This library is for Order/Degree Problem with a noweight undirected graph. You can use following.
- libodp.a : Serial version
- libodp_threads.a : Threads version
- libodp_cuda.a: CUDA (Compute Unified Device Architecture) version
- libodp_mpi.a : MPI (Message Passing Interface) version
- libodp_mpi_threads.a: MPI + Threads version
- libodp_mpi_cuda.a: MPI + CUDA version
When you write a paper using this library, please refer to the paper.
$ git clone https://github.com/mnakao/ODP.git
$ cd ODP
$ make
$ cd ./sample
$ make
$ ./general.x ./graph/general/n16d4.edges
Nodes = 16, Degrees = 4
Diameter = 3
Diameter Gap = 1 (3 - 2)
ASPL = 1.9166666667 (230/120)
ASPL Gap = 0.1833333333 (1.9166666667 - 1.7333333333)
$ git clone https://github.com/mnakao/ODP.git
$ cd ODP
$ make threads
$ cd ./sample
$ make threads
$ ./threads_general.x ./graph/general/n16d4.edges
Nodes = 16, Degrees = 4
Diameter = 3
Diameter Gap = 1 (3 - 2)
ASPL = 1.9166666667 (230/120)
ASPL Gap = 0.1833333333 (1.9166666667 - 1.7333333333)
$ git clone https://github.com/mnakao/ODP.git
$ cd ODP
$ make cuda
$ cd ./sample
$ make cuda
$ ./cuda_general.x ./graph/general/n16d4.edges
Nodes = 16, Degrees = 4
Diameter = 3
Diameter Gap = 1 (3 - 2)
ASPL = 1.9166666667 (230/120)
ASPL Gap = 0.1833333333 (1.9166666667 - 1.7333333333)
$ git clone https://github.com/mnakao/ODP.git
$ cd ODP
$ make mpi
$ cd ./sample
$ make mpi
$ mpiexec -n 1 ./mpi_general.x ./graph/general/n16d4.edges
Nodes = 16, Degrees = 4
Diameter = 3
Diameter Gap = 1 (3 - 2)
ASPL = 1.9166666667 (230/120)
ASPL Gap = 0.1833333333 (1.9166666667 - 1.7333333333)
$ git clone https://github.com/mnakao/ODP.git
$ cd ODP
$ make mpi_threads
$ cd ./sample
$ make mpi_threads
$ mpiexec -n 1 ./mpi_threads_general.x ./graph/general/n16d4.edges
Nodes = 16, Degrees = 4
Diameter = 3
Diameter Gap = 1 (3 - 2)
ASPL = 1.9166666667 (230/120)
ASPL Gap = 0.1833333333 (1.9166666667 - 1.7333333333)
$ git clone https://github.com/mnakao/ODP.git
$ cd ODP
$ make mpi_cuda
$ cd ./sample
$ make mpi_cuda
$ mpiexec -n 1 ./mpi_cuda_general.x ./graph/general/n16d4.edges
Nodes = 16, Degrees = 4
Diameter = 3
Diameter Gap = 1 (3 - 2)
ASPL = 1.9166666667 (230/120)
ASPL Gap = 0.1833333333 (1.9166666667 - 1.7333333333)
$ cd ODP
$ make [serial|threads|cuda|mpi|mpi_threads|mpi_cuda|all]
In order to create the executable, you need to include the header file ./include/odp.h and link it with one of the libraries.
