This repository contains projects related to KNN algorithm using Python.
K nearest neighbors is a simple algorithm that stores all available cases and classifies new cases based on a similarity measure (e.g., distance functions). KNN has been used in statistical estimation and pattern recognition already in the beginning of 1970’s as a non-parametric technique.
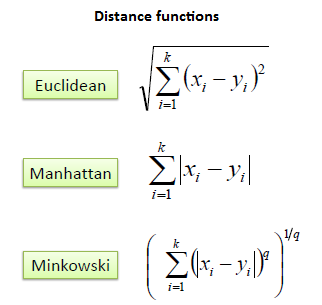
Knn uses follwoing as a distance function :
1)Euclidean distance is calculated as the square root of the sum of the squared differences between a new point (x) and an existing point (xi) across all input attributes j.
EuclideanDistance(x, xi) = sqrt( sum( (xj – xij)^2 ) )
2)Manhattan Distance: Calculate the distance between real vectors using the sum of their absolute difference. Also called City Block Distance.
3)Minkowski Distance: Generalization of Euclidean and Manhattan distance.
Different disciplines in KNN
1) Instance-Based Learning: The raw training instances are used to make predictions. As such KNN is often referred to as instance-based learning or a case-based learning (where each training instance is a case from the problem domain).
2) Lazy Learning: No learning of the model is required and all of the work happens at the time a prediction is requested. As such, KNN is often referred to as a lazy learning algorithm.
3)Non-Parametric: KNN makes no assumptions about the functional form of the problem being solved. As such KNN is referred to as a non-parametric machine learning algorithm.
How to Prepare Data for KNN
1) Rescale Data: KNN performs much better if all of the data has the same scale. Normalizing your data to the range [0, 1] is a good idea. It may also be a good idea to standardize your data if it has a Gaussian distribution.
2)Address Missing Data: Missing data will mean that the distance between samples can not be calculated. These samples could be excluded or the missing values could be imputed.
3)Lower Dimensionality: KNN is suited for lower dimensional data. You can try it on high dimensional data (hundreds or thousands of input variables) but be aware that it may not perform as well as other techniques. KNN can benefit from feature selection that reduces the dimensionality of the input feature space.
Source: https://tinyurl.com/y8fh9fgn