I am Subham Maity.
Welcome to this book on "Learning HTML In 4 Steps".
I love Programming. One of the aims I had when I started CodeXam was to make learning programming easy.
At CodeXam, we ask ourselves one question every day: "How do we create awesome learning experiences?"
- Level 3 (Master)
For Detailed with visualization
An HTML file contains the structure of the page itself.
It is kind of like the structure of the building.A CSS file contains the styling of the page.
It allows you to change colors, positioning and more.
It is kind of like the design of the building itself.A JavaScript file determines the dynamic and interactive elements on the page.
It determines what happens when users click, hover or type within certain elements.
This is kind of like the functionality of the building.1.Hyper Text Markup Language
2.HTML is the code that is used to
3.structure a web page and its content.
4.The component used to design the
5.structure of websites are called HTML tags
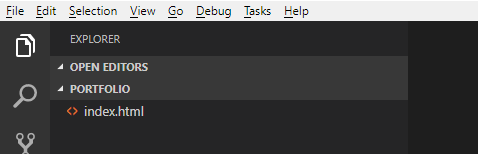
index.html(It is the default name for a website's homepage)
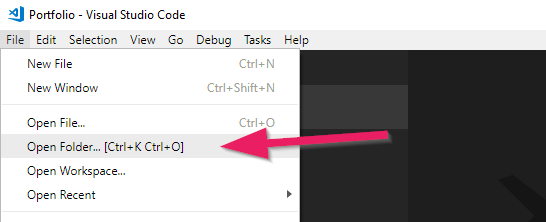
1.Create a folder on your computer for your project. Name the folder Portfolio (or anything you want).
2.Open VS Code.
3.Open the File menu and select Open Folder …. Browse for the folder you created and open it.
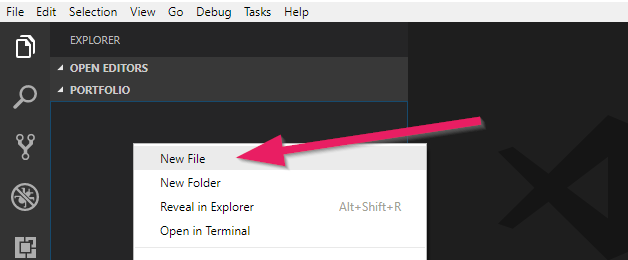
4 .Right-click below the folder and select New File. Name the file index.html.
5.Now you have a blank text file named index.html.
A container for some content or other HTML tags
1.Open vs Code
2. and type !
3.Body
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>1.Html tag is parent of head & body tag
<html lang="en"> </html>2.Most of html elements have opening & closing tags with content in between
<head> </head>3.Some tags have no content in between, eg -
<br>4.We can use inspect element/view page source to edit html -
Like This
view-source:https://www.google.com/This is part of code that should not be parsed.
<!-- This is an HTML Comment --><html> = <HTML>
<p> = <P>
<head> = <HEAD>
<body> = <BODY>Attributes are used to add more information to the tag
<html lang="en">Attributes are used to add more information to the tag
<h1>Heading 1</h1>
<h2>Heading 2</h2>
<h3>Heading 3</h3>
<h4>Heading 4</h4>
<h5>Heading 5</h5>
<h6>Heading 1</h6>Used to add paragraphs in HTML
<p> This is a sample paragraph </p>Used to add links to your page
<a href="https://google.com"> Google </a>How it looks
Used to add links to your page
<img src="/image.png" alt="Description">Used to add next line(line breaks) to your page
<br>Used to highlight text in your page
<b> Bold </b>
<i> Italic </i>
<u> Underline </u>Used to display big & small text on your page
<big> Big </big>
<small> Small </small>Used to display a horizontal ruler, used to separate content
<hr>Used to display a horizontal ruler, used to separate content
<sub> subscript </sub>
<sup> superscript </sup>Used to display text as it is (without ignoring spaces & next line)
<pre> This
is a sample
text.