$ cd ODP/sample
$ make [serial|threads|cuda|mpi|mpi_threads|mpi_cuda|all]
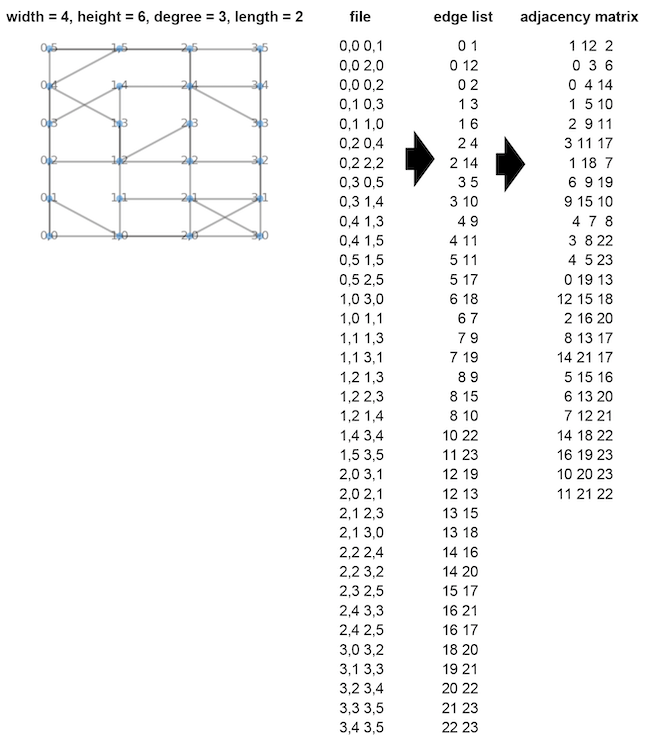
- For a general graph, each vertex name must be an integer starting from zero.
- For a grid graph, each vertex name must be a comma-separated string like "x,y" (no quotes, no spaces). x and y are integers starting from zero, which represent the coordinate of the vertex.
- Please see sample graphs in
./sample/graph/or http://research.nii.ac.jp/graphgolf/submit.html
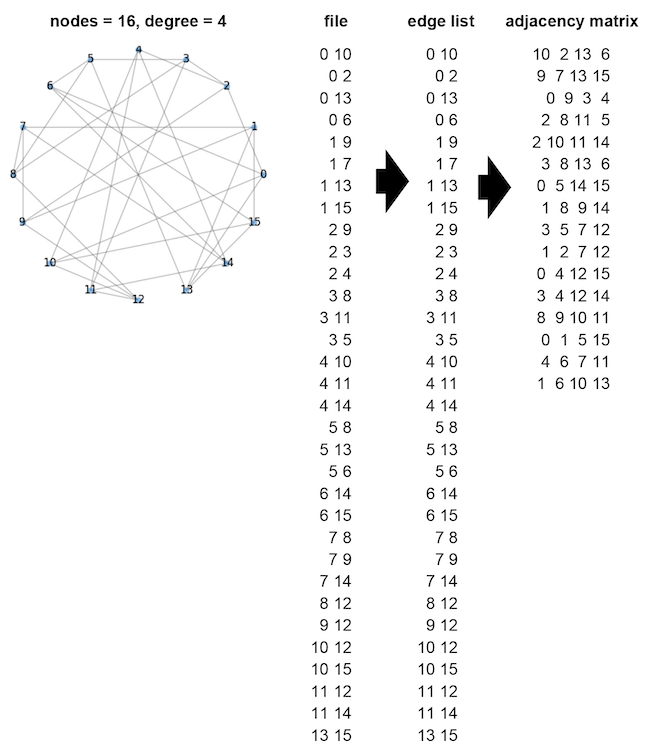
A file and an edge list are the same. The adjacency matrix represents the connection relationship between vertices. For example, the first line means that vertex number 0 is connected to 10, 2, 13, and 6.
A file and an edge list are different. The format of the edge list and adjacency matrix is the same for general and grid graphs.
This library provides three algorithms for ASPL.
MATRIX is selected if the amount of memory used is lower than the value of MEM_THRESHOLD in parameter.h.
If it is higher, MATRIX_SAVING is selected.
BFS only works if specified in an environment variable.
- MATRIX : Bit matrix is used for ASPL calculation. In most cases this is the fastest.
- MATRIX_SAVING : This is a memory-saving version of
MATRIX. - BFS : Breadth First Search is used for ASPL calculation. If the value of
(nodes/(procs*symmetries)is small enough or a diameter of a graph is large, it may be the fastest. Note that BFS with CUDA is not implemented.
