DeFi Overview
- Special Offer for big-delegator
- Follow the instruction How to become a VNA delegator
- VNA Pool never require your private key or seed phrases
- Delegate ADA does not require to transfer or send any ADA amount to Stake Pool
- Your key, your coin never share your key.
There are a lot of projects called themselves DeFi (Decentralized Finance).
However, DeFi is a complex definition relating to multiple components.
There are some essential components included such as Automated Market Maker, Order Book or Liquidity Pool.
Each component might cover other ones in some specific implementation (Unique Selling Point).
- Decentralized Finance -> DeFi
- Automated Market Maker -> AMM
- Decentralized Exchange -> DEX
As the previous article Blockchain-The-Easyway, there are several issues relate to centralized finance system such as information manipulation or cheats.
In addition, centralized finance is not accessible for anyone. It does require the identity information and accessibility to the local finance-service providers.
There is a demand to "migrate" conventional Centralized Finance Businesses to Decentralized ones such as lending or stock exchanging in order to provide more utilities/features in the Blockchain Networks.
(source : https://twitter.com/Cardians_/status/1419477237217120256/photo/1)
Furthermore, there is still a centralized point in Blockchain/Crypto Currencies world is the Crypto Exchanges. As of September 2021 the asset/liquidity in the exchanges is about 10-15% of market volume.
For trading crypto asset, the users must transfer their asset to Exchange's Wallet -> lose the asset ownership and suffer the risk of being hacked without any insurance.
DeFi could be an alternative exchange to solve this, however , there are a lot of DeFi implementations (as the image above).
Let's investigate about several DeFi components

source https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Order_book_depth_chart.gif
Order Book is a core component in centralized Exchanges such as Binance or Coinbase.
- Recording all Buy/Sell bid
- The price is calculated by the equilibirum range between Buy and Sell bids
Order Book require a large volume/liquidity for both Buy/Sell bid in order to process transaction quickly.
It is unsuitable for the low trading volume markets in which new kind tokens are released. It may cost several hours or days for a transaction.
AMM lower the entry barrier for the low trading volume markets by providing liquidity pool having dynamic ratio/price. Furthermore, it is enable traders to swap assets without losing the asset ownership.

Liquidity is an asset characteristic. It defines how ease to convert asset to another ones or cash.
In most of the case, cash is the most liquid asset (without high inflation-rate).
Quantitative metrics are:
- Required duration to convert asset (how quickly)
- Slippage (how much)
Take the image above as an example :
- Hung want to trade home for gold.
- P_hc is the home price in cash and this step cost T_hc days to complete
- P_cg the the gold price in cash and this step cost T_cg hours to complete
- Liquidity is calculated by how much slippage of gold in the interval T_hc + T_cg
Practically liquidity calculation is based on how quickly the asset is converted to cash with a small slippage.
This is a core component in almost DeFi projects. Total Value Locked is the metric to measure how big the pool is.
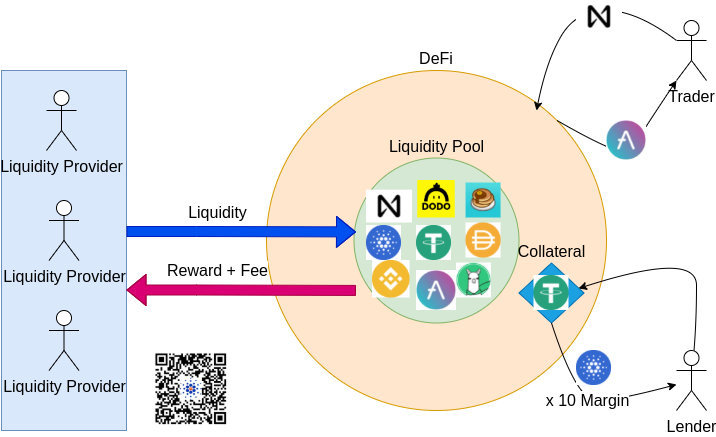
- Liquidity Provider transfer their asset to the pool -> Yield Farming by collecting fee and reward
- Trader trade/swap asset from the pool with a small fee
- Lender lock their collateral to the DeFi -> fixed the position with a specific asset.
There are a lot of implementations to maintain the assets/tokens in the liquidity pool.
There is no the best implementation, each implementation has it own pros/cons characteristics.

Multi-pairs in one central liquidity pool
- All trading-pairs share the same liquidity pool.
- The price or asset ratio is calculate based on Base Asset
- Provide better liquidity for all trading pairs
- Complicated price estimation -> higher slippage

Dedicated liquidity pool
- Each trading pair has a dedicated liquidity pool
- Liquidity is not fairly allocated
- Impermanent loss(1) may be over-amplified in low-liquidity pair
- Simple price estimation -> lower slippage
“Simply put, impermanent loss is the difference between holding tokens in an AMM and holding them in your wallet.” - Nate Hindman
Impermanent loss is the consequence of price fluctuation.

- Called x is quantity of ADA in liquidity pool
- Called y is quantity of USDT in liquidity pool
- x * y = 10^8 is a constant number at any given Time (T)
- Compare to hodling 100 ADA and 100 USDT at T0 -> T1, impermanent loss ~~ (300$ - 282.84$ + interest)
- Impermanent loss is Permanent loss if the x/y ratio are differ from add liquidity time(T0) and redeem liquidity time(T1)
- The shorter the T0 -> T1 duration the higher Impermanent loss, due to liquidity interest cannot conpensate the slippage.

source https://academy.binance.com/en/articles/impermanent-loss-explained
There is no Order Book to calculate equilibirum price -> the price is exactly the ratio of asset in each liquidity pool.
Price Estimation is the core-logic which make DeFi differential between good and bad one.
DeFi applications could interact to each other to automaticcaly update the liquidity/asset ratio
There are several DeFi projects build on another DeFi (e.g. Alpaca Finance)
DeFi applications are usually 100% on-chain(2) smart-contracts(3) running on a Blockchain Network.
Blockchain Network (or Decentralized Ledger) basic operation(read/write) characteristics are:
- Zero-fee or zero-cost for querying or getting data/balance from Decentralized Ledger
- Required a transaction fee (also called gas in ETH network) for inserting new data
Base on the above facts, DeFi applications mostly depend on AMM / Liquidity pool component. Order Book component in DeFi does require a insert operation for any order placed.
It seems unreasonable to cost Traders to pay Transaction fee in order to place a Buy/Sell bid.
AMM components is more suitable for DeFi than Order Book.
Notes:
- Some DeFi projects offer Order Book as their built-in feature
-
Order Book in DeFi has it trade-offs
- A centralized database or private chain to record order book (still zero fee but centralized)
- Cost a small-fee per Buy/Sell bid
-
DeFi usually a smart-contract running 100% on-chain.
- DeFi is a software running on blockchain, thus, it could have bugs Poly Network Hacked
- AMM could stimulate a market with a low liquidity.
- Lending in DeFi could not mimic 100% as real-world lending business.
- Order Book in DeFi has several drawbacks about bid-cost.
- (1) Impermanent loss : Detail explain
- (2) on-chain : fully execution on Blockchain network by the smart-contract implementation itself
- (3) smart-contract : Brief explain
