-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 62
threading.scad
Triangular and Trapezoidal-Threaded Screw Rods and Nuts. To use, add the following lines to the beginning of your file:
include <BOSL/constants.scad>
use <BOSL/threading.scad>
Description:
Constructs a generic trapezoidal threaded screw rod. This method makes
much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
For metric trapezoidal threads, use thread_angle=15 and thread_depth=pitch/2.
For ACME threads, use thread_angle=14.5 and thread_depth=pitch/2.
For square threads, use thread_angle=0 and thread_depth=pitch/2.
For normal UTS or ISO screw threads, use the threaded_rod() module instead to get the correct thread profile.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
d |
Outer diameter of threaded rod. |
l |
Length of threaded rod. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
thread_depth |
Depth of the threads. Default=pitch/2 |
thread_angle |
The pressure angle profile angle of the threads. Default = 14.5 degree ACME profile. |
left_handed |
If true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
bevel1 |
if true, bevel the axis-negative end of the thread. Default: false |
bevel2 |
if true, bevel the axis-positive end of the thread. Default: false |
starts |
The number of lead starts. Default = 1 |
internal |
If true, make this a mask for making internal threads. |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOPIt is effective only for internal=true. |
profile |
The shape of a thread, if not a symmetric trapezoidal form. Given as a 2D path, where X is between -1/2 and 1/2, representing the pitch distance, and Y is 0 for the peak, and -depth/pitch for the valleys. The segment between the end of one thread profile and the start of the next is automatic, so the start and end coordinates should not both be at the same Y at X = ±1/2. This path is scaled up by the pitch size in both dimensions when making the final threading. This overrides the thread_angle and thread_depth options. |
orient |
Orientation of the rod. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the rod. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
center |
If given, overrides align. A true value sets align=V_CENTER, false sets align=ALIGN_POS. |
Example 1:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=10, l=40, pitch=2, thread_angle=15, $fn=32);

Example 2:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=3/8*25.4, l=20, pitch=1/8*25.4, thread_angle=29, $fn=32);

Example 3:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=60, l=16, pitch=8, thread_depth=3, thread_angle=45, left_handed=true, $fa=2, $fs=2);

Example 4:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=60, l=16, pitch=8, thread_depth=3, thread_angle=45, left_handed=true, starts=4, $fa=2, $fs=2);

