-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 79
Solar Panel Board

KiCad files https://github.com/alanbjohnston/CubeSatSim/tree/master/kicad
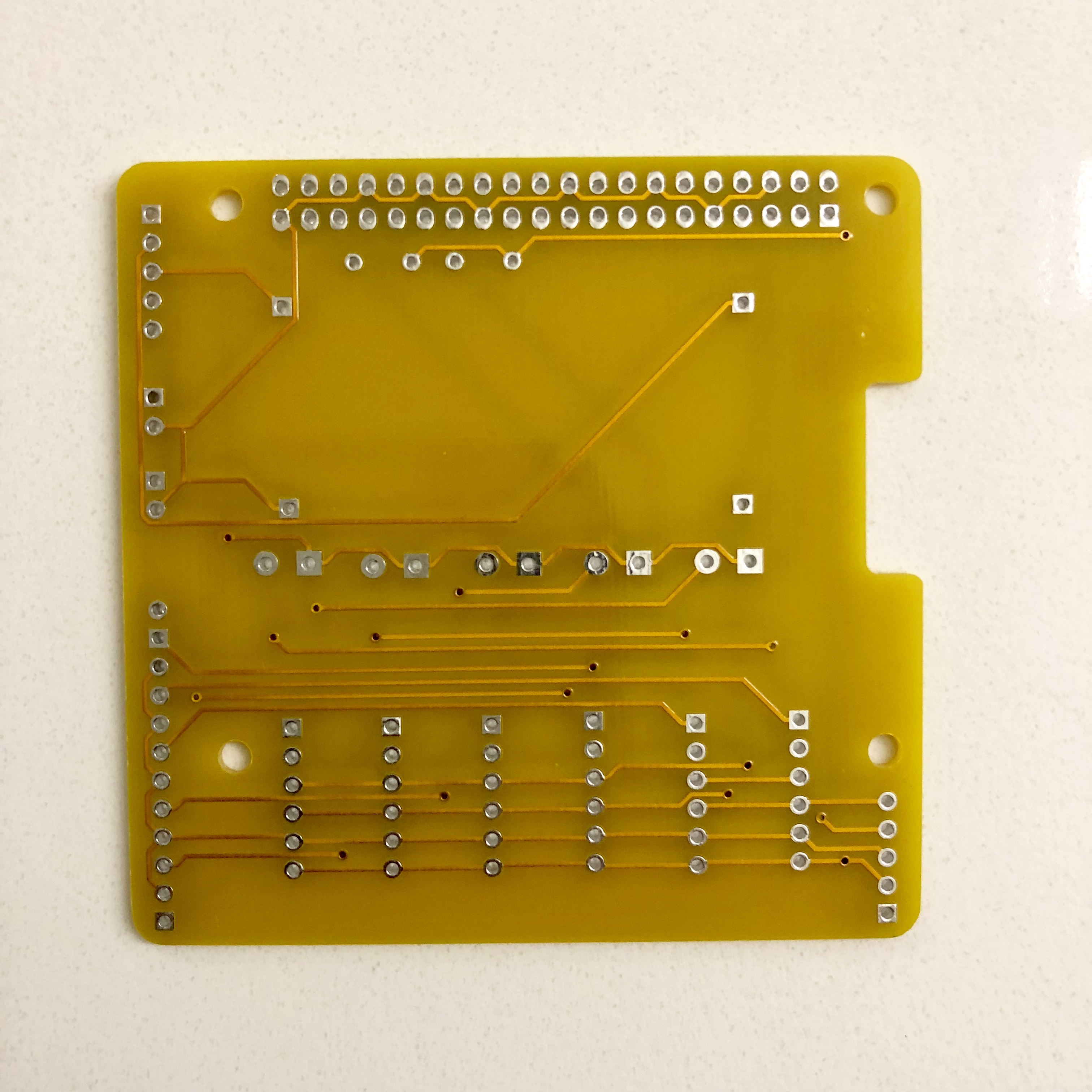
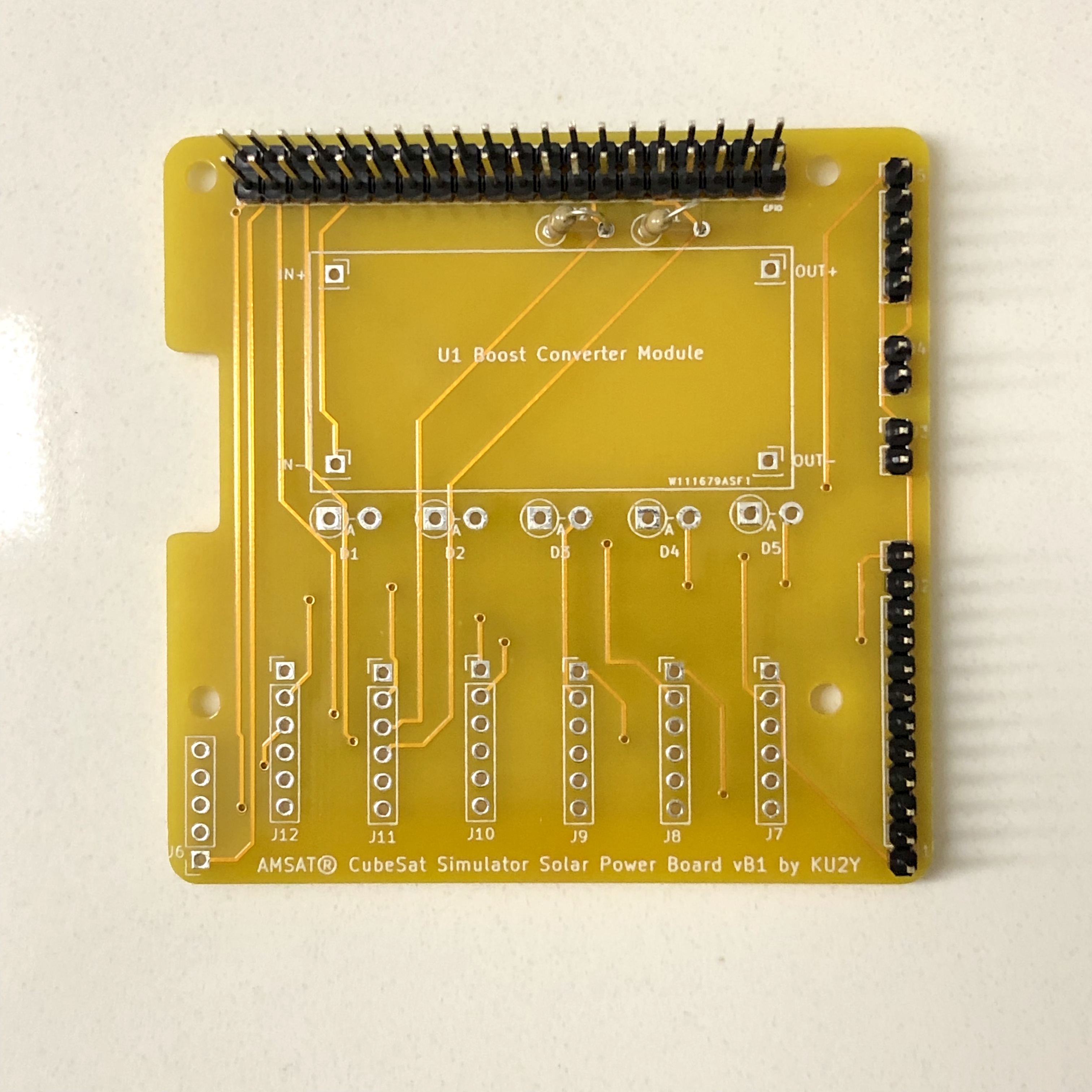
