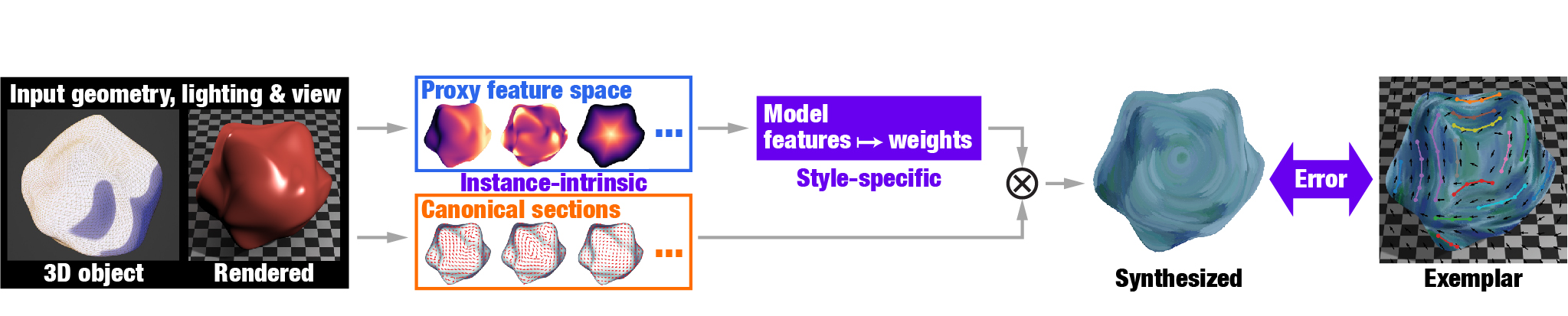
This repository contains the published code for the paper "Stroke Transfer: Example-based Synthesis of Animatable Stroke Styles".
The project was developed using Python 3 (Anaconda environment) with the following packages.
[Anaconda default packages]
- NumPy
- SciPy
- matplotlib
- PyQt5
[Additional dependencies]
- OpenCV
- PyOpenGL
- glumpy
- point cloud utils
- libigl
- pydec
- h5py
- imageio (OpenEXR format)
- tqdm
We provide example assets (e.g., "assets/monkey") for demo usage (you can quickly test the pipeline).
| Exemplar | Reference Rendering | Stroke Rendering |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
| Exemplar | Reference Rendering | Stroke Rendering |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
We have tested a workflow with the blender (3.0 or higher) for 3DCG asset preparation.
[src] single frame data mainly used for regression process.
- exemplar.png: exemplar image (.png) drawn by the artist.
- annotation.json: annotation file (.json) exported from annotation tool (0_annotation.py)
- texture.png: brush texture image used for stroke rendering.
- object_001.obj: 3D model data (.obj) exported from 3D CG software.
- camera_001.json: 3D camera parameter file (.json) exported from 3D CG software (blender/export_camera.py).
- diffuse_001.exr: diffuse image (.exr) exported from 3D CG software.
- specular_001.exr: specular image (.exr) exported from 3D CG software.
[target] animated sequences to apply stroke transfer.
- object/object_%03d.obj: 3D model data (.obj) exported from 3D CG software.
- camera/camera_%03d.json: 3D camera parameter file (.json) exported from 3D CG software (blender/export_camera.py).
- diffuse/diffuse_%03d.exr: diffuse image (.exr) sequences exported from 3D CG software.
- specular/specular_%03d.exr: specular image (.exr) sequences exported from 3D CG software.
If you are interested in preparing custom asset with the blender, please see the manual (3D CG Asset Preparation).
- camera parameters (.json).
- 3D model data (.obj).
The other diffuse or specular image can be generated with usual blender menus.
To run our pipeline, please first move to the target asset directory.
cd assets/deforming_sphereNow you can run each pipeline (command line tool) to output stroke transfer result.
Each command line tool accepts a single XML file to configure the settings.
e.g. you can run smoothing process in the following manner.
python ../../python/3_smoothing.py xml/3_smoothing.xmlThe XML includes input/output settings and parameters to change the results of the pipeline.
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<smoothing>
<!-- input setting -->
<orientation filename_template ="dst/transfer/orientation/orientation_%03d.json"/>
<object filename_template = "target/object/object_%03d.obj"/>
<!-- parameters -->
<params lambda_temporal = "0.5" lambda_spatial = "0.07" deform = "True"/>
<frames start = "1" end = "1"/>
<!-- for visualization purpose -->
<camera filename_template = "target/camera/camera_%03d.json"/>
<diffuse filename_template = "target/diffuse/diffuse_%03d.exr"/>
<!-- for debug -->
<verbose on = "True"/>
<!-- output setting -->
<output orientation = "dst/smoothing/orientation/orientation_%03d.json" />
<!-- internal data setting -->
<internal dirname = "temp" overwrite="False"/>
</smoothing>
0_annotation.py (optional for demo usage)
If you want to make new annotations for the asset, please run the following command.
python ../../python/0_annotation.py xml/0_annotation.xmlYou can annotate stroke orientations and width (length will be automatically computed) using a simple GUI and export annotation.json data (please see Annotation Tool Manual for more details).
The regression process generates the new models for orientations, colors, length, and width in the output directory (in demo: dst/regression).
python ../../python/1_regression.py xml/1_regression.xmlThe transfer process generates the transferred results of orientations, colors, length, and width in the output directory (in demo: dst/transfer).
python ../../python/2_transfer.py xml/2_transfer.xml| Orientation Transfer | Color Transfer | Width Transfer | Length Transfer |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
The smoothing process generates filtered orientations with spatial and temporal regularization parameters in the output directory (in demo: dst/smoothing)
python ../../python/3_smoothing.py xml/3_smoothing.xmlThis process generates the hierarchy of anchor points for stroke drawing process (in demo: dst/anchor_points).
python ../../python/4_anchor_points.py xml/4_anchor_points.xmlThe stroke renderer will generate the stroke layer (without undercoat) and the final result (with undercoat) in the output directory (in demo: dst/stroke)
python ../../python/5_stroke.py xml/5_stroke.xml| Undercoat | Stroke (without undercoat) | Final (with undercoat) |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
If you find Stroke Transfer useful for your research or work, please use the following BibTeX entry.
@inproceedings{ST:2022,
author = {Todo, Hideki and Kobayashi, Kunihiko and Katsuragi, Jin and
Shimotahira, Haruna and Kaji, Shizuo and Yue, Yonghao},
title = {Stroke Transfer: Example-based Synthesis of Animatable Stroke Styles},
booktitle = {SIGGRAPH '22 Conference Proceedings},
year = {2022},
pages = {1--10},
numpages = {10},
doi = {10.1145/3528233.3530703}
}This project is released under MIT License.