First check out Getting Started with EDK II for downloading the latest EDK II development project with your build environment.
Are you new to using git? If so, then the New to git page may be helpful.
-
Setup the EDK II tree if you do not have one
- This is document on the SourceForge to Github Quick Start page
-
Create and checkout a topic branch for new feature or bug fix
$ git checkout -b <new-dev-branch> origin/master -
Make changes in the working tree
-
Break up working tree changes into independent commits that do not break git bisect
-
To stage all modifications:
$ git add -u -
To add new files:
$ git add <path-to-new-file> -
To have git prompt you to selectively stage changes:
$ git add -p
-
Follow the commit message template given below when writing commit messages
-
To commit staged changes:
$ git commit- Add the
-sparameter to automatically append your Signed-off-by tag to the commit message.
- Add the
-
Use the ‘PatchCheck.py’ script under ‘edk2\BaseTools\Scripts’ directory to verify the commits are correctly formatted
-
To check the latest changes:
$ python BaseTools/Scripts/PatchCheck.py -<N>- For example, 2 changes would be:
$ python BaseTools/Scripts/PatchCheck.py -2
- For example, 2 changes would be:
-
It is strongly recommended that you run PatchCheck.py after each commit. You can then easily amend the commit to correct any issues.
-
-
Get the latest changes from origin
$ git fetch originNote: This updates origin/master, but not your local master branch. (origin/master may have newer commits than master.)
-
Rebase the topic branch onto master branch
$ git rebase origin/master -
Create patch (serial) to the edk2-devel mailing list
-
Clean out any old patches:
$ rm *.patch -
Generate new patch files:
$ git format-patch -M --thread origin/master-
Add the
--cover-letterparameter for long patch series. (Be sure to edit the cover-letter.) -
Add the
--subject-prefix="PATCH v2"if you are sending out a second version of the patch series.
-
-
$ git send-email *.patch
-
-
Modify local commits based on the review feedbacks and repeat steps 3 to 9
-
For the latest commit, you can use
$ git commit --amend -
For multiple commits use
$ git rebase -i origin/master -
Consult your git gurus on edk2-devel or irc channel if you have questions.
-
-
Determine if a patch has met the review requirements for the package
-
Update the origin/master from the server
$ git fetch origin -
Create and checkout an integration branch
$ git checkout -b <new-integration-branch> origin/master -
Add commits on the integration branch
$ git am <patch-file> -
Rebase commit message to include any reviewed-by or other attributions
$ git rebase -i origin/master- Edit lines to have an 'r' to 'reword' the commit. This will allow you to add the Reviewed-by attributions.
-
Push changes to the EDK II maintainer's fork of the EDK II project repository.
-
How to create a GitHub fork
-
Add remote to the EDK II maintainer's fork of the EDK II project
$ git remote add <maintainer id> https://github.com/<maintainer id>/edk2- Push the integration branch to
<maintainer id>/master. Add the--dry-runparameter to show exactly what is going to be updated before pushing to a public branch. Use this if you are paranoid. :)
$ git push <maintainer id> <new-integration-branch> -
-
Create a GitHub pull request from the EDK II maintainer's
<new-integration-branch>toedk2/mastersetting thepushlabel. If all checks pass, the changes are strict rebase merged. If thepushlabel is not set, then the checks are run, but no changes are merged.-
How to create a GitHub pull request
-
Add the TianoCore Bugzilla issue number(s) resolved by the pull request to the pull request title.