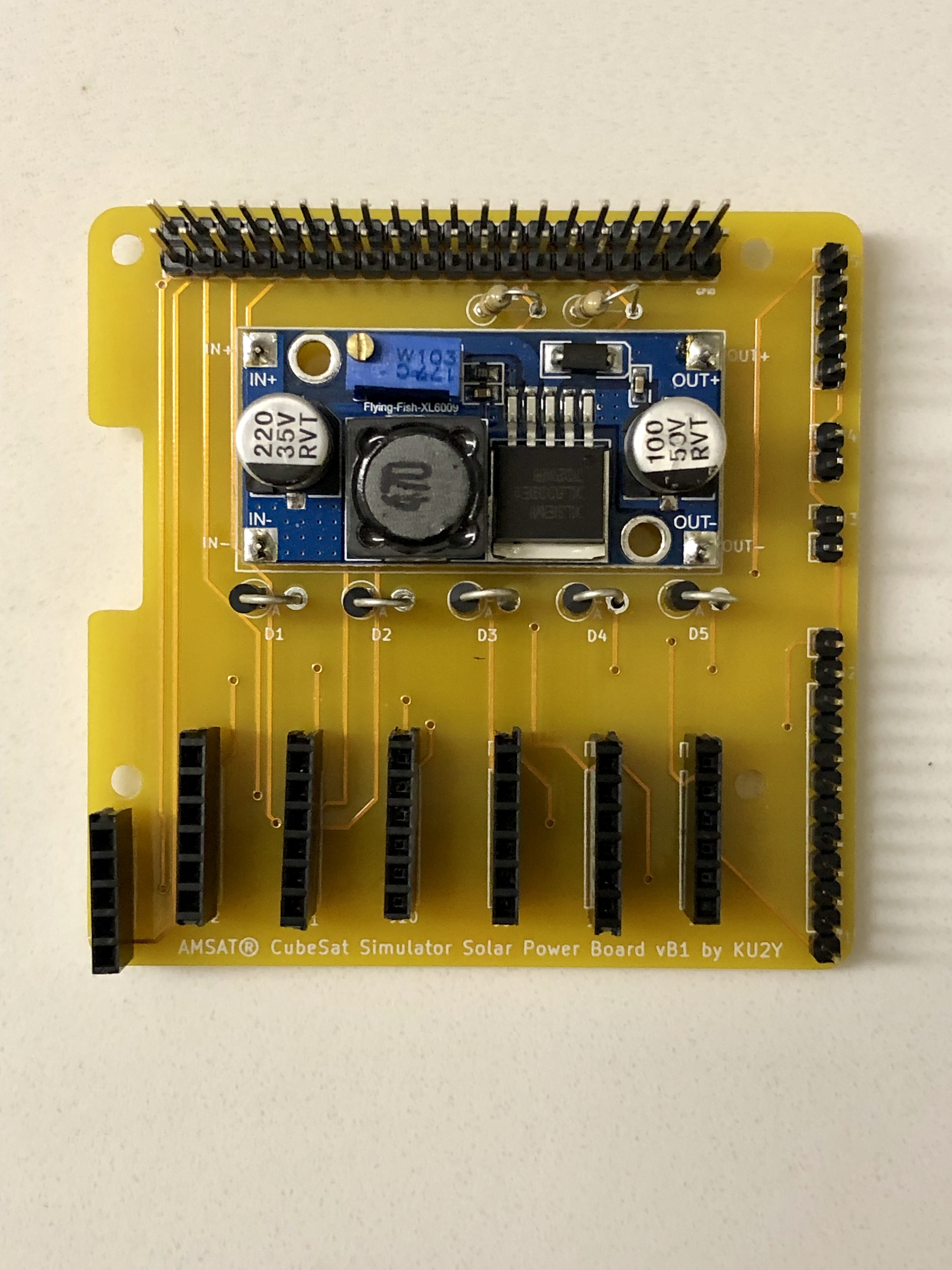
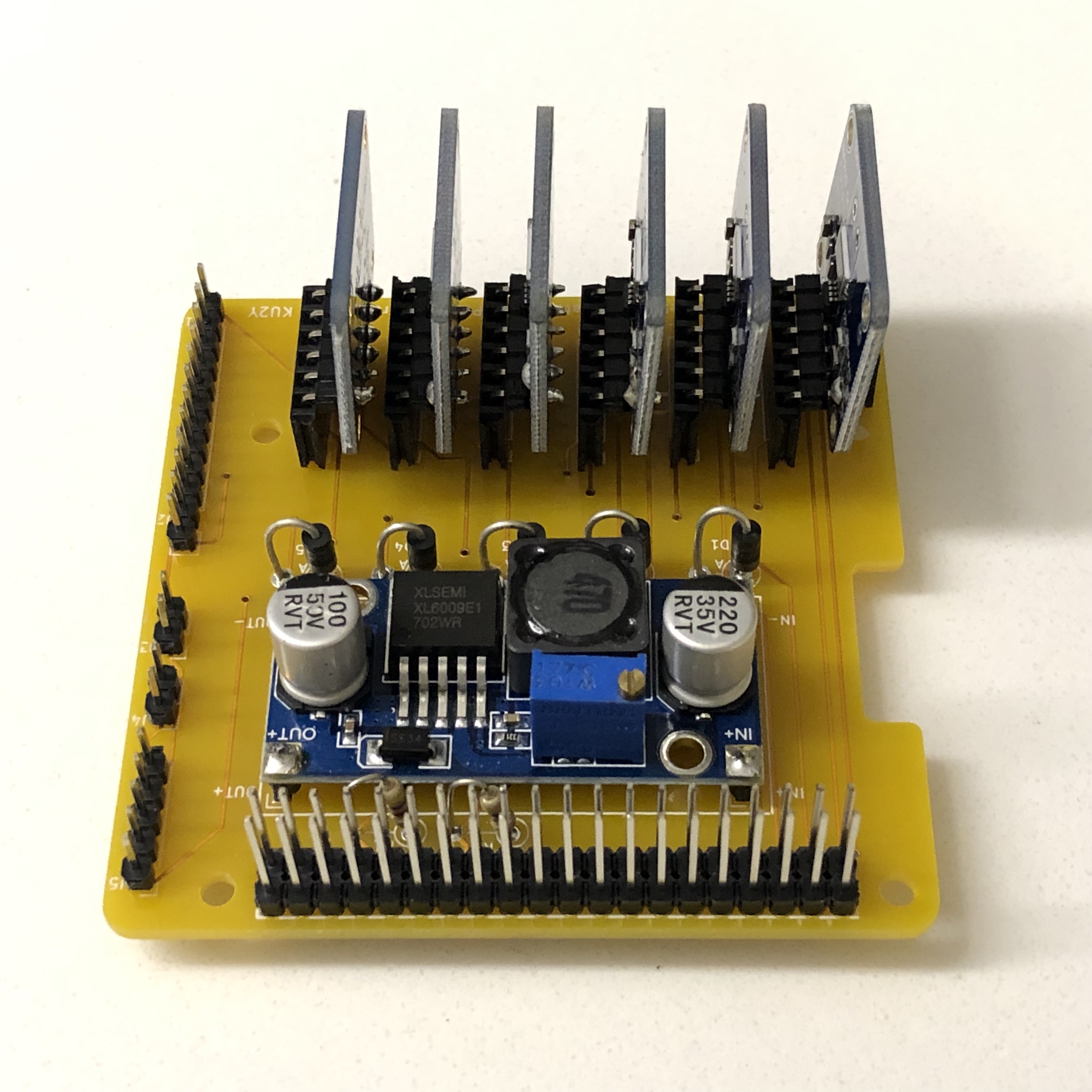
Here is the PCB Design

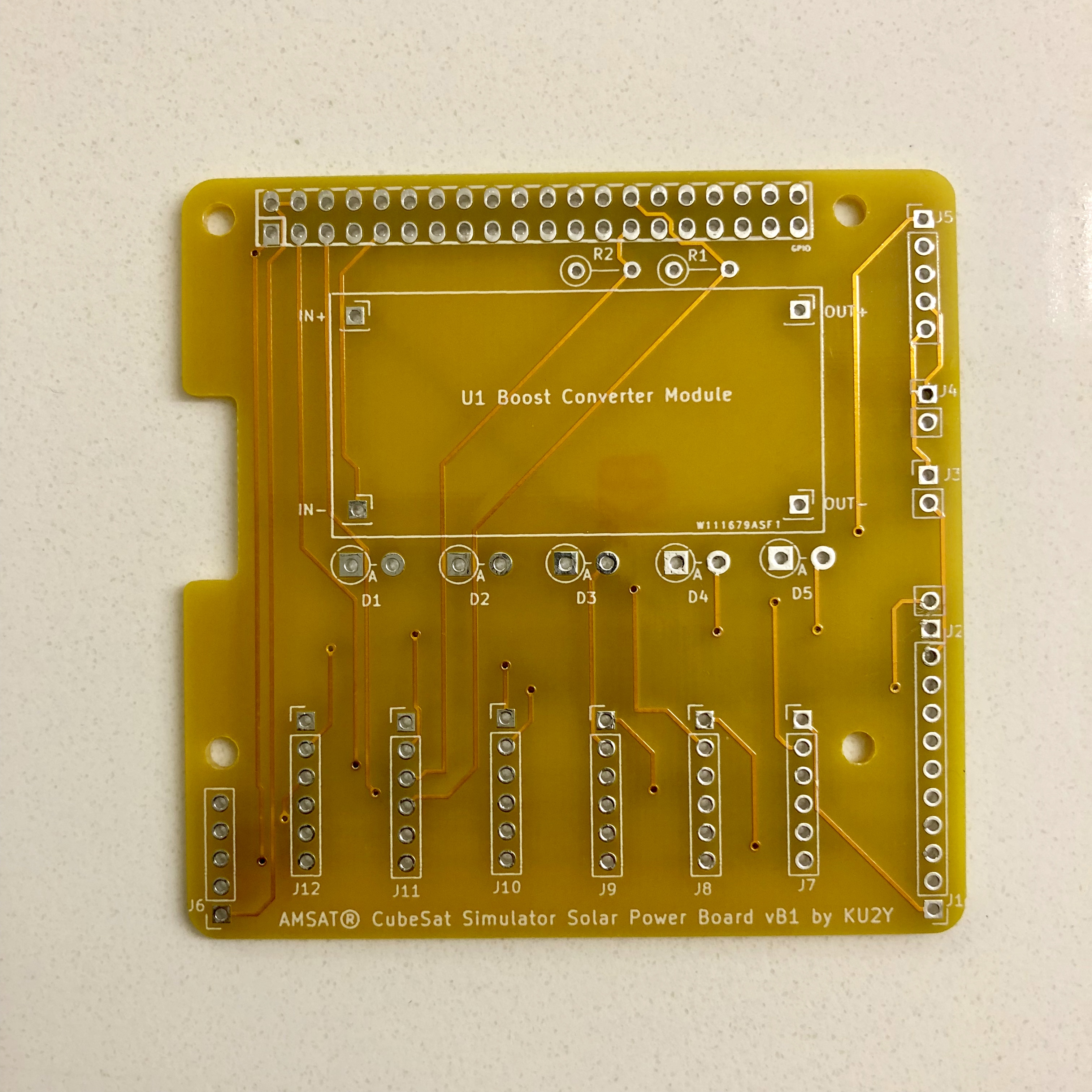
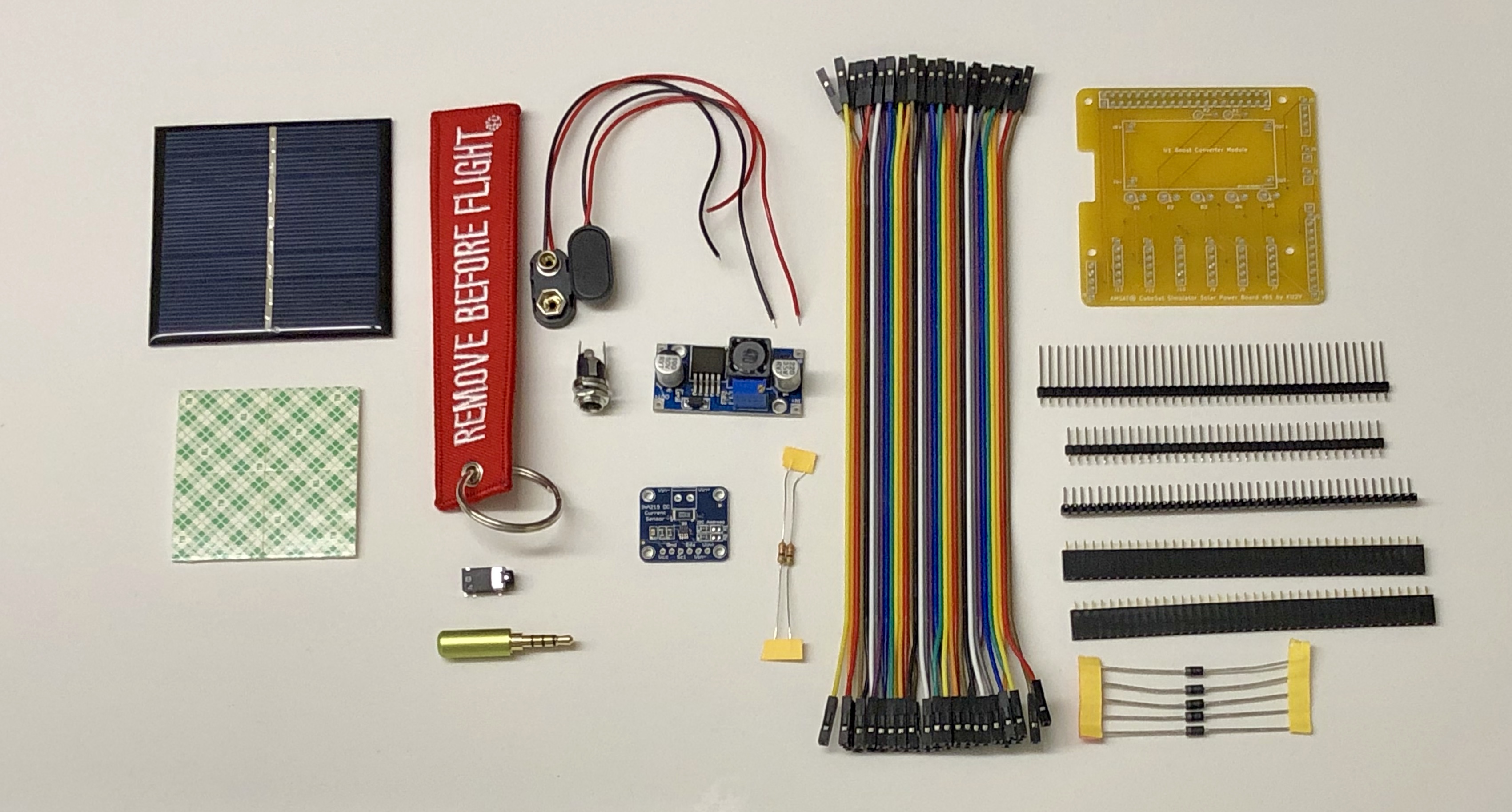
Materials:
- 1x AMSAT CubeSat Simulator Solar Power Board PCB