</pre>using Semantic tags for layout using the Right Tags
<header>
<main>
<footer><section><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The section element</h1>
<section>
<h2>WWF History</h2>
<p>The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) is an international organization working on issues regarding the conservation, research and restoration of the environment, formerly named the World Wildlife Fund. WWF was founded in 1961.</p>
</section>
<section>
<h2>WWF's Symbol</h2>
<p>The Panda has become the symbol of WWF. The well-known panda logo of WWF originated from a panda named Chi Chi that was transferred from the Beijing Zoo to the London Zoo in the same year of the establishment of WWF.</p>
</section>
</body>
</html><article><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The article element</h1>
<article>
<h2>Google Chrome</h2>
<p>Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google, released in 2008. Chrome is the world's most popular web browser today!</p>
</article>
<article>
<h2>Mozilla Firefox</h2>
<p>Mozilla Firefox is an open-source web browser developed by Mozilla. Firefox has been the second most popular web browser since January, 2018.</p>
</article>
<article>
<h2>Microsoft Edge</h2>
<p>Microsoft Edge is a web browser developed by Microsoft, released in 2015. Microsoft Edge replaced Internet Explorer.</p>
</article>
</body>
</html><aside><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>The aside element</h1>
<p>My family and I visited The Epcot center this summer. The weather was nice, and Epcot was amazing! I had a great summer together with my family!</p>
<aside>
<h4>Epcot Center</h4>
<p>Epcot is a theme park at Walt Disney World Resort featuring exciting attractions, international pavilions, award-winning fireworks and seasonal special events.</p>
</aside>
</body>
</html>
<a href="https://google.com" target="main"> Google </a><a href="https://google.com"> <img src="link"> </a><img src="link" height=50px ><img src="link" width=50px >List : Div Tags
<address>
<article>
<aside>
<blockquote>
<canvas>
<dd>
<div>
<dl>
<dt>
<fieldset>
<figcaption>
<figure>
<footer>
<form>
<h1>-<h6>
<header>
<hr>
<li>
<main>
<nav>
<noscript>
<ol>
<p>
<pre>
<section>
<table>
<tfoot>
<ul>
<video>List : Span Tags
<a>
<abbr>
<acronym>
<b>
<bdo>
<big>
<br>
<button>
<cite>
<code>
<dfn>
<em>
<i>
<img>
<input>
<kbd>
<label>
<map>
<object>
<tt>
<var>
<output>
<q>
<samp>
<script>
<select>
<small>
<span>
<strong>
<sub>
<sup>
<textarea>
<time>Lists are used to represent real life list data.
| Type 1 | Type 2 |
|---|---|
| unordered | ordered |
<ul>
<li> Apple </li>
<li> Mango </li>
</ul>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<header></header>
<main>
<ul>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Mango</li>
<li>Litchi</li>
</ul>
</main>
<footer></footer>
</body>
</html>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<header></header>
<main>
<ul>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Mango</li>
<ul>
<li>color : yellow</li>
<li>season : summer /li>
</ul>
<li>Litchi</li>
</ul>
</main>
<footer></footer>
</body>
</html><ol>
<li> Apple </li>
<li> Mango </li>
</ol>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<header></header>
<main>
<ol>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Mango</li>
<li>Litchi</li>
</ol>
</main>
<footer></footer>
</body>
</html>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<header></header>
<main>
<ol>
<li>Apple</li>
<li>Mango</li>
<ol>
<li>color : yellow</li>
<li>season : summer </li>
</ol>
<li>Litchi</li>
</ol>
</main>
<footer></footer>
</body>
</html>Tables are used to represent real life table data.
<tr> |
used to display table row |
|---|---|
<td> |
used to display table data |
<th> |
used to display table header |
Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The tr element</h1>
<p>The tr element defines a row in a table:</p>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Month</th>
<th>Savings</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$80</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The td element</h1>
<p>The td element defines a cell in a table:</p>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Cell A</td>
<td>Cell B</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Cell C</td>
<td>Cell D</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The th element</h1>
<p>The th element defines a header cell in a table:</p>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Month</th>
<th>Savings</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$80</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
<caption> Student Data </caption>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The caption element</h1>
<table>
<caption>Monthly savings</caption>
<tr>
<th>Month</th>
<th>Savings</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$50</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html><thead> to wrap table head
<tbody> to wrap table bodyImplement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The thead, tbody, and tfoot elements</h1>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>Month</th>
<th>Savings</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$80</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
<tfoot>
<tr>
<td>Sum</td>
<td>$180</td>
</tr>
</tfoot>
</table>
</body>
</html>
<th colspan="2" >
Sum: $180
</th><!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
table, th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>The td colspan attribute</h1>
<table>
<tr>
<th>Month</th>
<th>Savings</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>January</td>
<td>$100</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>February</td>
<td>$80</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">Sum: $180</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
Forms are used to collect data from the user
Eg- sign up/login/help requests/contact me
<form>
form content
</form>Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h2>Text input fields</h2>
<form>
<label for="fname">First name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="fname" name="fname" value="John"><br>
<label for="lname">Last name:</label><br>
<input type="text" id="lname" name="lname" value="Doe">
</form>
<p>Note that the form itself is not visible.</p>
<p>Also note that the default width of text input fields is 20 characters.</p>
</body>
</html>Action attribute is used to define what action needs to be performed when a form is submitted
<form action="/action.php" >Taking input from user and placeholder means what will be written down already in that blank space
<input type="text" placeholder="Enter Name">Screen reader users (will read out loud the label, when the user is focused on the element) Users who have difficulty clicking on very small regions (such as checkboxes) - because when a user clicks the text within the element, it toggles the input (this increases the hit area).
