Super test manager for JavaScript.
T-man is a refactor version of mocha, but more lightweight, more flexible. In most case, you can use tman replace of mocha directly.
- Examples
- Usage
- Use as CLI
- Use with npm
- Assertions
- Suites and tests
tman.suite(title, fn),tman.describe(title, fn)tman.test(title, fn),tman.it(title, fn)
- Hooks
tman.before(fn)tman.after(fn)tman.beforeEach(fn)tman.afterEach(fn)
- Exclusive or inclusive tests
tman.suite.only(title, fn)tman.it.only(title, fn)tman.suite.skip(title, fn)tman.it.skip(title, fn)tman.grep(pattern)tman.exclude(pattern)
- Timeouts
- Write tests in source code
tman(title, fn)tman.only(title, fn)tman.skip(title, fn)
- Run tests
tman.run([callback])tman.mocha()- T-man CLI
- T-man Test mode
- TypeScript Typings
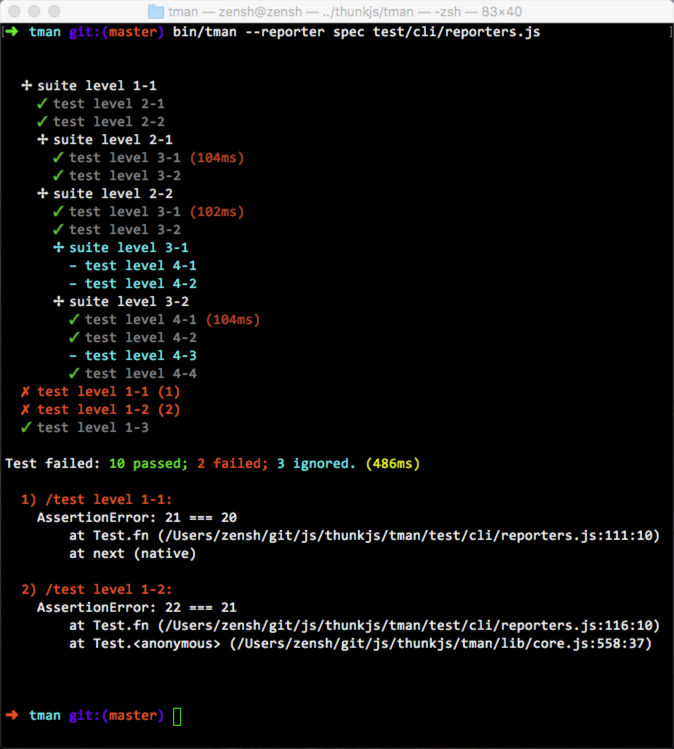
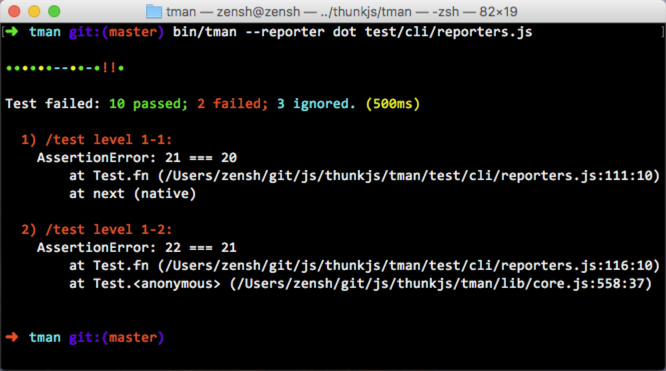
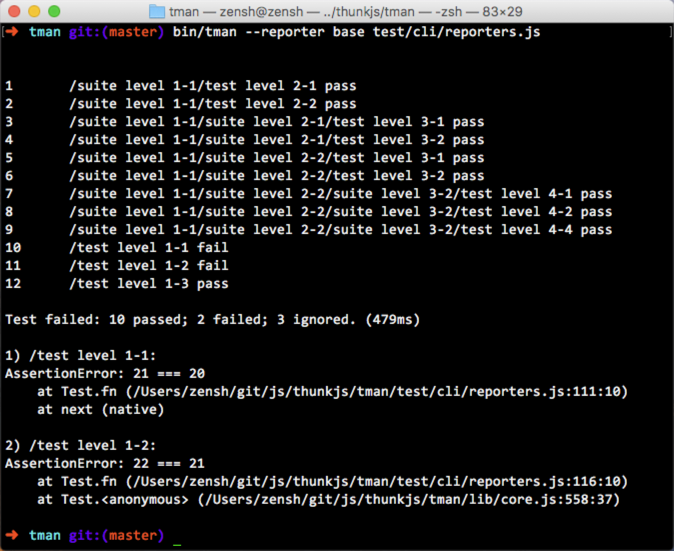
- Reporters
- FAQ
- License MIT
It define test cases in top level, and no suites.
