I built a character recognition web application (currently only digits) which let's you draw a random digit on HTML canvas and let deep ConvNet predict what you have drawn. The application is hosted on Flask.
| 1.png | 2.png | 3.png |
|---|---|---|
 |
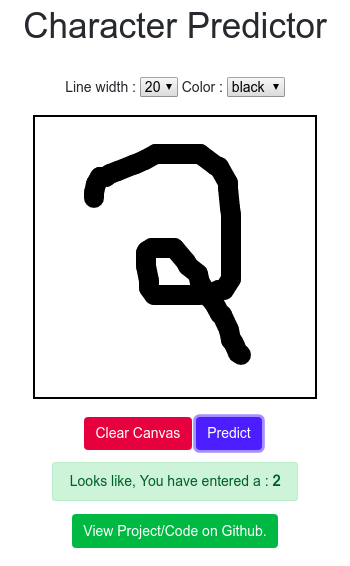 |
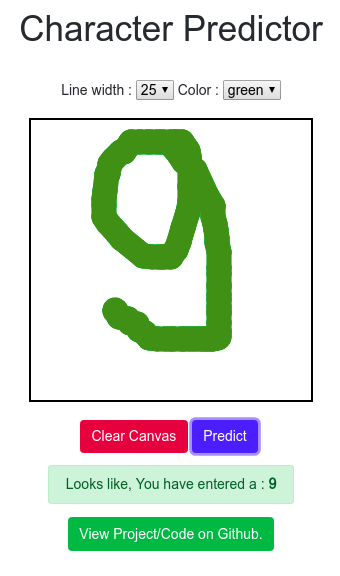 |
Here I will explain how to train the model, also how to setup the app running in your own environment. Also I will try to explain basics of Convolution Neural Network.
You will need Python 3.X.X with some packages which you can install direclty using requirements.txt.
pip install -r requirements.txt
Run the notebook named CNN_model.ipynb and model will be saved as model_cnn_1.h5 in the same directory.
Use the following command in the app directory to run the app.
python3 __init__.py
- The app still takes some time to recognize image. So one thing is to make the pipeline fast.
- Extend the application to be able to detect english alphabets also.
- Also, to detect garbage if anyone draws random shape which do not represent any character.
Convolutional Neural Networks, like neural networks, are made up of neurons with learnable weights and biases. Each neuron receives several inputs, takes a weighted sum over them, pass it through an activation function and responds with an output. The whole network has a loss function and all the tips and tricks that we developed for neural networks still apply on Convolutional Neural Networks.
There are four layered concepts we should understand in Convolutional Neural Networks:
- Convolution,
- ReLu,
- Pooling and
- Full Connectedness (Fully Connected Layer).
Convolution: Convolution has the nice property of being translational invariant. Intuitively, this means that each convolution filter represents a feature of interest (e.g pixels in letters) and the Convolutional Neural Network algorithm learns which features comprise the resulting reference (i.e. alphabet). We have 4 steps for convolution:
- Line up the feature and the image
- Multiply each image pixel by corresponding feature pixel
- Add the values and find the sum
- Divide the sum by the total number of pixels in the feature
ReLu: ReLU is an activation function. Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) transform function only activates a node if the input is above a certain quantity, while the input is below zero, the output is zero, but when the input rises above a certain threshold, it has a linear relationship with the dependent variable.
Pooling: In this layer we shrink the image stack into a smaller size. Pooling is done after passing through the activation layer. We do this by implementing the following 4 steps:
- Pick a window size (usually 2 or 3)
- Pick a stride (usually 2)
- Walk your window across your filtered images
- From each window, take the maximum value
Fully Connected Layer: So to get the time-frame in one picture we can reduce the image size after passing the input through 3 layers. We can further reduce the image to something lesser. We need to perform the 3 operations in an iteration after the first pass and so on. The last layers in the network are fully connected, meaning that neurons of preceding layers are connected to every neuron in subsequent layers. Also, fully connected layer is the final layer where the classification actually happens. Here we take our filtered and shrinked images and put them into one single list.
- Aditya Jain : Portfolio
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE.md file for details