kriging is a basic implementation of
kriging, a method of
interpolation using Gaussian process regression. kriging supports
ordinary kriging and universal kriging (using a polynomial drift
term), and several variogram models.
In the presence of drift (a varying mean value across the data space),
the observed variogram can be biased (see Starks & Fang, 1982,
Mathematical Geology, 14, 4;
https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01032592). kriging attempts to remove this
bias by subtracting a fitted polynomial drift term before generating
the variogram.
kriging also handles data uncertainties and covariances. If the
data have associated errors, then the data variances and
covariances are factored into the kriging system of equations (see,
for example, Cecinati et al., 2018, Atmosphere, 9(11), 446; https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9110446).
Install directly from this repository:
pip install git+https://github.com/tvwenger/kriging.gitOr, clone the repository and:
python setup.py installfrom kriging import kriging
krig = kriging.Kriging(obs_pos, obs_data, e_obs_data=e_obs_data, obs_data_cov=obs_data_cov)
variogram_fig = krig.fit(
model=model, deg=deg, nbins=nbins, bin_number=bin_number, lag_cutoff=lag_cutoff)
interp_data, interp_var = krig.interp(interp_pos, resample=resample)Intialize a new Kriging object.
krig = kriging.Kriging(obs_pos, obs_data, e_obs_data=e_obs_data, obs_data_cov=obs_data_cov)obs_posis theNxMscalar array of theNobserved Cartesian positions inMdimensions.obs_datais theN-length scalar array of observations at each position.e_obs_data(optional) is theN-length scalar array of observed value uncertainties (standard deviation). IfNone(default), then the data covariance matrix can be supplied viaobs_data_cov. If both areNone, then data uncertainies are not considered in the kriging solution.obs_data_cov(optional) is theNxNscalar array of observed data covariances. IfNone(default), then the (uncorrelated) data uncertainties can be supplied viae_obs_data. If both areNone, then data uncertainies are not considered in the kriging solution.
Fit and remove a polynomial drift component and then fit a variogram model to the drift-subtracted data.
variogram_fig = krig.fit(
model=model, deg=deg, nbins=nbins, bin_number=bin_number, lag_cutoff=lag_cutoff, plot=plot)model(optional) is the assumed variogram model. Available values can be found via:from kriging import kriging; print(kriging._MODELS.keys())deg(optional) is the degree of the polynomial drift term.deg=0(default) is equivalent to ordinary kriging (no drift).nbins(optional) is the number of lag bins to use when generating the variogram. The default value is6.bin_number(optional) is a flag to set how the lag bins are spaced. The default value isFalse, which means that the lag bins have equal width covering the full range of observed lags. IfTrue, then each lag bin includes the same number of data.lag_cutoff(optional) is the maximum lag used to fit the variogram relative to the maximum separation of the observed data. The value of this parameter should be between0.0(not inclusive) and1.0(inclusive, default).plot(optional) if True, generate and return variogram model plot.variogram_fig(optional) fitted variogram model plot (gammavariance vs. lag). Value isNoneifplot=False.
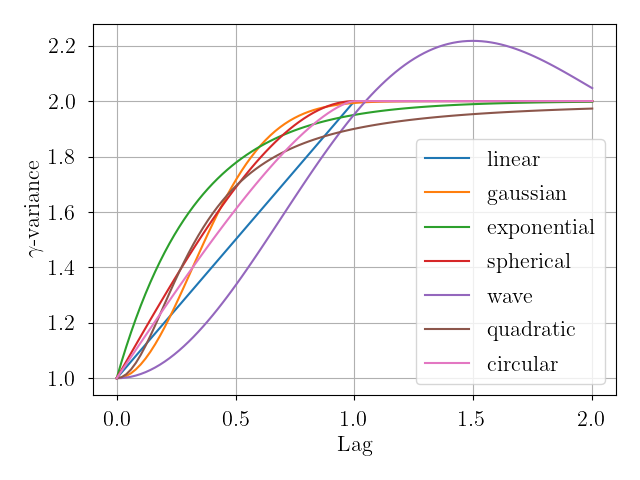
Here is a visual representation of the available variogram models, each having
parameters nugget = 1.0, sill = 1.0, and range = 1.0.
Solve the kriging system of equations and evaluate the interpolation and variance a given positions.
interp_data, interp_var = krig.interp(interp_pos, resample=resample)interp_posis theLxMscalar array ofLCartesian positions at which to calculate interpolated values.resample(optional) is a flag to use resampled observed data to solve the kriging system of equations. The observed data samples are drawn from a multivariate normal distribution defined by the observed data covariance matrix.interp_datais theL-length scalar array of interpolated values at eachinterp_posposition.interp_varis theL-length scalar array of variances at eachinterp_posposition.
For more examples, see the notebooks in the example directory.