const assert = require('assert')
const tman = require('tman')
const Rx = require('rxjs')
var count = 0
tman.it('synchronous test', function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 0)
})
tman.it('callback style asynchronous test', function (done) {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 1)
setTimeout(done, 100)
})
tman.it('promise style asynchronous test', function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 2)
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 3)
setTimeout(resolve, 100)
})
})
tman.it('thunk style asynchronous test', function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 4)
return function (done) {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 5)
setTimeout(done, 100)
}
})
tman.it('generator style asynchronous test', function * () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 6)
yield function (done) { setTimeout(done, 50) }
yield new Promise(function (resolve) { setTimeout(resolve, 50) })
assert.strictEqual(count++, 7)
})
tman.it('Rx.Observable asynchronous test', function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 8)
return Rx.Observable.fromPromise(new Promise(function (resolve) {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 9)
setTimeout(resolve, 100)
}))
})Run by T-man CLI (need npm i tman -g):
tman example/simpleIt is a mocha style tests. It only can be run by T-man CLI: tman example/mocha.
Through T-man CLI, some method are registered to node global object.
And you can use generator as well, it is equal to mocha + thunk-mocha.
const assert = require('assert')
var count = 0
describe('mocha style', function () {
before(function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 0)
})
after(function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 9)
})
it('synchronous test', function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 1)
})
it('callback style asynchronous test', function (done) {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 2)
setTimeout(done, 100)
})
it('promise style asynchronous test', function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 3)
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 4)
setTimeout(resolve, 100)
})
})
it('thunk style asynchronous test', function () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 5)
return function (done) {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 6)
setTimeout(done, 100)
}
})
it('generator style asynchronous test', function * () {
assert.strictEqual(count++, 7)
yield function (done) { setTimeout(done, 100) }
assert.strictEqual(count++, 8)
})
})tman -r babel-register -r babel-polyfill example/es-next.es:
import assert from 'assert'
import tman from 'tman'
var count = 0
// async "after hook"
tman.after(async () => {
assert.strictEqual(await Promise.resolve(count++), 4)
})
tman.it('async/await asynchronous test', async function () {
assert.strictEqual(await Promise.resolve(count++), 0)
assert.strictEqual(await new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(count++)
}, 100)
}), 1)
})
tman.it('generator asynchronous test', function * () {
// yield Promise
assert.strictEqual(yield Promise.resolve(count++), 2)
// yield thunk function
assert.strictEqual(yield (done) => {
setTimeout(() => {
done(null, count++)
}, 100)
}, 3)
})It shows writing tests in source code. The tests will run in test mode.
It includes nested suites and tests, just simulate practical use case.
It is the test of tman, not only nested suites and tests, but also several tman instance compose!
T-man is easiest to use when installed with npm:
npm install tman -gRun test in myproject_dir:
cd myproject_dir && tmanT-man will try to load myproject_dir/test/*.{js,ts,es,coffee} and run it.
npm script in package.json(, also with istanbul):
"scripts": {
"test": "tman",
"test-cov": "istanbul cover _tman"
}Then run:
npm testor
npm run test-covThe tman will try to load tests with glob test/*.js and run them.
You may also run tests with your own globs: tman test/index.js test/service/*.js test/api/*.js.
T-man has no built-in assertion method, but allows you to use any assertion library you want, if it throws an error, it will work! You can utilize libraries such as:
- assert Node.js built-in assertion module
- should.js BDD style shown throughout these docs
- expect.js expect() style assertions
- chai expect(), assert() and should style assertions
You may use suite to organize huge scale tests. describe is an alias of suite. You can define any level of nested suites and test cases.
tman.suite('User', function () {
tman.suite('#save()', function () {
tman.it('should save without error', function * () {
yield new User('Tman').save()
})
})
})Define test logic, support synchronous or asynchronous test. it is an alias of test.
tman.it('synchronous test', function () {
// test body
})
tman.it('callback style asynchronous test', function (done) {
// test body
setTimeout(done, 100)
})
tman.it('promise style asynchronous test', function () {
// test body
return new Promise(function (resolve) {
// test body
setTimeout(resolve, 100)
})
})
tman.it('thunk style asynchronous test', function () {
// test body
return function (done) {
// test body
setTimeout(done, 100)
}
})
tman.it('generator style asynchronous test', function * () {
// test body
yield thunk.delay(100)
// test body
})This hooks can be used to set up preconditions and clean up after your tests. All of them support synchronous or asynchronous function, just like tman.it. You can define any level hooks for suite or test.
tman.suite('hooks', function () {
tman.before(function () {
// runs before all tests in this block
})
tman.after(function () {
// runs after all tests in this block
})
tman.beforeEach(function () {
// runs before each test in this block
})
tman.afterEach(function () {
// runs after each test in this block
})
// test cases
tman.it('test', function () {
// ...