Example 5:
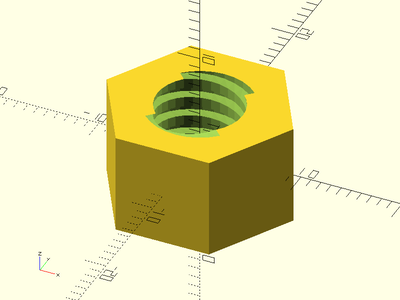
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=16, l=40, pitch=2, thread_angle=30);
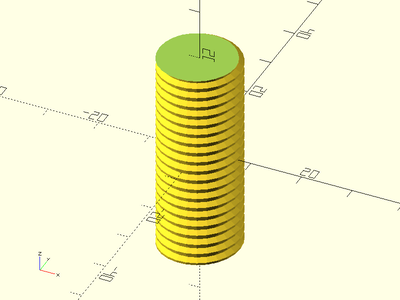
Example 6:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=10, l=40, pitch=3, thread_angle=15, left_handed=true, starts=3, $fn=36);
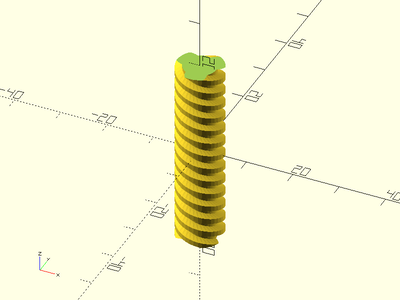
Example 7:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=25, l=40, pitch=10, thread_depth=8/3, thread_angle=50, starts=4, center=false, $fa=2, $fs=2);
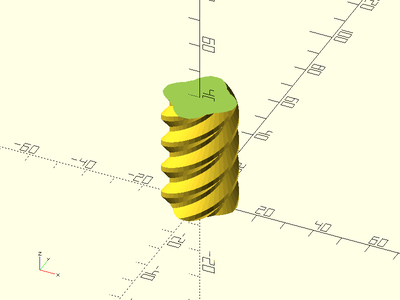
Example 8:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=50, l=35, pitch=8, thread_angle=30, starts=3, bevel=true);
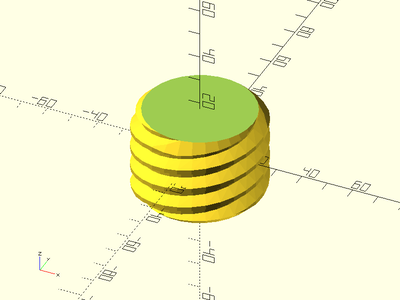
Example 9:
trapezoidal_threaded_rod(l=25, d=10, pitch=2, thread_angle=15, starts=3, $fa=1, $fs=1, orient=ORIENT_X, align=V_UP);
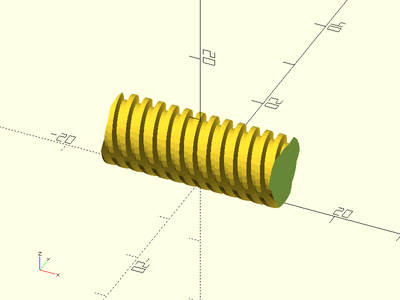
Description: Constructs a hex nut for a threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method. For metric screw threads, use thread_angle=30 and leave out thread_depth argument. For SAE screw threads, use thread_angle=30 and leave out thread_depth argument. For metric trapezoidal threads, use thread_angle=15 and thread_depth=pitch/2. For ACME threads, use thread_angle=14.5 and thread_depth=pitch/2. For square threads, use thread_angle=0 and thread_depth=pitch/2.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
od |
diameter of the nut. |
id |
diameter of threaded rod to screw onto. |
h |
height/thickness of nut. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
thread_depth |
Depth of the threads. Default=pitch/2. |
thread_angle |
The pressure angle profile angle of the threads. Default = 14.5 degree ACME profile. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
starts |
The number of lead starts. Default = 1 |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: true |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOP
|
profile |
The shape of a thread, if not a symmetric trapezoidal form. Given as a 2D path, where X is between -1/2 and 1/2, representing the pitch distance, and Y is 0 for the peak, and -depth/pitch for the valleys. The segment between the end of one thread profile and the start of the next is automatic, so the start and end coordinates should not both be at the same Y at X = ±1/2. This path is scaled up by the pitch size in both dimensions when making the final threading. This overrides the thread_angle and thread_depth options. |
orient |
Orientation of the nut. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the nut. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1:
trapezoidal_threaded_nut(od=16, id=8, h=8, pitch=2, slop=0.2, align=V_UP);
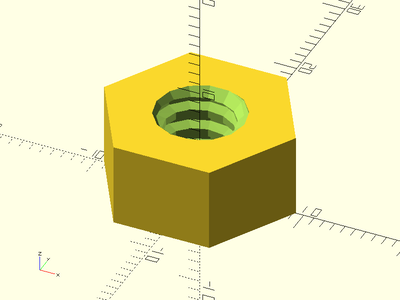
Example 2:
trapezoidal_threaded_nut(od=17.4, id=10, h=10, pitch=2, slop=0.2, left_handed=true);
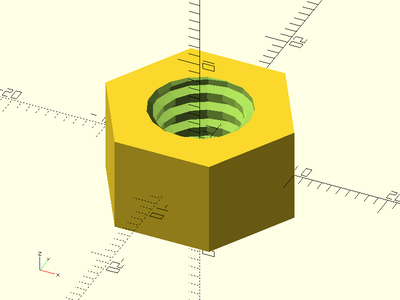
Example 3:
trapezoidal_threaded_nut(od=17.4, id=10, h=10, pitch=2, thread_angle=15, starts=3, $fa=1, $fs=1);
Description: Constructs a standard metric or UTS threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
d |
Outer diameter of threaded rod. |
l |
length of threaded rod. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
bevel1 |
if true, bevel the axis-negative end of the thread. Default: false |
bevel2 |
if true, bevel the axis-positive end of the thread. Default: false |
internal |
If true, make this a mask for making internal threads. |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOPIt is effective only for internal=true. |
orient |
Orientation of the rod. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the rod. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
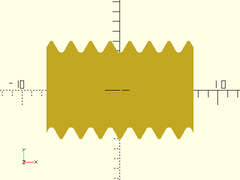
Example 1:
projection(cut=true)
threaded_rod(d=10, l=15, pitch=2, orient=ORIENT_X);
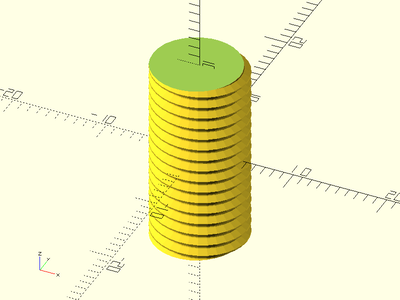
Example 2:
threaded_rod(d=10, l=20, pitch=1.25, left_handed=true, $fa=1, $fs=1);
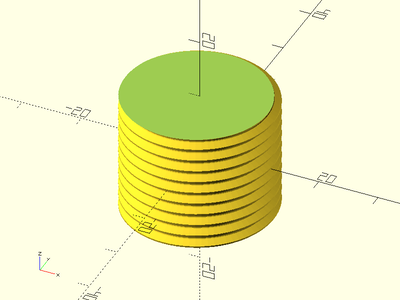
Example 3:
threaded_rod(d=25, l=20, pitch=2, $fa=1, $fs=1);
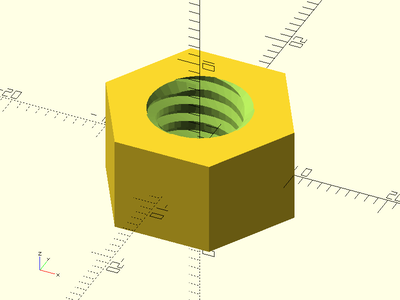
Description: Constructs a hex nut for a metric or UTS threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
od |
diameter of the nut. |
id |
diameter of threaded rod to screw onto. |
h |
height/thickness of nut. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOP
|
orient |
Orientation of the nut. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the nut. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example:
threaded_nut(od=16, id=8, h=8, pitch=1.25, left_handed=true, slop=0.2, $fa=1, $fs=1);
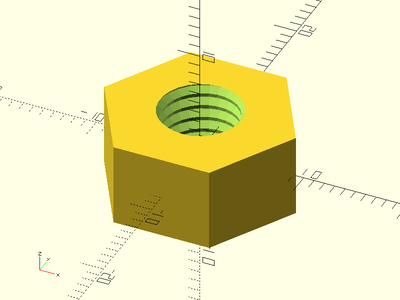
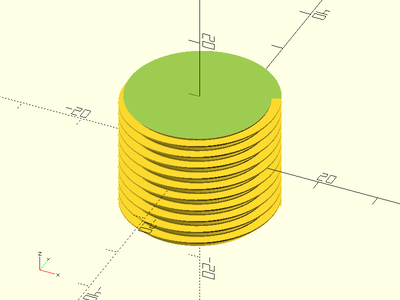
Description: Constructs a simple buttress threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
d |
Outer diameter of threaded rod. |
l |
length of threaded rod. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
bevel1 |
if true, bevel the axis-negative end of the thread. Default: false |
bevel2 |
if true, bevel the axis-positive end of the thread. Default: false |
internal |
If true, this is a mask for making internal threads. |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOPIt is effective only for internal=true. |
orient |
Orientation of the rod. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the rod. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1:
projection(cut=true)
buttress_threaded_rod(d=10, l=15, pitch=2, orient=ORIENT_X);