<input type="radio" value="class X" name="class" id="id1">
<label for="id1">
</label>
<input type="radio" value="class X" name="class" id="id2">
<label for="id2">
</label>Radio buttons let a user select only one of a limited number of choices:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<h1>Display Radio Buttons</h1>
<form action="/action_page.php">
<p>Please select your favorite Web language:</p>
<input type="radio" id="html" name="fav_language" value="HTML">
<label for="html">HTML</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="css" name="fav_language" value="CSS">
<label for="css">CSS</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="javascript" name="fav_language" value="JavaScript">
<label for="javascript">JavaScript</label>
<br>
<p>Please select your age:</p>
<input type="radio" id="age1" name="age" value="30">
<label for="age1">0 - 30</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="age2" name="age" value="60">
<label for="age2">31 - 60</label><br>
<input type="radio" id="age3" name="age" value="100">
<label for="age3">61 - 100</label><br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>The HTML class attribute is used to specify a class for an HTML element. A class name can be used by multiple HTML elements, while an id name must only be used by one HTML element within the page:
<div id="id1" class="group1">
</div>
<div id="id2"> class="group1">
</div>Let the user select one or more options of a limited number of choices:
<label for="id1">
<input type="checkbox" value="class X" name="class" id="id2">
</label>
<label for="id2">
<input type="checkbox" value="class X" name="class" id="id2">
</label>A multi-line text input control (text area):
<textarea name="feedback" id="feedback" placeholder="Please add Feedback">
</textarea>The <select> element is used to create a drop-down list.
The <select> element is most often used in a form, to collect user input.
<select name="city" id="city">
<option value="Delhi"> Delhi </option>
<option value="Mumbai"> Delhi </option>
<option value="Bangalore"> Delhi </option>
</select><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<h4>Registration Form</h4>
<form action="/action.php">
<input type="text" placeholder="username" />
<br />
<br />
<input type="password" placeholder="password" />
<br /><br />
<h5>Select your class</h5>
<label for="101">
<input type="radio" value="class XI" name="class" id="101" />class XI
</label>
<br /><br />
<label for="102">
<input type="radio" value="class XII" name="class" id="102" />class XII
</label>
<br /><br />
<h5>Select Fav Subjects</h5>
<label for="math">
<input type="checkbox" value="math" name="subject" id="101" /> Math
</label>
<br /><br />
<label for="phy">
<input type="checkbox" value="phy" name="subject" id="102" /> Physics
</label>
<br /><br />
<label for="chem">
<input type="checkbox" value="chem" name="subject" id="103" /> Chemistry
</label>
<br /><br />
<label for="CS">
<input type="checkbox" value="CS" name="subject" id="104" /> Computer
Science
</label>
<br /><br />
Select your city
<select name="city">
<option value="Delhi">Delhi</option>
<option value="Banglore">Banglore</option>
<option value="Pune">Pune</option>
<option value="Mumbai">Mumbai</option>
</select>
<br /><br />
<textarea
name="feedback"
id="101"
placeholder="please give your valuable feedback here"
rows="5"
></textarea>
<br />
<input type="submit" value="submit" />
</form>
<body></body>
</html>
website inside website
<iframe src="link">Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<iframe
width="424"
height="238"
src="https://www.youtube.com/embed/q933Vpo-Naw"
title="YouTube video player"
frameborder="0"
allow="accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture"
allowfullscreen
></iframe>
</body>
</html>
The <video> tag is used to embed video content in a document, such as a movie clip or other video streams.
The <video> tag contains one or more
The text between the <video> and </video> tags will only be displayed in browsers that do not support the <video> element.
<video src="myVid.mp4"> My Video </video>Attributes
- controls
- height
- width
- loop
- autoplay
Implement
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<video width="560" height="315" src="/myVideo.mov" controls> my video
<!-- <video width="560" height="315" src="/myVideo.mov" autoplay> my video -->
<!-- <video width="560" height="315" src="/myVideo.mov" loop> my video -->
</video>
</body>
</html>
/1.png?raw=true)
/2.png?raw=true)
/3.png?raw=true)
/4.png?raw=true)
/5.png?raw=true)


/6.png?raw=true)
/7.png?raw=true)
/8.png?raw=true)
/9.png?raw=true)
/10.png?raw=true)
/11.png?raw=true)
/13.png?raw=true)
/12.png?raw=true)
/14.png?raw=true)
/15.png?raw=true)
/16.png?raw=true)
/17.png?raw=true)
/18.png?raw=true)
/19.png?raw=true)
/20.png?raw=true)
/21.png?raw=true)
/22.png?raw=true)
/24.png?raw=true)
/25.png?raw=true)
/23.png?raw=true)
/26.png?raw=true)
/27.png?raw=true)
/28.png?raw=true)
/29.png?raw=true)
/30.png?raw=true)
/31.png?raw=true)
/32.png?raw=true)
/33.png?raw=true)
/34.png?raw=true)