This project is about how to classify land use image using Convolutional Neural Network . Land use data provided by UC Merced. This project is developed by using Python3.6, Tensorflow as a backend and Keras as high level deep learning library. Based on dataset, there are 2100 land use images that categorized into 21 classes, so each category has 100 land use images with dimension 256 x 256 pixel. In this project, we will use 85 data for each class as training data and 5 data for each class as testing data, so total 1785 land use images use as training data with 21 class/label and 105 land use images use as testing data with 21 class/label.
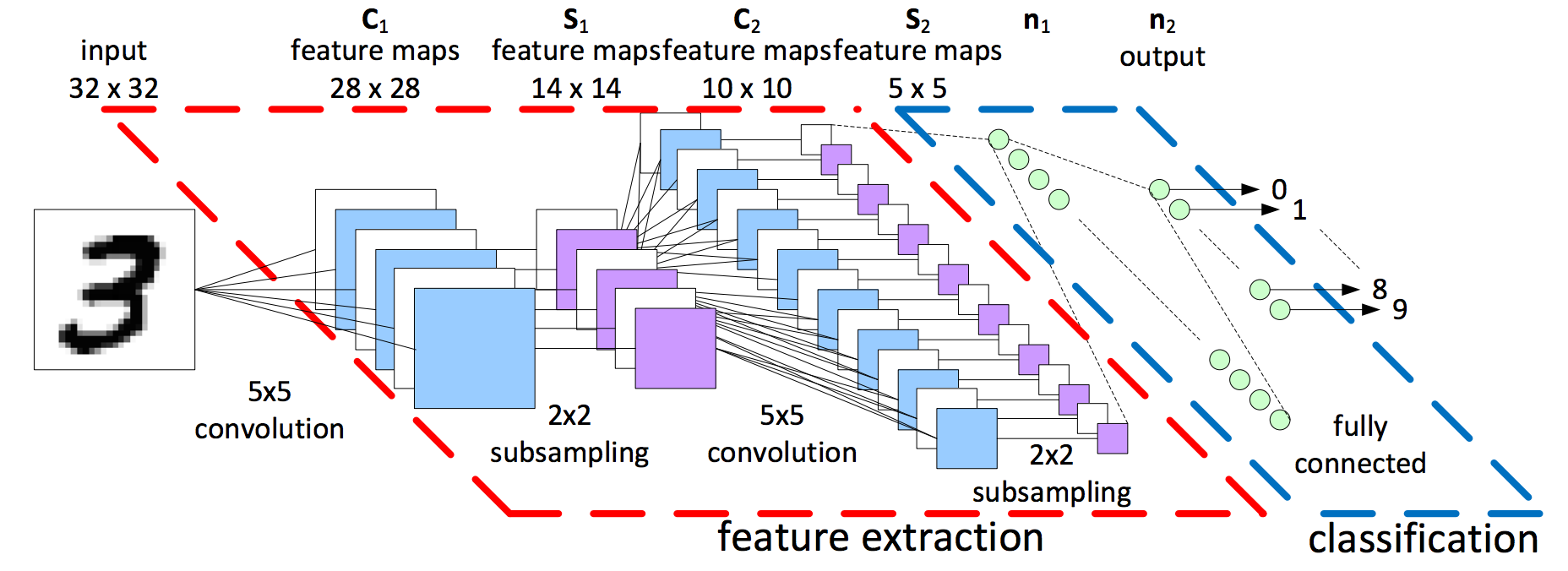
Deep Learning model used in this project is Convolutiona Neural Network (CNN). The illustration of CNN works can be seen as follow Figure below taken from Kernix:
Let say we have MNIST dataset(60k images with 10 labels ( 0 - 9 )) with size each image 32x32 pixels that will be fed into CNN model. the first layer is Convolutional 2D layer with 5x5 kernel size. It means, kernel 5x5 will be convolve (overlapping) each input image pixels until end of pixel. The result of convolution is feature maps with size 28x28. After that, Max Pooling layer will be performed as subsampling with kernel 2x2 (non-overlapping). The result of max pooling layer is feature maps with size 14x14 (because of non-overlapping so stride/movement of kernel is 2).Convolution layer and Max Pooling layer then will be performed again until produce feature maps with size 5x5. Each output in convolutional layer can be activated by using ReLU. After obtaining appropriate feature maps, Fully Connected layer will be performed until produce output y. output can be produced by using Softmax. Detail Description can be found here: CS231 Stanford
- Import libraries
from PIL import Image #import Python Image Library
import numpy as np
import os
import glob
import re
import keras
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Activation, Flatten
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
from keras.utils import np_utils
from keras import backend as K- Read Images
path = os.path.abspath('.cnn.py') #absolute path of program
path = re.sub('[a-zA-Z\s._]+$', '', path) #remove unintended file
dirs = os.listdir(path+'UCMerced_LandUse/Images/') #list directory in Land Use Images folder
label = 0
for i in dirs: #loop all directory
count = 0
for pic in glob.glob(path+'UCMerced_LandUse/Images/'+i+'/*.tif'): #loop all picture in directory
im = Image.open(pic) #open image
im = np.array(im) #change into array
if((im.shape[0]==256) and (im.shape[1] ==256) and count <90): #get only 90 data with image shape only 256x256
r = im[:,:,0]; g = im[:,:,1]; b = im[:,:,2];
if(n<5): # 5 data in beginning set as test data