-
If
<new-integration-branch>is a patch series, then copy the patch #0 summary commit message into the pull request description. -
If the EDK II Maintainer wants the patches from
<new-integration-branch>to be merged intoedk2/masterusing strict rebase, then thepushlabel must be set. By default, pull requests toedk2/masterare personal builds that perform checks and provide results, but no commits are automatically made toedk2/master. An EDK II Maintainer has the option of requesting a personal build first. If all checks pass, then thepushlabel can be set and the pull request can be re-opened to request the patches to be committed toedk2/master. -
Email notifications for pull requests, pushes, and check status results are enabled by watching the EDK II repository (https://github.com/tianocore/edk2). How to Watch a GitHub repository
-
The figure below shows an example creating a GitHub pull request. The red box at the top shows that the edk2 repository is being watched. It also shows that GitHub observed that a new EDK II Maintainer branch
Bug_2315_Example_GitHub_Pull_Requestwas pushed and is now available to create a pull request againstedk2/masterby selecting the button labeledCompare & pull request.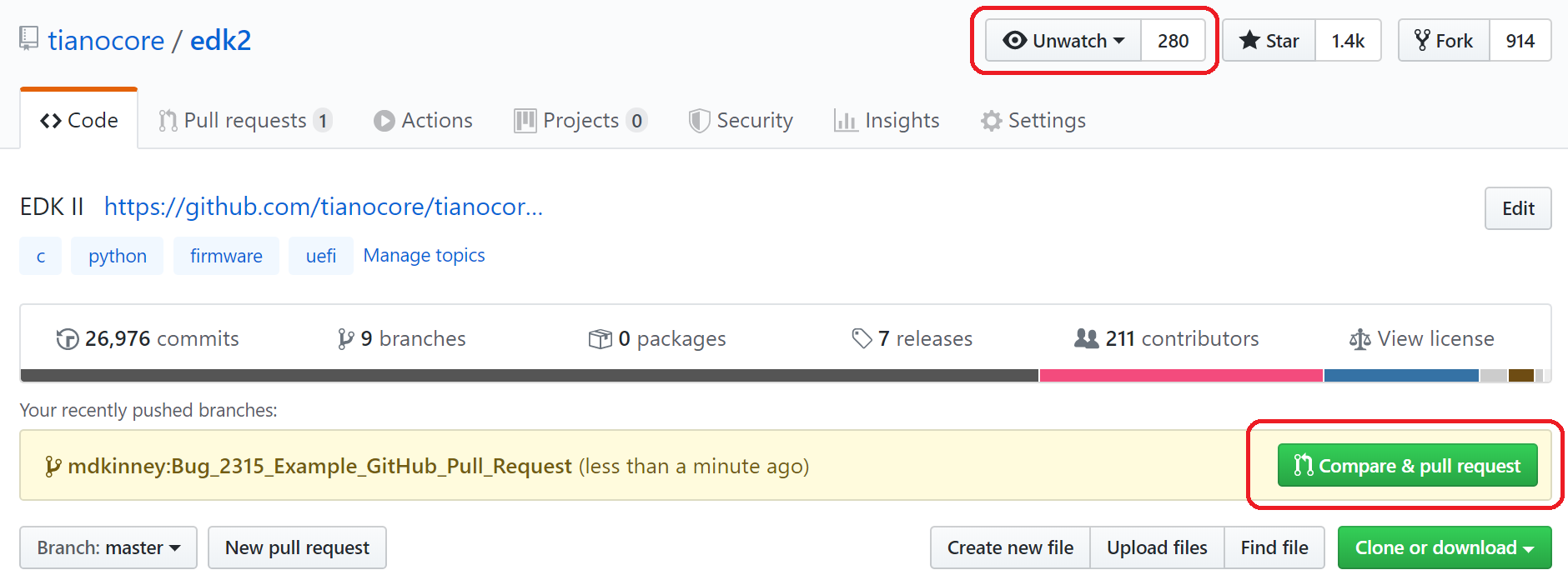
-
The figure below shows the title and description of the pull request as well as the
Labelsbutton on the right that is used to enable/disable thepushlabel.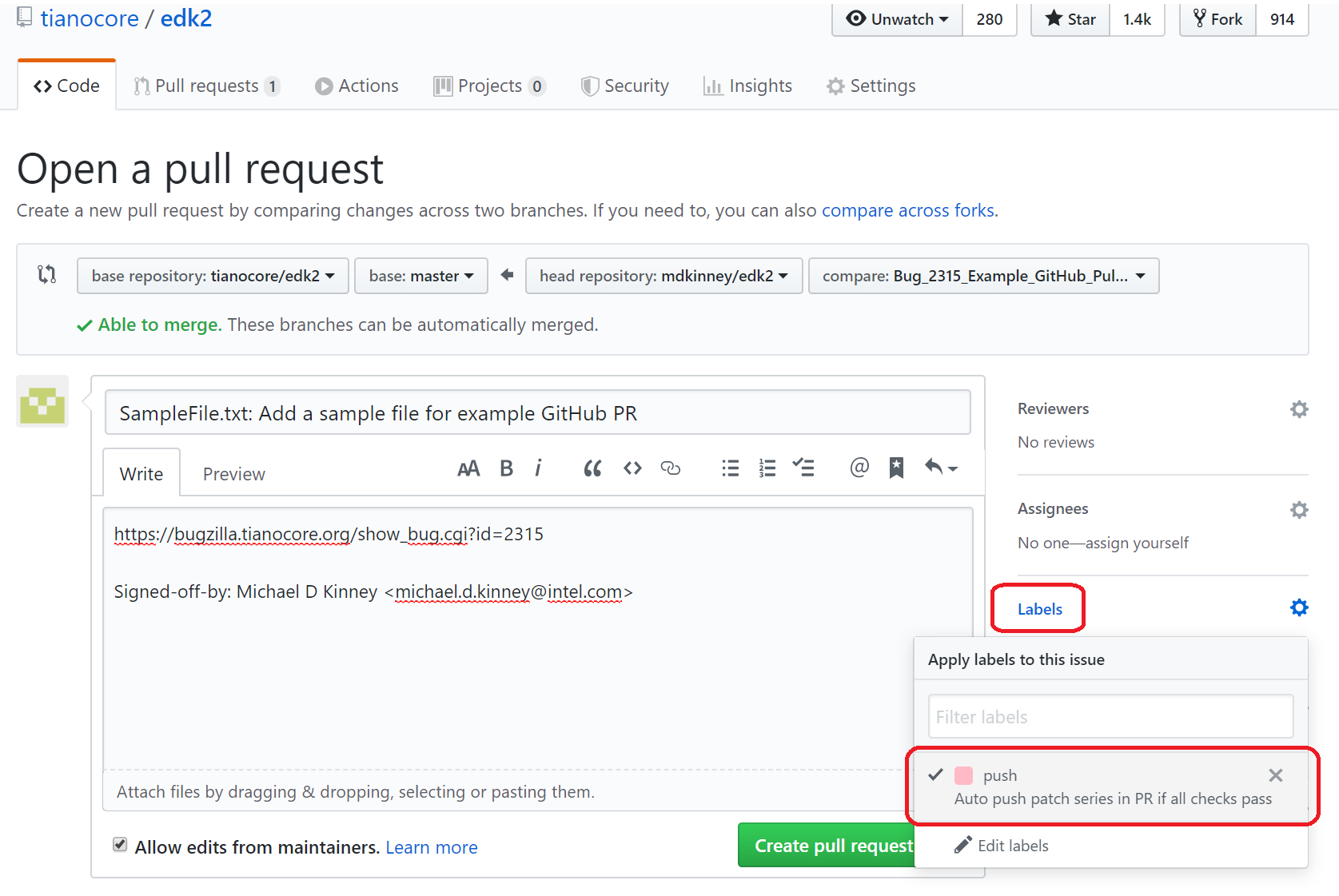
-
-
Resolve GitHub pull request issues. A pull request to
edk2/mastermay fail for the following conditions:-