- 1x 40 pin extra long (19mm) male breakaway headers, straight
- 1x 40 pin regular length male breakaway headers, straight
- 2x 40 pin regular length female headers
- 1x 40 pin right angle male breakaway headers
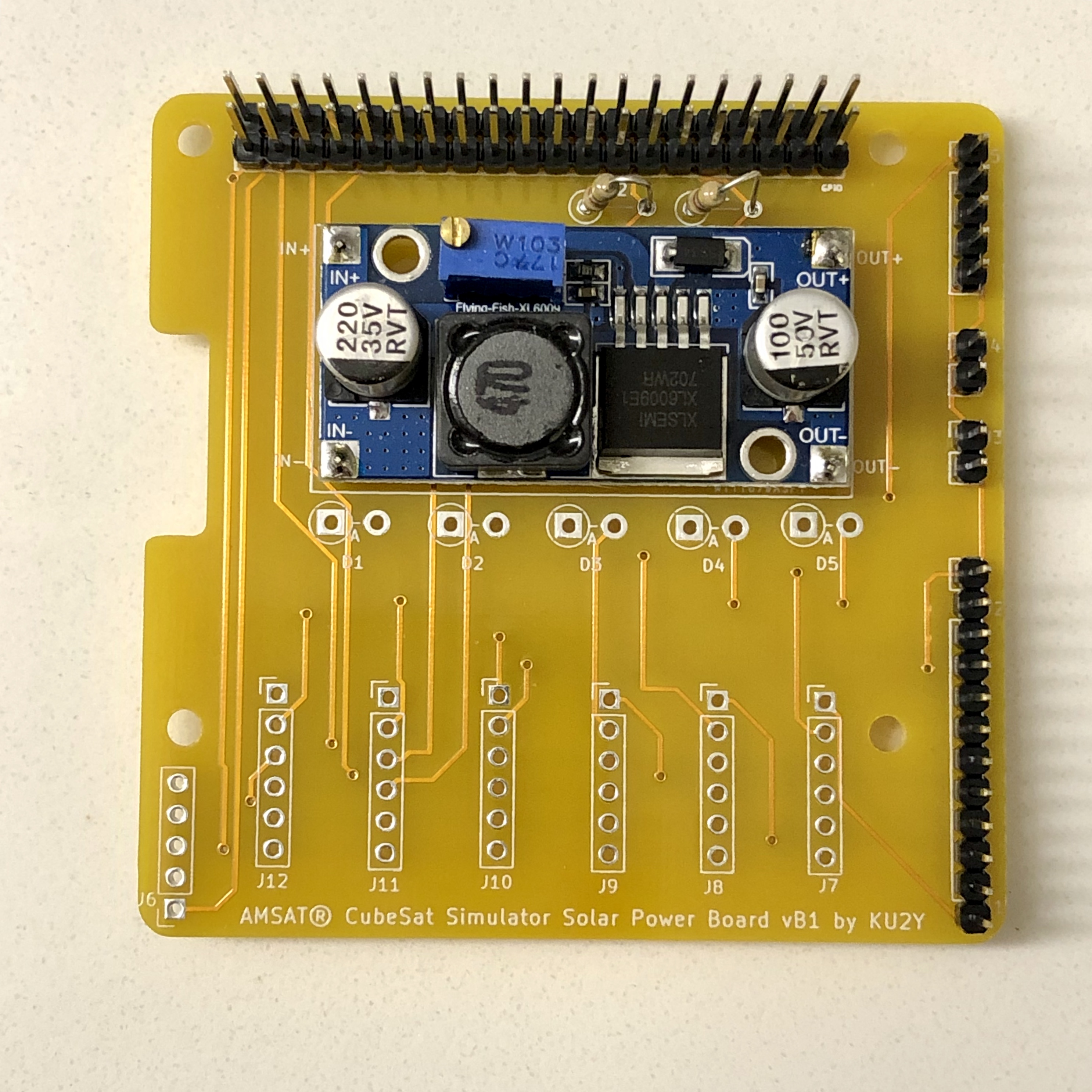