Example 2:
buttress_threaded_rod(d=10, l=20, pitch=1.25, left_handed=true, $fa=1, $fs=1);

Example 3:
buttress_threaded_rod(d=25, l=20, pitch=2, $fa=1, $fs=1);
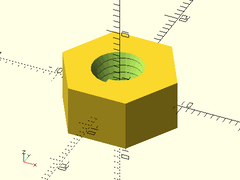
Description: Constructs a hex nut for a simple buttress threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
od |
diameter of the nut. |
id |
diameter of threaded rod to screw onto. |
h |
height/thickness of nut. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOP
|
orient |
Orientation of the nut. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the nit. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example:
buttress_threaded_nut(od=16, id=8, h=8, pitch=1.25, left_handed=true, slop=0.2, $fa=1, $fs=1);
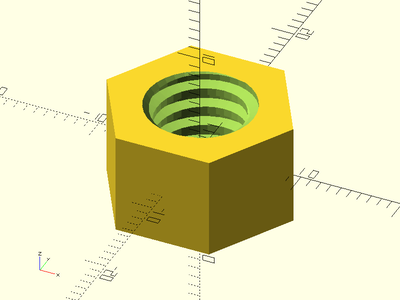
Description: Constructs a metric trapezoidal threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
d |
Outer diameter of threaded rod. |
l |
length of threaded rod. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
bevel1 |
if true, bevel the axis-negative end of the thread. Default: false |
bevel2 |
if true, bevel the axis-positive end of the thread. Default: false |
starts |
The number of lead starts. Default = 1 |
orient |
Orientation of the rod. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the rod. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1:
projection(cut=true)
metric_trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=10, l=15, pitch=2, orient=ORIENT_X);

Example 2:
metric_trapezoidal_threaded_rod(d=10, l=30, pitch=2, left_handed=true, $fa=1, $fs=1);