A merge conflict is detected. The pull request remains open. The EDK II maintainer resolves all merge conflicts locally and does a forced push to
<new-integration-branch>. The pull request checks are automatically restarted. -
The pull request fails the
PatchCheck.pycheck. The pull request remains open. The EDK II maintainer resolves thePatchCheck.pyissues locally and does a forced push to<new-integration-branch>. The pull request checks are automatically restarted. Follow links to Azure Pipelines results to view thePatchCheck.pyissues. -
The pull request fails Windows or Ubuntu checks. The pull request remains open. The EDK II maintainer resolves the checks locally and does a forced push to
<new-integration-branch>. The pull request checks are automatically restarted. Follow links to Azure Pipelines results to view the test results for checks that failed. -
The pull request submitter is not a member of the TianoCore EDK II Maintainers team and the
pushlabel is set. The pull request is ignored and automatically closed.
-
-
Update TianoCore Bugzilla issue(s) resolved by the commit(s).
-
Add a pointer to the GitHub pull request (e.g. https://github.com/tianocore/edk2/pull/153).
-
Add the SHA hash range pushed to
edk2/master(e.g. Pushed as cc6854506c..f8dd7c7018). -
Mark BZ issues as Resolved/Fixed.
-
-
Get the latest changes from origin
$ git fetch origin -
Change to the local master branch
$ git checkout master -
Apply the latest server changes to you local master branch.
$ git rebase origin/master