Output the performance profile for ODP_Set_aspl(). This profile is output when ODP_Finalize_aspl() is executed.
$ ODP_ASPL=SAVING ODP_PROFILE=1 ./general.x ./graph/general/n16d4.edges
------ Profile for SET_ASPL ------
Date = Mon Jan 4 23:14:03 2021
Hostname = kiwi
Number of Times = 1
Total Time = 0.000005 sec.
Average Time = 0.000005 sec.
Algorithm = SAVING (SERIAL)
Symmetries = 1
Memory Usage = 0.006 MB
Num of Procs = 1
Num of Threads = 1
--------- End of Profile ---------
Nodes = 16, Degrees = 4
Diameter = 3
Diameter Gap = 1 (3 - 2)
ASPL = 1.9166666667 (230/120)
ASPL Gap = 0.1833333333 (1.9166666667 - 1.7333333333)
The meaning of each item in the profile is as follows.
- Date : The time when the profile was output.
- Hostname : Name of the machine on which the program ran.
- Number of Times : Number of times ODP_Set_aspl() was executed.
- Total Time : Total execution time of ODP_Set_aspl().
- Average Time : Average execution time of ODP_Set_aspl().
- Algorithm : MATRIX, MATRIX_SAVING or BFS. The parentheses are the types of libraries used. That is, SERIAL, THREADS, CUDA, MPI, MPI+THREADS, or MPI+CUDA.
- Symmetries : Numer of symmetries in a graph.
- Memory Usage : Estimated ammount of memory used in the library.
- Num of Procs : Number of processes used in the library.
- Num of Threads : Number of threads used in the library.
Basic function calculates ASPL and diameter of a graph.
#include "odp.h"
int main()
{
...
ODP_Init_aspl_*(...);
for(int i=0;i<ITERATIONS;i++){
/* Optimization */
ODP_Set_aspl(...);
}
ODP_Finalize_aspl();
...
return 0;
}
There are four types of ODP_Init_aspl_*(), to support combinations of general and grid graphs, serial and MPI. ODP_Set_aspl() calculates APSL and diameter of a graph. While ODP_Init_aspl_*() initializes for ODP_Set_aspl(), ODP_Finalize_aspl() finalizes for ODP_Set_aspl(). Thus, ODP_Set_aspl() should be called between ODP_Init_aspl_*() and ODP_Finalize_aspl(). Note that ODP_Init_aspl_*() and ODP_Finalize_aspl() will basically be called only once each in a program.
Perform the initialization process before executing ODP_Set_aspl().
void ODP_Init_aspl_general (int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes])
void ODP_Init_aspl_grid (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes])
void ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_general(int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], MPI_Comm comm)
void ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_grid (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], MPI_Comm comm)
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree: Degree in a graph.
- [IN] num_degrees : Specify NULL for a regular graph. Or specify the degrees in each vertex for a non-regular graph.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] comm : MPI communicator.
When using ODP_Init_aspl_general() or ODP_Init_aspl_grid(), please link libodp.a, libodp_threads.a, or libodp_cuda.a.
When using ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_general() or ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_grid(), please link libodp_mpi.a, libodp_mpi_threads.a, or libodp_mpi_cuda.a.
Set diameter, sum, and ASPL. In the case of an unconnected graph, INT_MAX, LONG_MAX, and DBL_MAX are assigned to the values of diameter, sum, and ASPL, respectively.
void ODP_Set_aspl(int adjacency[nodes][degree], int *diameter, long *sum, double *ASPL)
- [IN] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
- [OUT] diameter : Diameter of a graph.
- [OUT] sum : Total value of the distances between each vertex in a graph.
- [OUT] ASPL : Average shortest path length of a graph (sum = ASPL*(nodes*(nodes-1)/2)).
Release the resources allocated in ODP_Init_aspl*().
void ODP_Finalize_aspl()
void ODP_Read_edge_general(char* fname, int edge[lines][2])
void ODP_Read_edge_grid (char *fname, int *width, int *height, int edge[lines][2])
- [IN] fname : File name of a graph.
