This project was one of the assignments I did for Data Science Fresh Graduate Academy from Binar Academy (the rest of the challenges and exercises can be found here).
First, I performed Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to know more about the features' characteristics and ensure the completeness, consistency, and accuracy of each data points. Specifically, I worked on univariat data analysis on both numerical and categorical variables (with high cardinality!), and observed the relationships between those features using dython library where it is possible to calculate nominal variable's correlation with both numerical and another nominal features.
Then, based on the information I had gathered, I did some basic feature engineering where I eliminated the redundant and unnecessary features (which were discovered to have almost perfect correlation with another variables and thus were very likely colinear with each other), performed binning based on geographical area for categorical data state to reduce its unique values, and used Pandas' get_dummies() to perform One Hot Encoding and transform nominal features to integers.
(Although this approach worked fine in this particular project, I also fully understood that this, in fact, was not the best practice to do it. I might come back and do this step properly using sklearn's transformers or its equivalent at a later time.)
To create the machine learning model itself, I compared 2 different methods: Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier using sklearn's SVC(), and eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) classifier using its sklearn API's XGBClassifier(). The main difference between the two is while SVM is a distance-based model which assumes data normality, XGB is an ensemble form of decision tree algorithm which works well with any type of distribution.
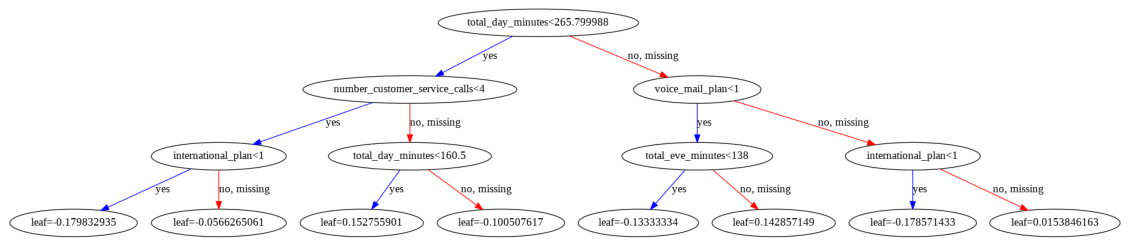
Based on the average of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score for each fold in cross-validation, XGB was chosen as the best model to predict the churn label for this particular dataset. Using the best hyperparameters I had tried in the tuning process using GridSearchCV, I created a final XGB model instance which I trained using all data in train.csv. Here is how the decision tree of said model instance looks like:
This final model was later used to predict customer's churn status from unseen data (test.csv).