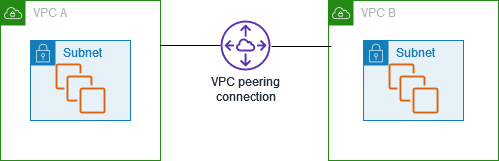
This Terraform code deploys a simple infrastructure in two different AWS regions that includes private EC2 instances without internet access and allows them to communicate with each other using AWS SSM for added security.
This Terraform infrastructure deploys the following components:
- Two separate Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs) in different AWS regions.
- VPC peering connection between the two VPCs.
- Two private EC2 instances without internet access (one in each VPC).
- Security groups to allow ICMP (ping) traffic between the instances.
- AWS IAM roles and profiles to enable AWS SSM for secure access.
This infrastructure focuses on security by:
- Implementing VPC peering for private communication.
- Restricting ICMP traffic to the instances via security groups.
- Enabling AWS SSM for secure access - instances can only be accessed via SSM, not publicly.
A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IPv4 addresses or IPv6 addresses.
You can create a VPC peering connection between your own VPCs and the VPCs can be in different Regions (also known as an inter-Region VPC peering connection). Instances in either VPC can communicate with each other as if they are within the same network.
When establishing peering relationships between VPCs across different AWS Regions, resources in the VPCs (for example, EC2 instances) in different AWS Regions can communicate with each other using private IP addresses, without using a gateway, VPN connection, or network appliance.
- The traffic remains in the private IP space
- Traffic always stays on the global AWS backbone
- Inter-Region VPC peering provides a simple and cost-effective way to share resources between regions
- SSM Agent is preinstalled on AMI Amazon Linux 2023
As more and more organizations adopt cloud computing, managing resources on cloud platforms like AWS becomes increasingly important. The need to manage multiple instances of EC2 instances effectively has led to the development of various tools to simplify the process. One such tool is the AWS Systems Manager (SSM), which enables users to manage EC2 instances, as well as other AWS resources, using a single interface. One of the most powerful features of SSM is the ability to perform SSH-less login to EC2 machines, which i used.
To use SSM for SSH-less login, follow the steps below:
Security Group for EC2 Instance: The minimum traffic you need to allow for SSM access to work is to add an Outbound HTTPS (port 443) in the security group for EC2 instance.
Create an IAM Role: To use SSM to log in to EC2 instances, you must first create an IAM role with the required permissions. The role must have the AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore policy attached to it, which allows SSM to access the EC2 instances.
Install SSM Agent: After creating the IAM role, you need to install the SSM agent on each EC2 instance you want to access using SSM. The SSM agent is pre-installed on Amazon Linux 2 and Amazon Linux AMIs, but you must install it manually on other instances.
Configure EC2 Instances: Once the SSM agent is installed, you need to configure your EC2 instances to allow SSM access. You can do this by creating a VPC endpoint for SSM. VPC endpoints which are required when using Private Subnets are below:
- com.amazonaws.region.ec2messages
- com.amazonaws.region.ssmmessages
- com.amazonaws.region.ssm
Once the infrastructure is deployed, you can test the connectivity between the EC2 instances. Proof of connectivity:
The private ip of EC2 instance in us-east-1 region: 10.0.1.53
The private ip of EC2 instance in us-west-1 region: 10.1.1.179
Ping from EC2 instance in us-east-1 region to 10.1.1.179
Ping from EC2 instance in us-west-1 region to 10.0.1.53
Before deploying this infrastructure, you should have the following:
- AWS CLI configured with necessary access.
- Terraform installed on your local machine.
- AWS access and secret keys set as environment variables or in your AWS credentials file.
Clone the project
git clone https://github.com/shmuelSigler/Provision_AWS_Infrastructure_With_Terraform.gitGo to the project directory
cd Provision_AWS_Infrastructure_With_TerraformInitialize Terraform
terraform initApply the Terraform configuration
terraform applyAmazon Machine Images (AMIs) with SSM Agent preinstalled : SSM Agent is preinstalled on some Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) provided by AWS.
AmazonSSMManagedInstanceCore: The policy for Amazon EC2 Role to enable AWS Systems Manager service core functionality.
How to Attach an IAM Role to EC2 Instance using Terraform
VPC peering: A VPC peering connection is a networking connection between two VPCs that enables you to route traffic between them using private IPv4 addresses.
create VPC endpoints for Systems Manager: create VPC endpoints so that I can use Systems Manager to manage private EC2 instances without internet acces.