- [OUT] edge : Edge list of a graph.
- [OUT] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [OUT] height : Height of a grid graph.
void ODP_Write_edge_general(int lines, int edge[lines][2], char *fname)
void ODP_Write_edge_grid (int lines, int height, int edge[lines][2], char *fname)
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [OUT] fname : File name of a graph.
void ODP_Print_adjacency(int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int adjacency[nodes][degree])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree : Degree in a graph.
- [IN] num_degrees : Specify NULL for a regular graph. If not, specify the degrees for each vertex.
- [IN] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
void ODP_Print_edge_general(int lines, int edge[lines][2])
void ODP_Print_edge_grid (int lines, int height, int edge[lines][2])
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
ODP_Print_edge_grid() outputs a value with coordinates.
void ODP_Conv_edge2adjacency_general(int nodes, int lines, int degree, int edge[lines][2], int adjacency[nodes][degree])
void ODP_Conv_edge2adjacency_grid (int width, int height, int lines, int degree, int edge[lines][2], int adjacency[nodes][degree])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] degree : Degree in a graph.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [OUT] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
void ODP_Conv_adjacency2edge_general(int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int adjacency[nodes][degree], int edge[lines][2])
void ODP_Conv_adjacency2edge_grid (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int adjacency[nodes][degree], int edge[lines][2])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree : Degree in a graph.
- [IN] num_degrees : Specify NULL for a regular graph. If not, specify the degrees for each vertex.
- [IN] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [OUT] edge : Edge list of a graph.
void ODP_Set_lbounds_general(int nodes, int degree, int *low_diameter, double *low_ASPL)
void ODP_Set_lbounds_grid (int width, int height, int degree, int length, int *low_diameter, double *low_ASPL)
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree : Degree in a graph.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] length : Maximum length of a grid graph.
- [OUT] low_diameter : Theoretical lower bound of diameter in a graph.
- [OUT] low_ASPL : Theoretical lower bound of ASPL in a graph.
void ODP_Set_degrees(int nodes, int lines, int edge[lines][2], int num_degrees[nodes])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
- [OUT] num_degrees : Degree in each vertex.
Since a random number is used in ODP_Generate_random_*() and ODP_Mutate_adjacency_*(), ODP_Srand() must be executed before those functions.
void ODP_Srand(unsigned int seed)
- [IN] seed : Seed for random.
Generate a regular graph with randomly connected vertices. Note that the graph may contain multiple edges and loops.
void ODP_Generate_random_general(int nodes, int degree, int edge[lines][2])
void ODP_Generate_random_grid (int width, int height, int degree, int length, int edge[lines][2])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree : Degree in a graph.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] length : Maximum length of a grid graph.
- [OUT] edge : Edge list of a graph.
Mutate an adjacency matrix slightly. Specifically, the operation equivalent to the 2-opt method is performed. The changes are stored in the ODP_Resotre structure variable.
void ODP_Mutate_adjacency_general(int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], ODP_Restore *restore, int adjacency[nodes][degree])
void ODP_Mutate_adjacency_grid (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int length, ODP_Restore *restore, int adjacency[nodes][degree])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree : Degree in a graph.
- [IN] num_degrees : Degree in each vertex.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] length : Maximum length of a grid graph.
- [OUT] restore : Changes.
- [OUT] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
Changes are undone by the ODP_Resotre structure variable.
void ODP_Restore_adjacency_general(ODP_Restore restore, int adjacency[nodes][degree])
void ODP_Restore_adjacency_grid (ODP_Restore restore, int adjacency[nodes][degree])
- [IN] restore : Changes.
- [OUT] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
int ODP_Get_lines(char* fname)
- [RETURN] : Number of lines in a file.
- [IN] fname : File name of a graph.
int ODP_Get_nodes(int lines, int edge[lines][2])
- [RETURN] : Number of nodes in an edge list.
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
int ODP_Get_degree(int nodes, int lines, int edge[lines][2])
- [RETURN] : Degree in an edge list.