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from kriging import kriging
# set a random seed for reproduciblity
np.random.seed(1234)
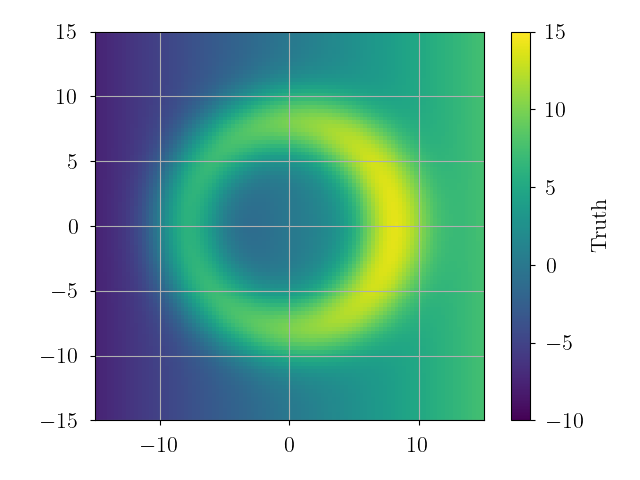
# the "true" field
def truth(pos):
# pos = (N, M) array of N scalar positions in M dimensions
# true field is a horizontal gradient + Gaussian ring
horiz_gradient = 0.5
data = horiz_gradient * pos[:, 0]
radius = np.sqrt((pos**2.0).sum(axis=1))
ring_amp = 10.0
ring_rad = 8.0
ring_sig = 2.0
data += ring_amp * np.exp(-0.5 * ((radius - ring_rad)/ring_sig)**2.0)
return data
# interpolation grid
xgrid, ygrid = np.mgrid[-15:15:100j, -15:15:100j]
extent = [xgrid.min(), xgrid.max(), ygrid.min(), ygrid.max()]
grid_pos = np.vstack((xgrid.flatten(), ygrid.flatten())).T
# plot "truth"
true_data = truth(grid_pos)
plt.imshow(true_data.reshape(xgrid.shape).T, origin='lower', extent=extent, vmin=-10, vmax=15)
plt.colorbar(label="Truth")
plt.tight_layout()# randomly sample observations of the "true" field
num_data = 100
obs_pos = np.random.uniform(-15.0, 15.0, size=(num_data, 2))
obs_data = truth(obs_pos)
# add some Gaussian noise
e_obs_data = 1.0 * np.ones(len(obs_data))
obs_data += e_obs_data * np.random.randn(len(obs_data))
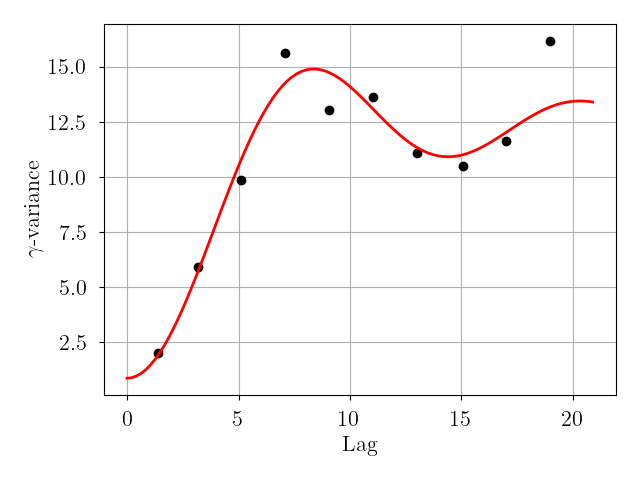
# universal kriging (deg=1)
krig = kriging.Kriging(obs_pos, obs_data, e_obs_data=e_obs_data)
variogram_fig = krig.fit(
model="wave", deg=1, nbins=10, bin_number=False, lag_cutoff=0.5)
interp_data, interp_var = krig.interp(grid_pos)
variogram_fig.show()# plot interpolation
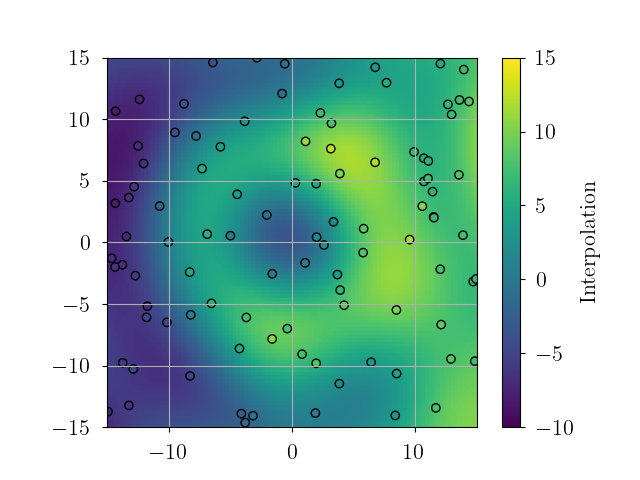
plt.imshow(interp_data.reshape(xgrid.shape).T, origin='lower', extent=extent, vmin=-10.0, vmax=15.0)
plt.scatter(obs_pos[:, 0], obs_pos[:, 1], c=obs_data, edgecolor='k', marker='o', vmin=-10.0, vmax=15.0)
plt.colorbar(label="Interpolation")
plt.show()
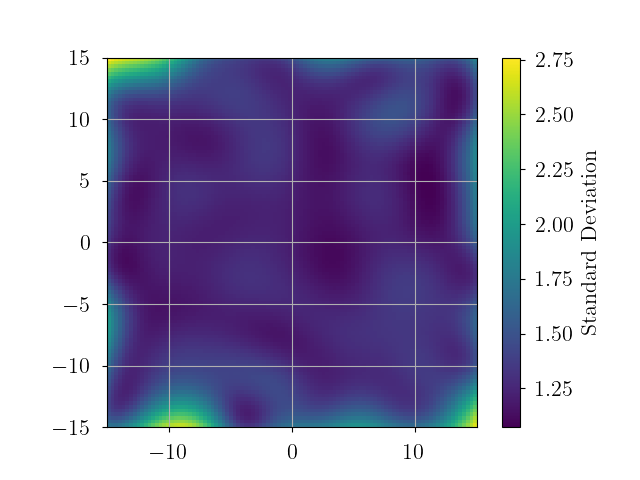
# plot standard deviation
interp_std = np.sqrt(interp_var)
plt.imshow(interp_std.reshape(xgrid.shape).T, origin='lower', extent=extent)
plt.colorbar(label="Standard Deviation")
plt.show()Please submit issues or pull requests via Github.
GNU General Public License v3 (GNU GPLv3)
This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details.
You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses/.