Basically, this repository re-implements CNN image classifier training logic over CIFAR10 dataset implemented in this repository. However, unlike previous attempt where model is trained on local Apple M2 silicon machine, this repository implements same logic to be executed on remote AWS GPU instance. Specifically, this repository includes following steps:
- Launch instance using Deep Learning AMI
- Train model within the instance
- Validate model using streamlit demo
- Clean-up created resources
Assuming that we created administrator user, configured its profile into AWS CLI and got boto3, typer installed in the virtual environment using following commands, we are good to go.
aws configure # configure administrator profile
python3 -V # Python 3.10.10
python3 -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate
pip install boto3 typerCommands in commands directory are mostly copied and pasted from existing repository, so check it for related details. One difference is AMI ID fetching part, since application would require special drivers to be installed in the instance to run implemented logic successfully. As a result, instance has to be launched on specific Deep Learning AMI, so its AMI ID has to be fetched accordingly like below.
def get_ami_id(ec2_client):
response = ec2_client.describe_images(
Owners=["amazon"],
IncludeDeprecated=False,
IncludeDisabled=False,
DryRun=False,
Filters=[
{
"Name": "name",
"Values": ["Deep Learning AMI GPU TensorFlow 2.11.? (Ubuntu 20.04) ????????"]
},
{
"Name": "state",
"Values": ["available"]
}
]
)
ami = sorted(response["Images"], key=lambda x: x["CreationDate"], reverse=True)[0]
return ami["ImageId"]In above method, response["Images"] would include list of any active image information that matches filter specified in name. Each element is a dictionary of corresponding information as below example shows.
{
'Architecture': 'x86_64',
'ImageId': 'ami-01acd3893bc7a0121',
'ImageLocation': 'amazon/Deep Learning AMI GPU TensorFlow 2.11.0 (Ubuntu 20.04) 20230325',
'ImageOwnerAlias': 'amazon',
'Name': 'Deep Learning AMI GPU TensorFlow 2.11.0 (Ubuntu 20.04) 20230325',
'OwnerId': '898082745236',
'CreationDate': '2023-03-29T09:56:06.000Z',
'DeprecationTime': '2025-03-29T09:56:06.000Z',
'Description': 'Supported EC2 instances: G3, P3, P3dn, P4d, G5, G4dn. Release '
'notes: '
'https://docs.aws.amazon.com/dlami/latest/devguide/appendix-ami-release-notes.html',
...
}Other minor changes on existing codes include:
- Since streamlit demo has to be launched in the instance, so public access on port 8501 is opened. Ports for jupyter applications are all closed.
- As private subnet is unnecessary, corresponding case handling part is removed from the method.
Series of commands to execute the logic is just same as previous demo. For example, if profile name for administrator user is admin.kim, type in following commands consecutively.
python main.py vpc create admin.kim
python main.py subnet create admin.kim
python main.py key-pair create admin.kim
python main.py instance run admin.kim
python main.py instance describe admin.kim Instance type is set to be g3.4xlarge by default, and it contains single GPU. So after connecting to the instance, since AMI that is being used makes the instance to get Tensorflow2 installed while setup, we can use following command to make sure that a GPU is indeed visible.
python -c "import tensorflow as tf; print(tf.config.list_physical_devices('GPU'))"If a non-empty list of single GPU device showed up on the console, we are ready to accelerate the training process. By default, this series of commands will download CIFAR10 dataset from Keras hub, save the training log and corresponding model to /tmp/cifar10 directory within the instance.
git clone https://github.com/sunsikim/aws-cifar10-classifier
cd aws-cifar10-classifier
python model.pyThen, install following packages that will be used to launch model prediction demo. After that, demo can be deployed using following command.
pip install pandas streamlit matplotlib protobuf~=3.19.0
streamlit run demo.pyAfter checking the message that demo page is launched successfully, get public DNS of the launched instance to access the demo page.
python main.py instance describe admin.kimThen demo page will be accessible by sending HTTPS request to the 8501 port of the host. This is an example of a request that can be sent via any web browser.