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
int ODP_Get_length(int lines, int height, int edge[lines][2])
- [RETURN] : Maximum length in an edge list.
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
bool ODP_Check_general(char *fname)
- [RETURN] : When an input is a general graph, it returns true.
- [IN] fname : File name of a graph.
bool ODP_Check_multiple_edges(int lines, int edge[lines][2])
- [RETURN] : If a graph has multiple edges, it returns true.
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
bool ODP_Check_loop(int lines, int edge[lines][2])
- [RETURN] : If a graph has a self-loop, it returns true.
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
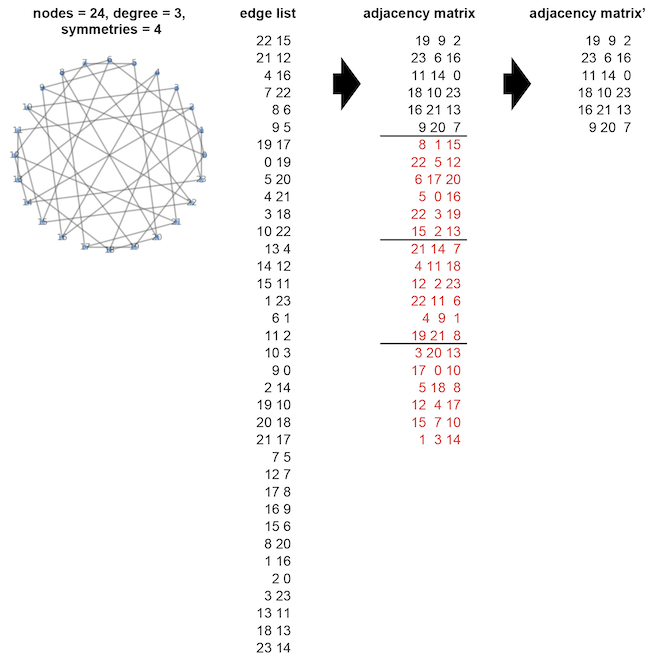
Symmetry in this library means that the original graph matches when the graph is rotated 360/symmetries degrees.
Therefore, a value of symmetries must be a divisor of nodes.
When symmetries=1, target the graph without symmetry.
The image is an example of a graph with (nodes, degree, symmetries) = (24, 3, 4).
The adjacency matrix can be divided into four groups (= symmetries).
The values on the 1st row are 19, 9, and 2.
It means that the vertex number 0 has three edges, 0-19, 0-9, and 0-2.
The edges plus 6 (= nodes/symmetries) matches the 1st row in the next group (in line 7).
2 + 6 = 8 and 9 + 6 = 15.
Here, 19 + 6 = 25, but the number of nodes is 24, so it goes around and becomes 25 - 24 = 1.
This rule holds for all groups.
The elements in lins 7-24 of the adjacency matrix can be calculated from those in lines 1-6.
Thus, the new adjacency matrix', in which the red part of adjacency matrix is deleted, is used.
The size of the adjacency matrix' is int adjacency[nodes/symmetries][degree].