- 1x Boost module
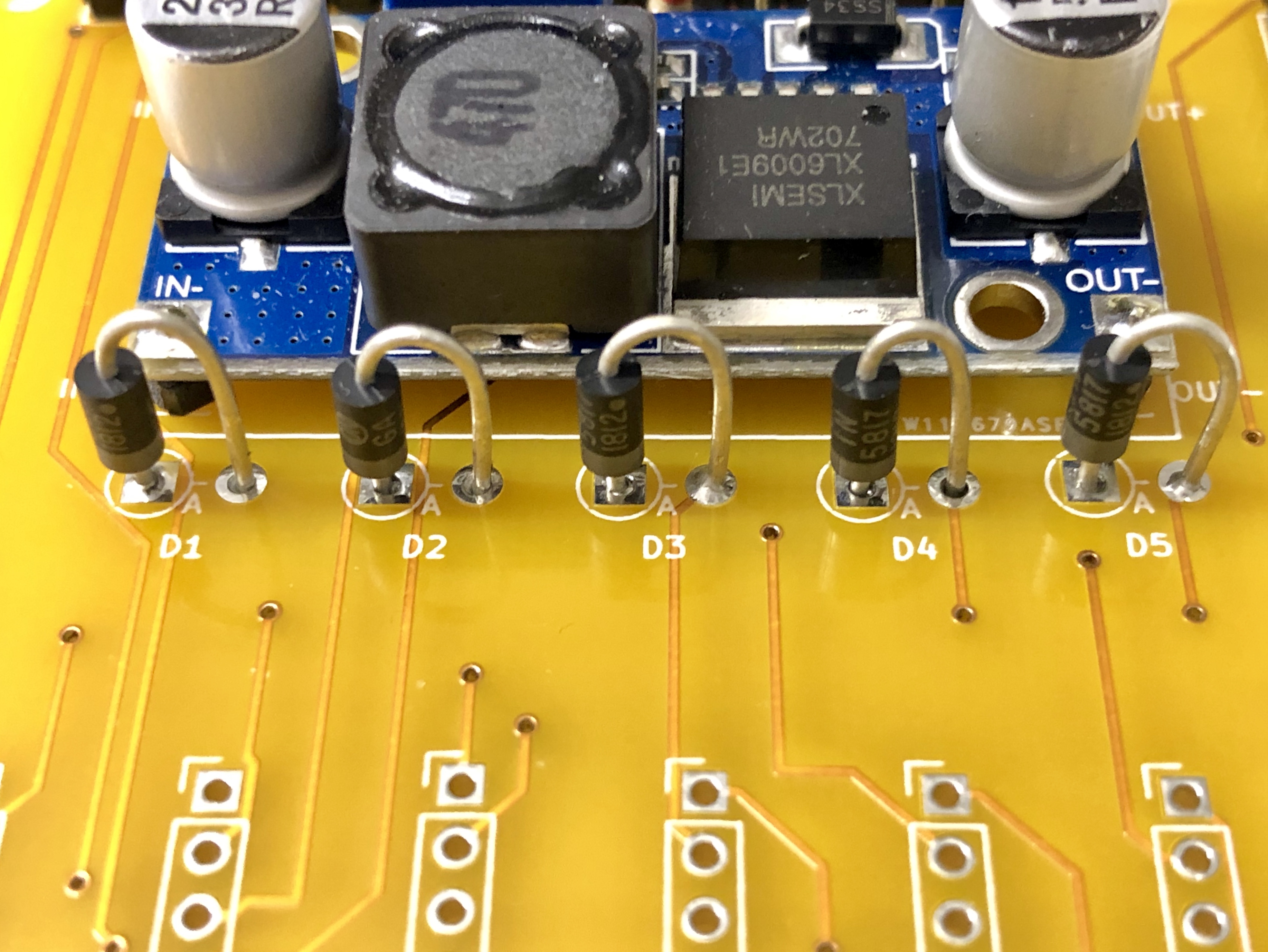
- 5x diodes, 1N5817
- 2x resistors 4.7k Ohm, 1/4 watt
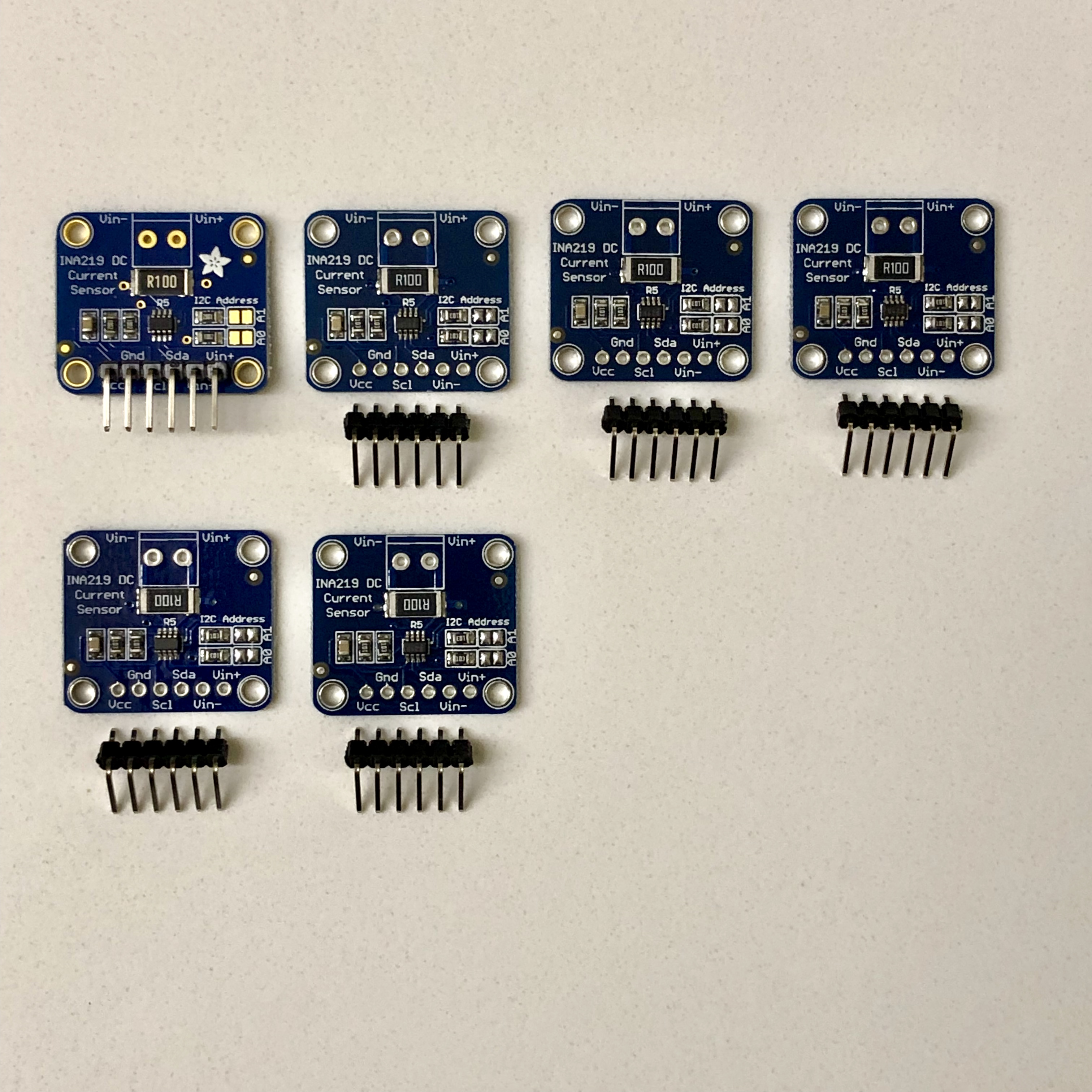
- 6x INA219 Sensor boards
Steps:
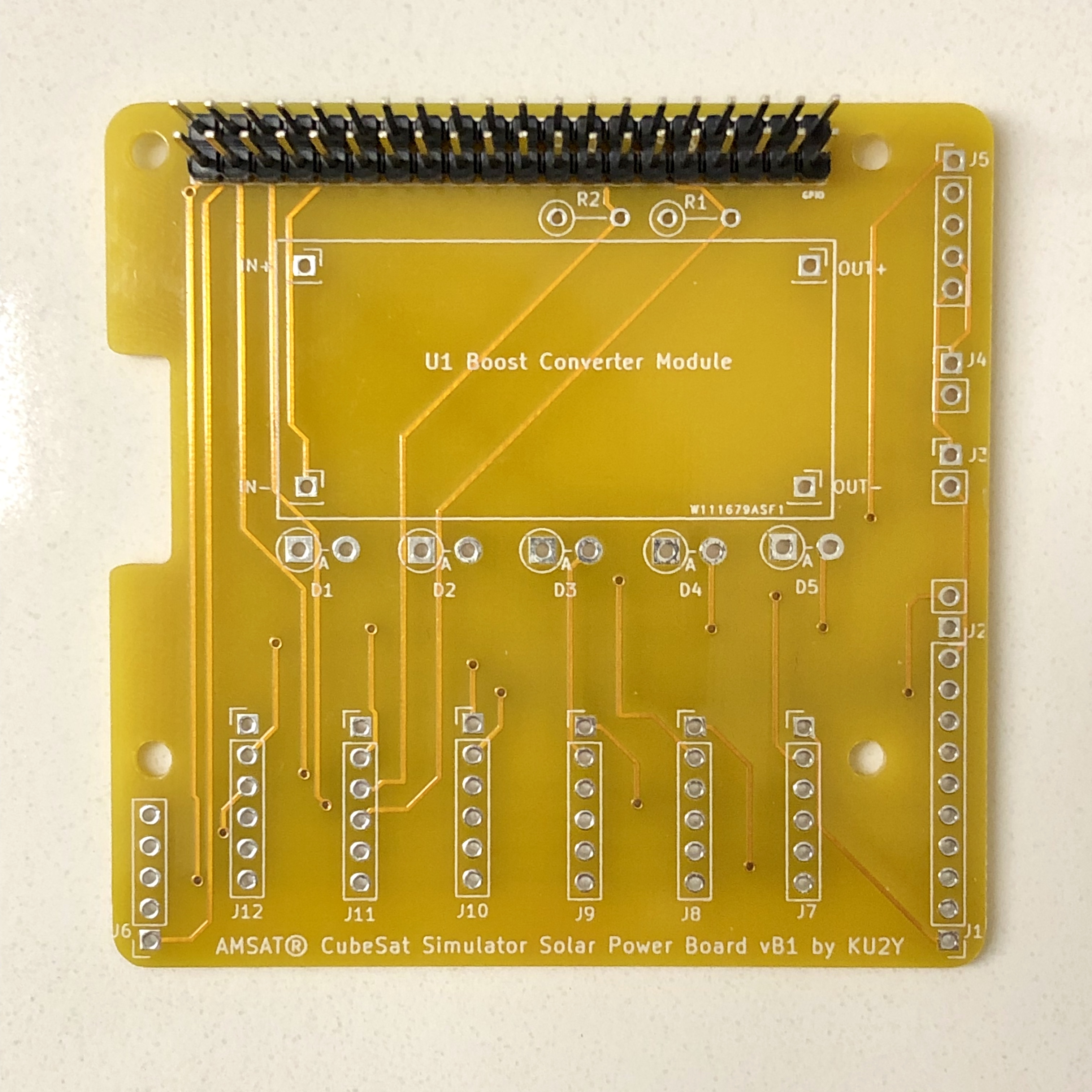