Description: Constructs a hex nut for a metric trapezoidal threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
od |
diameter of the nut. |
id |
diameter of threaded rod to screw onto. |
h |
height/thickness of nut. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
starts |
The number of lead starts. Default = 1 |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOP
|
orient |
Orientation of the nut. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the nut. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example:
metric_trapezoidal_threaded_nut(od=16, id=10, h=10, pitch=2, left_handed=true, bevel=true, $fa=1, $fs=1);
Description: Constructs an ACME trapezoidal threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
d |
Outer diameter of threaded rod. |
l |
length of threaded rod. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
thread_depth |
Depth of the threads. Default = pitch/2 |
thread_angle |
The pressure angle profile angle of the threads. Default = 14.5 degrees |
starts |
The number of lead starts. Default = 1 |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
bevel1 |
if true, bevel the axis-negative end of the thread. Default: false |
bevel2 |
if true, bevel the axis-positive end of the thread. Default: false |
orient |
Orientation of the rod. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the rod. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1:
projection(cut=true)
acme_threaded_rod(d=10, l=15, pitch=2, orient=ORIENT_X);
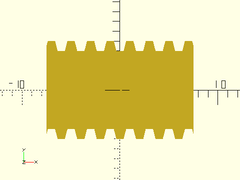
Example 2:
acme_threaded_rod(d=3/8*25.4, l=20, pitch=1/8*25.4, $fn=32);

Example 3:
acme_threaded_rod(d=10, l=30, pitch=2, starts=3, $fa=1, $fs=1);
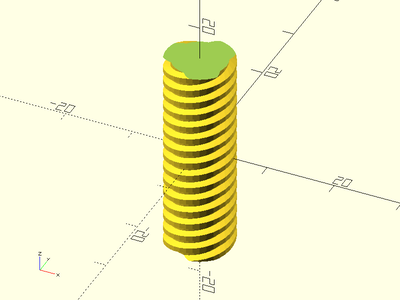
Description: Constructs a hex nut for an ACME threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
od |
diameter of the nut. |
id |
diameter of threaded rod to screw onto. |
h |
height/thickness of nut. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
thread_depth |
Depth of the threads. Default=pitch/2 |
thread_angle |
The pressure angle profile angle of the threads. Default = 14.5 degree ACME profile. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOP
|
orient |
Orientation of the nut. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the nut. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1:
acme_threaded_nut(od=16, id=3/8*25.4, h=8, pitch=1/8*25.4, slop=0.2);
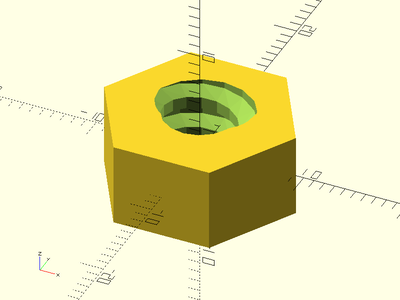
Example 2:
acme_threaded_nut(od=16, id=10, h=10, pitch=2, starts=3, slop=0.2, $fa=1, $fs=1);
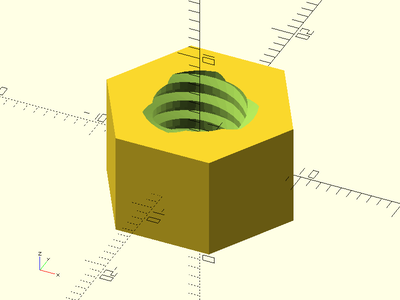
Description: Constructs a square profile threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
d |
Outer diameter of threaded rod. |
l |
length of threaded rod. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
bevel1 |
if true, bevel the axis-negative end of the thread. Default: false |
bevel2 |
if true, bevel the axis-positive end of the thread. Default: false |
starts |
The number of lead starts. Default = 1 |
orient |
Orientation of the rod. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the rod. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example 1:
projection(cut=true)
square_threaded_rod(d=10, l=15, pitch=2, orient=ORIENT_X);
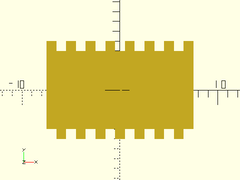
Example 2:
square_threaded_rod(d=10, l=20, pitch=2, starts=2, $fn=32);

Description: Constructs a hex nut for a square profile threaded screw rod. This method makes much smoother threads than the naive linear_extrude method.
| Argument | What it does |
|---|---|
od |
diameter of the nut. |
id |
diameter of threaded rod to screw onto. |
h |
height/thickness of nut. |
pitch |
Length between threads. |
left_handed |
if true, create left-handed threads. Default = false |
bevel |
if true, bevel the thread ends. Default: false |
starts |
The number of lead starts. Default = 1 |
slop |
printer slop calibration to allow for tight fitting of parts. Default: PRINTER_SLOP
|
orient |
Orientation of the nut. Use the ORIENT_ constants from constants.scad. Default: ORIENT_Z. |
align |
Alignment of the nut. Use the V_ constants from constants.scad. Default: V_CENTER. |
Example:
square_threaded_nut(od=16, id=10, h=10, pitch=2, starts=2, slop=0.15, $fn=32);