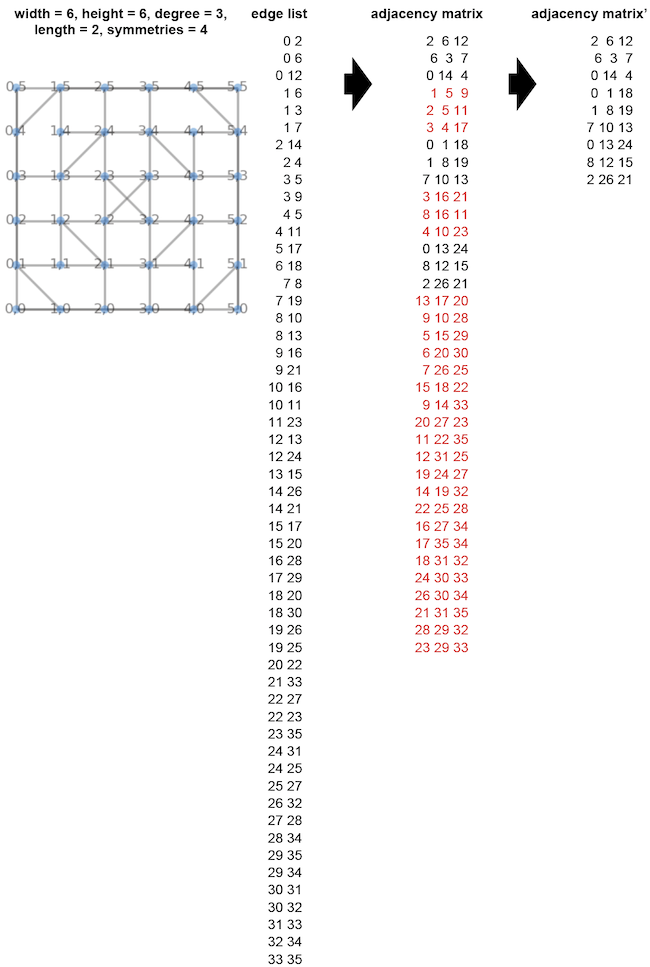
Grid graphs are almost the same as general graphs, but only values of 1, 2 or 4 are valid for symmetries.
When symmetries=2, width is a multiple of 2.
When symmetries=4, width and height are a multiple of 2, and width=height.
The image is an example of a graph with (width, height, degree, length, symmetries) = (6, 6, 3, 2, 2). As with the general graph, the bottom half can be calculated from the top half. However, the calculation method is different from the general graph. For example, the vertex number 0 is connected to 7, 2, and 12. The coordinates of for 7, 2, and 12 are (1,1), (0,2), and (2,0). The vertex number 0 corresponds to the vertex number 35, its coordinaten is (5,5). Rotate (1,1), (0,2), (2,0) by 180 degrees to get (4,4), (5,3), (3,5). The vertex numbers for (4,4), (5,3), and (3,5) are 28, 33, and 23. These values match the 36th row of the adjacency matrix.
The image is an example of a graph with (width, height, degree, length, symmetries) = (6, 6, 3, 2, 4). Only the vertices in the lower left part of the image are used to calculate the other vertices. Specifically, the nine points are (0,0), (0,1), (0,2), (1,0), (1,1), (1,2), (2,0), (2,1), and (2,2). Their vertex numbers are 0, 1, 2, 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, and 14. The vertex number 0 corresponds to the vertex numbers 5, 35, and 30. Their coordinates are (0,5), (5,5), and (5,0). For example, the vertex number 0 is connected to 2, 6, and 12. Their coordinates are (0,2), (1,0), and (2,0). Rotate (0,2), (1,0), (2,0) by 90 degrees to get (2,5), (0,4), (0,3). Their vertex numbers are 17, 4, and 3. These values match the 6th row of the adjacency matrix.
Note that the new adjacency matrix' is not created from contiguous region of the adjacency matrix.
void ODP_Init_aspl_general_s (int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int symmetries)
void ODP_Init_aspl_grid_s (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int symmetries)
void ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_general_s(int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], MPI_Comm comm, int symmetries)
void ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_grid_s (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], MPI_Comm comm, int symmetries)
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree: Degree in a graph.
- [IN] num_degrees : Specify NULL for a regular graph. If not, specify the degrees for each vertex.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] comm : MPI communicator.
- [IN] symmetries : Numer of symmetries in a graph.
When using ODP_Init_aspl_general_s() or ODP_Init_aspl_grid_s(), please link libodp.a, libodp_threads.a, or libodp_cuda.a.
When using ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_general_s() or ODP_Init_aspl_mpi_grid_s(), please link libodp_mpi.a, libodp_mpi_threads.a, or libodp_mpi_cuda.a.