x_test.append([r,g,b]) #append image into x_test
y_test.append([label]) #append label in y_test
else: #after obtaining 5 data for testing, remaining data will be used as training
x_train.append([r,g,b]) #append image into x_train
y_train.append([label]) #append label in y_train
count = count + 1 #count image
label = label + 1 #after finishing in the first folder, label will be incremented 0,1..,20
np.array(x_train);np.array(y_train);np.array(x_test);np.array(y_test); #setting x_train,y_train,x_test,y_test as numpy array- Data Normalization
x_train = x_train.astype('float32') #set x_train data type as float32
x_test = x_test.astype('float32') #set x_test data type as float32
x_train /= 255 #change x_train value between 0 - 1
x_test /= 255 #change x_test value between 0 - 1
y_train = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_train, 21) #change label to binary / categorical: [1 0 0 0] = 0, [0 1 0 0] = 1, so on
y_test = keras.utils.to_categorical(y_test, 21) #change label to binary / categorical- Define a model
model = Sequential() #model = sequential
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3),activation='relu',input_shape=input_shape)) #layer convolutional 2D
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))) #max pooling with stride (2,2)
model.add(Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu')) #layer convolutional 2D
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2,2))) #max pooling with stride (2,2)
model.add(Dropout(0.25)) #delete neuron randomly while training and remain 75%
model.add(Flatten()) #make layer flatten
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu')) #fully connected layer
model.add(Dropout(0.5)) #delete neuron randomly and remain 50%
model.add(Dense(21, activation='softmax')) #softmax works- Training
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy',optimizer='adam',metrics=['accuracy']) #setting loss function and optimizer
model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=50, nb_epoch=100, verbose=1, validation_data=(x_test, y_test)) #training with epochs 100, batch size = 50
loss, acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test, verbose=0) #evaluate testing data and calculate loss and accuracy
print('\nTesting loss: {}, acc: {}\n'.format(loss, acc))- accuracy 10 epochs: 47%
- accuracy 50 epochs: 60%
- accuracy 100 epochs: ?
You can try another type of convolutional neural network model like:
- Alex Krizhevsky et al. (2012). ImageNet Classification with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks.
- Simonyan K et al. (2015). VGG Net.
- He et al. (2015). Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
- U Merced Land Use. Uc Merced.
- Keras Blogg. @fchollet.
- Keras Documentation. Keras IO.
- Adnan Ardhian. @adnanardhian.