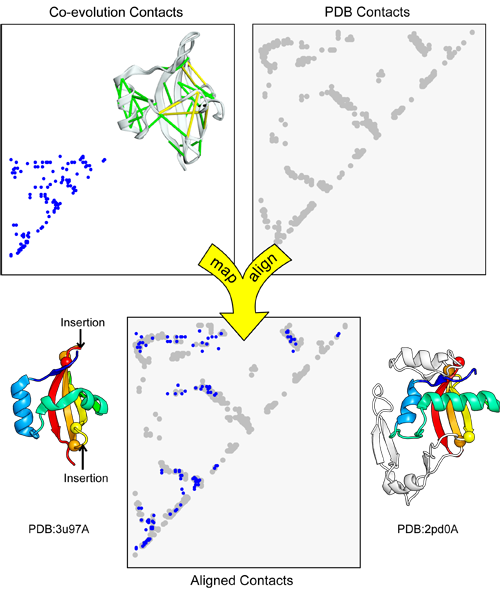
map_align takes two contact maps and returns an alignment that attempts to maximize the number of overlapping contacts while minimizing the number of gaps.
- (20Feb2018) A new implementation that works directly with PDB structures: https://github.com/gjoni/map_align
$ g++ -O3 -std=c++0x -o map_align main.cppFor parallel version:
$ g++ -O3 -std=c++0x -o map_align_omp main_omp.cpp -fopenmp-------------------------------------------------------------------
MAP_ALIGN
-------------------------------------------------------------------
-a contact map A [REQUIRED]
-b contact map B [REQUIRED]
-gap_o gap opening penalty [Default=-1]
-gap_e gap extension penalty [Default=-0.01]
-sep_cut seq seperation cutoff [Default=3]
-iter number of iterations [Default=20]
-silent
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Advanced options
-------------------------------------------------------------------
-range_a trim map A to specified range(s) (eg. 0-20 50-100)
-range_b trim map B to specified range(s)
-------------------------------------------------------------------
Experimental features
-------------------------------------------------------------------
-use_gap_ss penalize gaps at secondary structure elements(SSE)
-gap_ss_w gap penality weight at SSE [Default=2]
-use_prf use sequence profile
-prf_w profile weight [Default=1]
-------------------------------------------------------------------
$ map_align -a A.map -b B.mapLEN 440- [len]gthCON 0 4 1.0- [con]tact, i, j and weight.PRF 0 A H 0.01 ... 0.01(optional) profile, i, amino acid (AA), secondary structure (SS) and profile frequencies (20 values). The order of the frequencies does not matter, as long as they match between the two contact maps being compared. H = Helix; E = Sheet; all other characters treated equally.
- the output will be a single line (if -silent is used).
MAX params map_a map_b contact_sco gap_sco total_sco aln_len 0:0 1:1 2:2 ...- the alignment is provided as
0:0with index of first and second map. - if "-use_prf" flag is used, the output will include an extra profile_sco column:
MAX params map_a map_b contact_sco gap_sco profile_sco total_sco aln_len 0:0 1:1 2:2 ...
- WARNING: these are experimental features and may not work correctly!
- "gap_ss" uses the SS info provided in the "PRF" line to increasing gap penalities within secondary structure elements, favoring gaps in loop or regions of missing density.
- "prf" uses the frequencies provided in the "PRF" line to assist in alignment. This option was intented to help align regions void of contact information. The average frequencies of input profiles (from both maps) is used to compute the background frequencies. WARNING: This option may hurt finding the optimial alignment when aligning non-homologous proteins that share the same fold due to convergent evolution.
- See mk_map directory!
- See mk_map directory!