https://ec2-43-202-44-233.ap-northeast-2.compute.amazonaws.com:8501
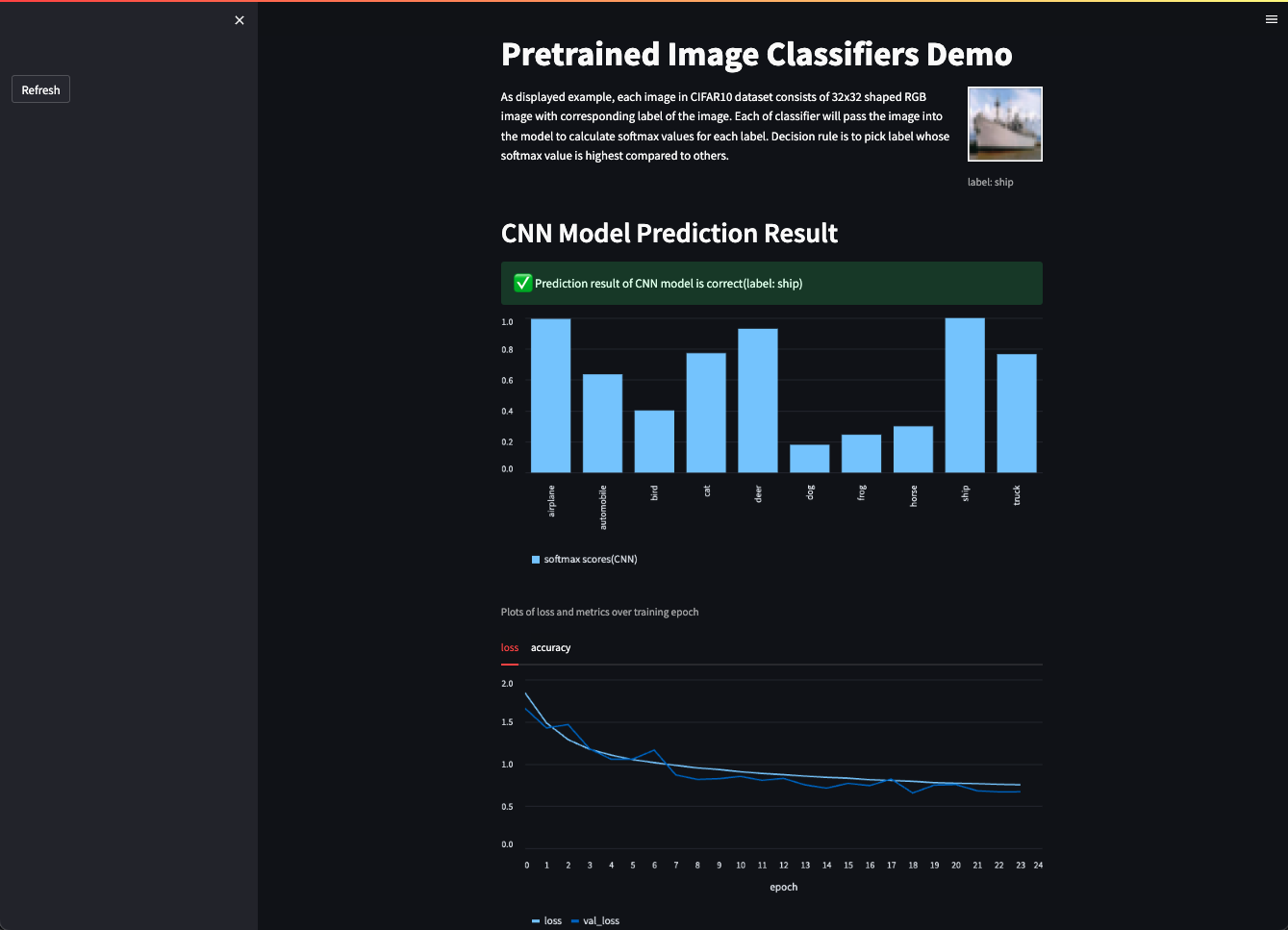
Then you will be able to try out single page demo that displays sampled prediction result with training history below.
After trying out demo page, execute following commands consecutively to prevent any unexpected charge.
python main.py instance terminate admin.kim
python main.py key-pair delete admin.kim
python main.py subnet delete admin.kim
python main.py vpc delete admin.kim