Example of LSTM learning (MariFlow - Self-Driving Mario Kart w/Recurrent Neural Network) (5:49): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ipi40cb_RsI&t=254s
LSTM's have made a lot of news lately with things powering things like deepfakes and much of the AI work coming out of Google. They are essentially neural nets or "brains in the computer" that can be taught a sequence of data, and have the ability to use their memory from past data to predict future events/data. They work really well with learning from things like video, audio, or games because there is a uniform time step or "tick" in between each piece of data. Video is often 24 frames per second, Audio is often 48000 samples per second, board games often involve sequential "turn taking", and video games can run anywhere from 60 to 200+ "ticks" per second.
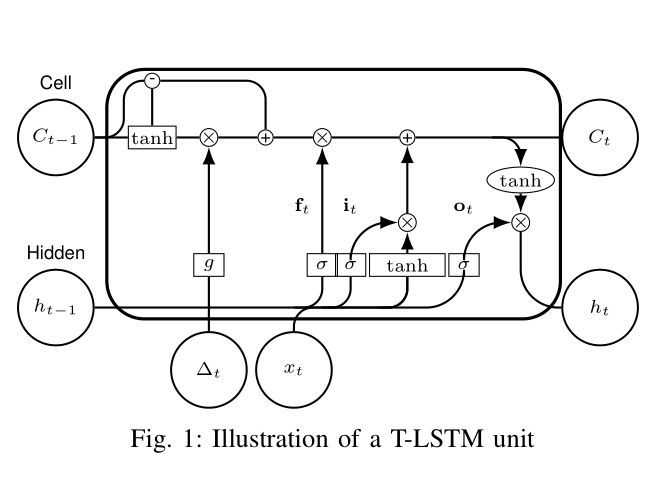
T-LSTM's or "Time-Aware Long Short Term Memory" cells are a modified version of these neurons which are designed to allow them to better understand more kinds of real world data where the time step is not uniform, such as in healthcare when doctor's visits can be either grouped close together or further apart (observe "delta T" and the upper left section in the following image to see the modification on the cell).
This time spacing, or temporal, information is critical in some datasets. In credit prediction for instance, a person's clickstream (how they click on things on a website) combined with the time spacing between loan attempts can be leveraged extremely well to predict a person's risk of default (not paying back on the loan) to the tune of 87 or 90% accuracy, even without any traditional background credit check or information on the person.
T-LSTM's are currently only being used in some narrow realms, but could prove to be a very powerful model for analyzing many kinds of data. LSTM's are being pretty widely used currently, but they tend to only be able to undertand data well when the time step is uniform.
In addition, using T-LSTM's with Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) could allow for extremely powerful predictive capability on many different kinds of real world data (e.g. stocks, etc.).
IQVIA seems to have the most advanced research and usage with this technology of those publicly publishing so far.
More info:
https://people.cs.uchicago.edu/~ravenben/publications/pdf/deepcredit-icwsm18.pdf
https://export.arxiv.org/pdf/1810.00490
https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8767922
https://www.ijcai.org/proceedings/2019/0607.pdf
Example of a GAN used with regular LSTM cells: http://roseyu.com/time-series-workshop/submissions/2019/timeseries-ICML19_paper_37.pdf
Rehosted Code as used in the DeepCredit paper: https://github.com/mkrupczak3/DeepCredit
Medium article on LSTM cells: https://medium.com/mlreview/understanding-lstm-and-its-diagrams-37e2f46f1714
(modifications of original code from https://github.com/illidanlab/T-LSTM) Regularity of the duration between consecutive elements of a sequence is a property that does not always hold. An architecture that can overcome this irregularity is necessary to increase the prediction performance.
Time Aware LSTM (T-LSTM) was designed to handle irregular elapsed times. T-LSTM is proposed to incorporate the elapsed time information into the standard LSTM architecture to be able to capture the temporal dynamics of sequential data with time irregularities. T-LSTM decomposes memory cell into short-term and long-term components, discounts the short-term memory content using a non-increasing function of the elapsed time, and then combines it with the long-term memory.
Code is compatible with tensorflow version 1.6.0 and Pyhton 3.6.4.
- Allow users to customize the number of encoders and decoders and the dimensions within each encoder/decoder.