})
})only and skip will work as your expectation. If you have more than one only in your tests or suites, only the first only will take effect, all other will not be read.
tman.suite('Array', function () {
tman.suite('#indexOf()', function () {
tman.it.only('should return -1 unless present', function () {
// ...
})
tman.it('should return the index when present', function () {
// ...
})
})
})Sets grep pattern and run tests matching pattern, same as --grep <pattern> CLI option.
Sets exclude pattern and exclude tests matching pattern, same as --exclude <pattern> CLI option.
Default timeout is 2000ms.
Suite-level timeouts may be applied to entire test "suites", or disabled via this.timeout(0). This will be inherited by all nested suites and test-cases that do not override the value.
tman.suite('a suite of tests', function () {
this.timeout(500)
tman.it('should take less than 500ms', function (done) {
setTimeout(done, 300)
})
tman.it('should take less than 500ms as well', function (done) {
setTimeout(done, 200)
})
})Test-specific timeouts may also be applied, or the use of this.timeout(0) to disable timeouts all together.
tman.it('should take less than 500ms', function (done) {
this.timeout(500)
setTimeout(done, 300)
});You can write tests in your source code:
exports.stringify = function (val) {
return val == null ? '' : String(val)
}
tman('test in source code', function () {
const assert = require('assert')
tman.it('stringify', function () {
assert.strictEqual(exports.stringify(), '')
assert.strictEqual(exports.stringify(null), '')
assert.strictEqual(exports.stringify(0), '0')
assert.strictEqual(exports.stringify(false), 'false')
assert.strictEqual(exports.stringify(NaN), 'NaN')
})
})The tests will only run in test mode.
You can run the tests programmatically:
// Run: `node example.js`
tman.suite('User', function () {
tman.suite('#save()', function () {
tman.it('should save without error', function * () {
yield new User('Tman').save()
})
})
// others
})
tman.run()If you run tests with CLI, you will not need to use tman.run, the tman command will run tests automatically.
Enable mocha compatible mode, same as --mocha CLI option.
Clear all tests of tman instance.
Load test files to tman, it will clear previous tests file that in require.cache.
Set the given globals.
$ tman --help
Usage: tman [debug] [options] [files]
Options:
-h, --help output usage information
-V, --version output the version number
-c, --colors force enabling of colors
-C, --no-colors force disabling of colors
-d, --debug enable node\'s debugger, synonym for node --debug
-e, --exclude <pattern> exclude tests matching <pattern>
-g, --grep <pattern> run tests matching <pattern>
-gc, --expose-gc expose gc extension
-r, --require <name> require the given module
-R, --reporter <name> specify the reporter to use [spec]
-t, --timeout <ms> set test-case timeout in milliseconds [2000]
--debug-brk enable node\'s debugger breaking on the first line
--es_staging enable all staged features
--globals <names> allow the given comma-delimited global [names]
--harmony<_classes,_generators,...> all node --harmony* flags are available
--icu-data-dir include ICU data
--mocha Mocha compatible mode
--no-sort don\'t sort test files
--no-timeout disables timeouts, given implicitly with --debug
--no-exit require a clean shutdown of the event loop: T-man will not call process.exit
--opts <path> specify opts path
--perf-basic-prof enable perf linux profiler (basic support)
--preserve-symlinks Instructs the module loader to preserve symbolic links when resolving and caching modules
--reporters display available reporters
--throw-deprecation throw an exception anytime a deprecated function is used
--trace trace function calls
--trace-deprecation show stack traces on deprecations
--use_strict enforce strict modeThere are 3 ways to run with test mode:
tman example/test_in_source_code.jsnode example/test_in_source_code.js --testTEST=* node example/test_in_source_code.js
import * as tman from 'tman'
import { tman, suite, it, before, after, beforeEach, afterEach } from 'tman'Use --require option:
tman -r coffee-script/register test/*.coffeetman -r ts-node/register test/*.ts
Here is a simple example. You can require one more modules.
T-man is licensed under the MIT license. Copyright © 2016 thunks.