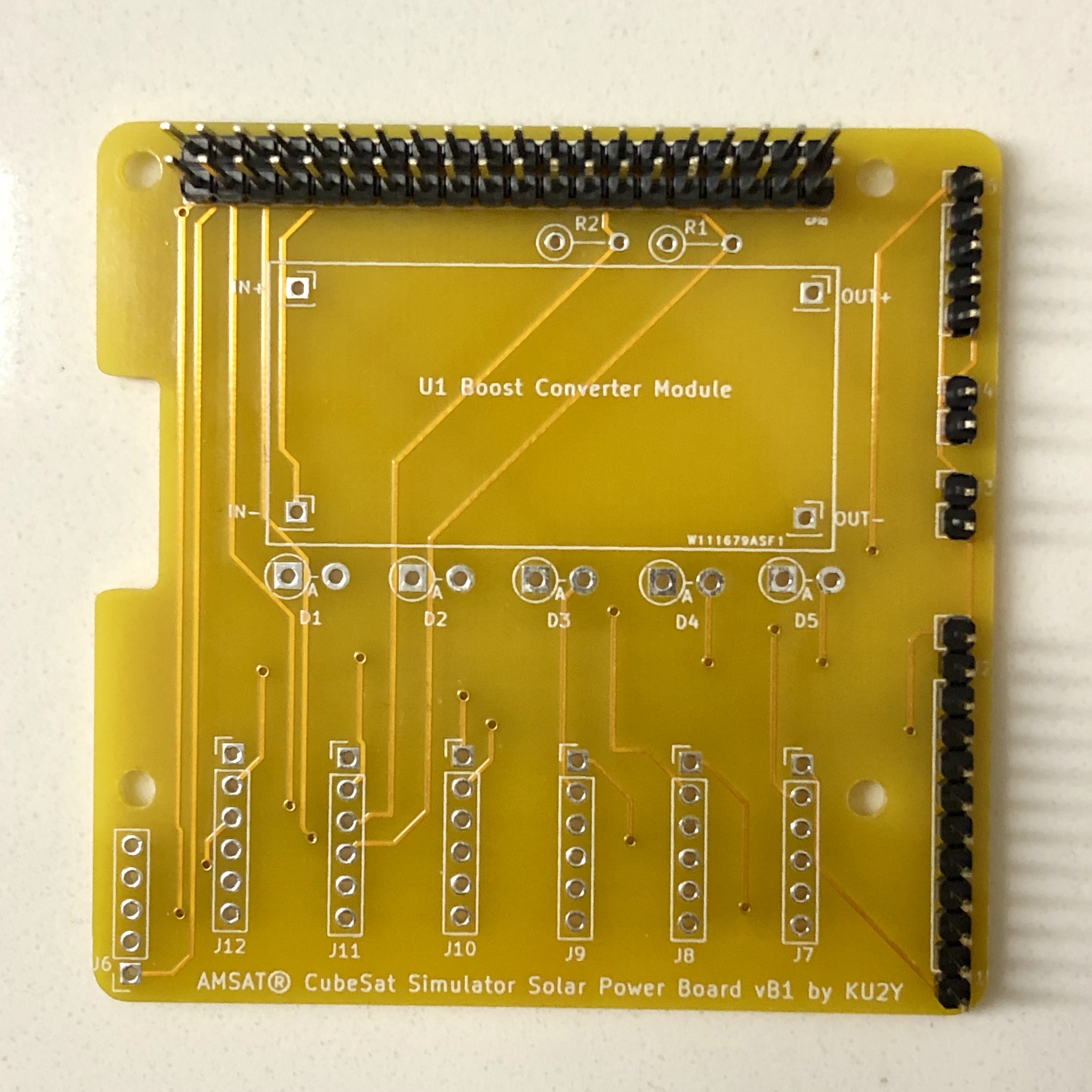
- Break 40 pin extra long male breakaway header into two 20 pin headers, and use for GPIO connector. Solder into place, being careful that the two rows are parallel and at right angle to the board (A 2x20 pin stackable header could be inserted into them a short way to ensure this). After it cools, test plugging Pi Zero W board with stackable header into the PCB. Note: not every pin needs to be soldered: required pins: 1,2,3,4,5,6,9,14,20,25,27,28,30,34,39.
- Break 40 pin regular length male breakaway header into 1x 12 pin (A combined J1 and J2 connector), 2x 2 pin (J3, J4), and 1x 5 pin (J5). Solder J1/J2, and J3, J4, and J5 into board.
- Solder resistors R1 and R2 vertically.