Note that the ODP_Set_aspl() and ODP_Finalize_aspl() can be used in common.
void ODP_Conv_edge2adjacency_general_s(int nodes, int lines, int degree, int edge[lines][2], int symmetries, int adjacency[nodes/symmetries][degree])
void ODP_Conv_edge2adjacency_grid_s (int width, int height, int lines, int degree, int edge[lines][2], int symmetries, int adjacency[nodes/symmetries][degree])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] lines : Number of lines in an edge list.
- [IN] degree: Degree in a graph.
- [IN] edge : Edge list of a graph.
- [IN] symmetries : Numer of symmetries in a graph. This value must be a divisor of nodes.
- [OUT] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
void ODP_Conv_adjacency2edge_general_s(int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int adjacency[nodes/symmetries][degree], int symmetries, int edge[lines][2])
void ODP_Conv_adjacency2edge_grid_s (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int adjacency[nodes/symmetries][degree], int symmetries, int edge[lines][2])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree: Degree in a graph.
- [IN] num_degrees : Specify NULL for a regular graph. If not, specify the degrees for each vertex.
- [IN] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
- [IN] symmetries : Numer of symmetries in a graph. This value must be a divisor of nodes.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [OUT] edge : Edge list of a graph.
void ODP_Generate_random_general_s(int nodes, int degree, unsigned int seed, int symmetries, int edge[lines][2])
void ODP_Generate_random_grid_s (int width, int height, int degree, int length, unsigned int seed, int symmetries, int edge[lines][2])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree: Degree in a graph.
- [IN] seed : Seed for random.
- [IN] symmetries : Numer of symmetries in a graph. This value must be a divisor of nodes.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] length : Maximum length of a grid graph.
- [OUT] edge : Edge list of a graph.
Mutate an adjacency matrix slightly. Specifically, the operation equivalent to the 2-opt method is performed.
void ODP_Mutate_adjacency_general_s(int nodes, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int symmetries, int adjacency[nodes][degree])
void ODP_Mutate_adjacency_grid_s (int width, int height, int degree, int num_degrees[nodes], int length, int symmetries, int adjacency[nodes][degree])
- [IN] nodes : Number of nodes in a graph.
- [IN] degree : Degree in a graph.
- [IN] num_degrees : Degree in each vertex.
- [IN] width : Width of a grid graph.
- [IN] height : Height of a grid graph.
- [IN] length : Maximum length of a grid graph.
- [IN] symmetries: Numer of symmetries in a graph. This value must be a divisor of nodes.
- [OUT] adjacency : Adjacency matrix of a graph.
Note that the ODP_Restore_adjacency_general() and ODP_Restore_adjacency_grid() can be used in common.
- On Cygnus system in University of Tsukuba, Japan
- Xeon Gold 6126 2.6GHz (12cores) x 2
- Tesla V100 PCIe
- InfiniBand HDR100 x 4channel (400Gbpsx4)
- gcc/8.3.1, cuda/10.2, openmpi/3.1.6
- Graph with (nodes, degree) = (1000000, 32)
- http://research.nii.ac.jp/graphgolf/solutions/n1000000d32k5l433.20191014-pnxc8n.edges.gz
- libapsp.a : 3364.2 sec.
- libapsp_mpi_threads.a with 12 threads: 320.2 sec. (1 CPU), 166.5 sec. (2 CPUs), 84.4 sec. (4 CPUs), 41.9 sec. (8 CPUs)
- libapsp_mpi_cuda.a : 28.6 sec. (1 GPU), 14.4 sec. (2 GPUs). 7.3 sec. (4 GPUs), 3.7 sec. (8 GPUs), 1.9 sec. (16 GPUs)
- libapsp.a : 0.596 sec.
- libapsp_threads.a with 12 threads : 0.063 sec. (1 CPU)
- libcuda.a : 0.005 sec. (1 GPU)
The library also supports non-regular graphs, but usage of memory may be not efficient.
Because the format of the adjacency matrix is int adjacency[nodes][degree], which is commanly used in regular and non-regular graphs.
This wastes memory when the number of edges that each vertex has varies greatly.
This library is inherited from https://github.com/ryuhei-mori/graph_ASPL.git.