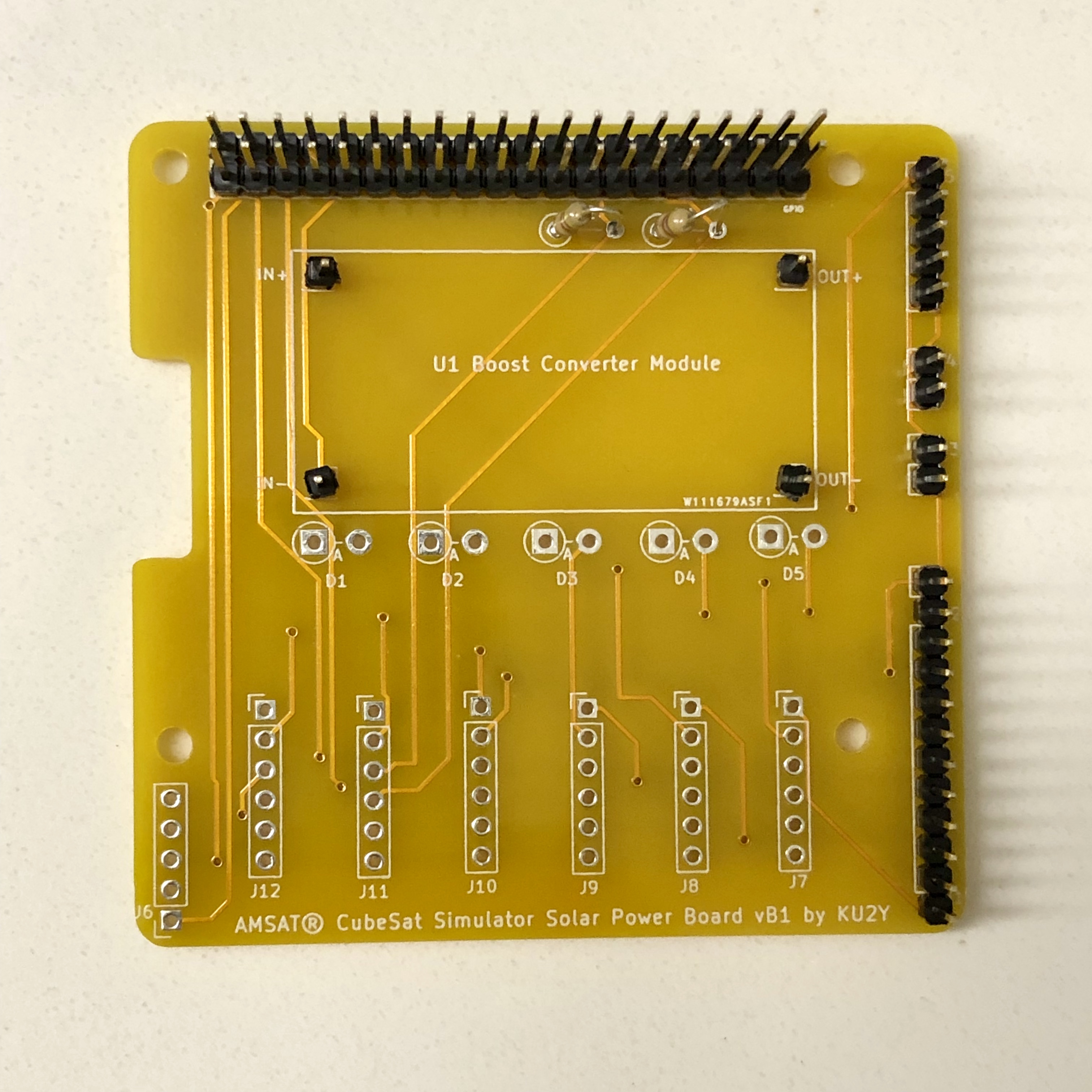
- Break off 4 single pins from the regular length male breakaway header and solder into the four terminals of the PCB U1 for the Boost Converter Module for IN+, IN-, OUT+, and OUT-.
Mount Boost Converter Module U1 onto the pins and solder in place.
- Solder diodes D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5 vertically. Cathode (marked by a band on diode package) goes into the square hole (on left), while the Anode goes into the round hole (on right). Note: some solar panels have a built in diode, in which case the diode can be replaced with a jumper wire.
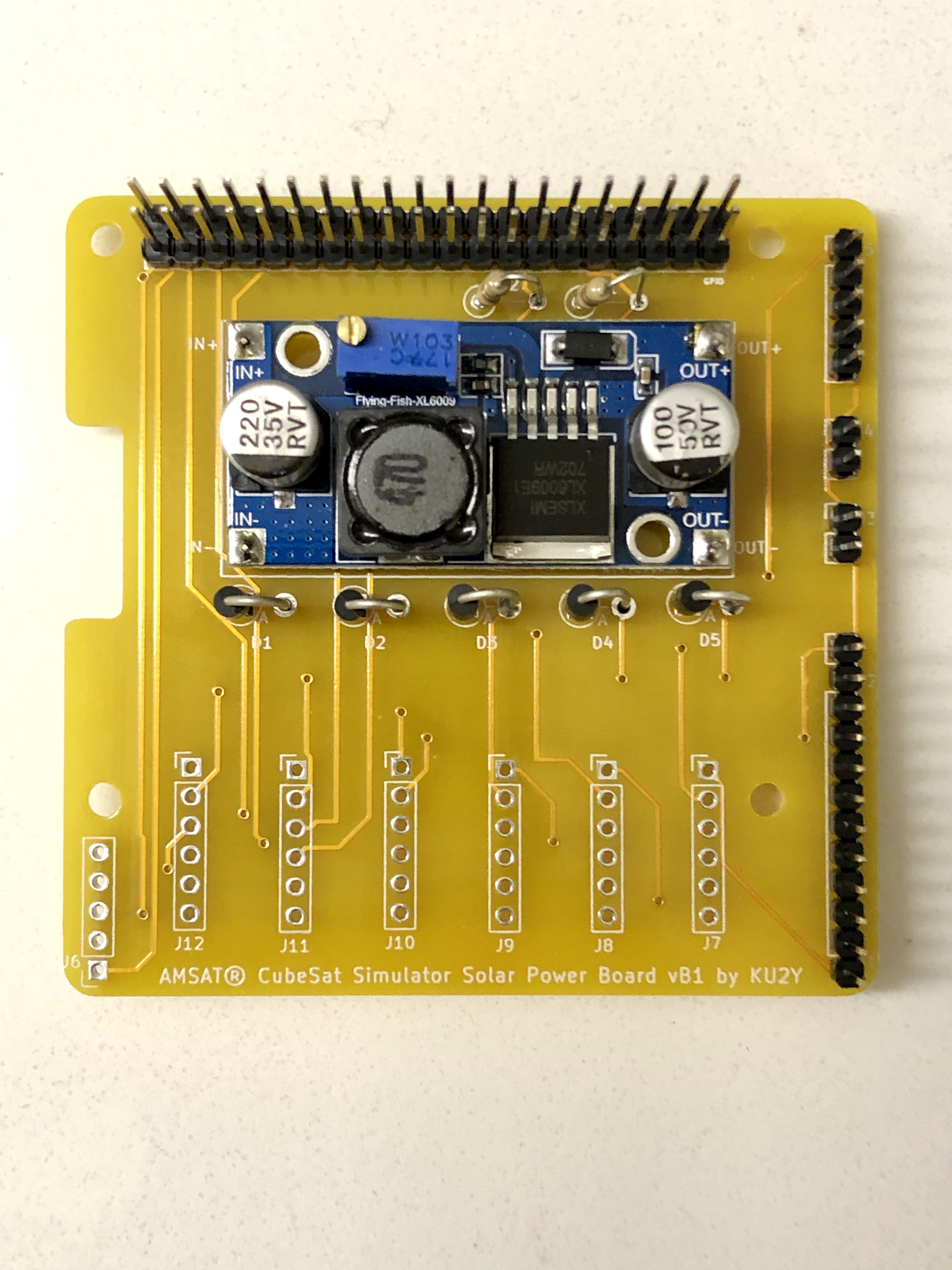
- Cut 90 degree breakaway headers into 6x 6 pin lengths.
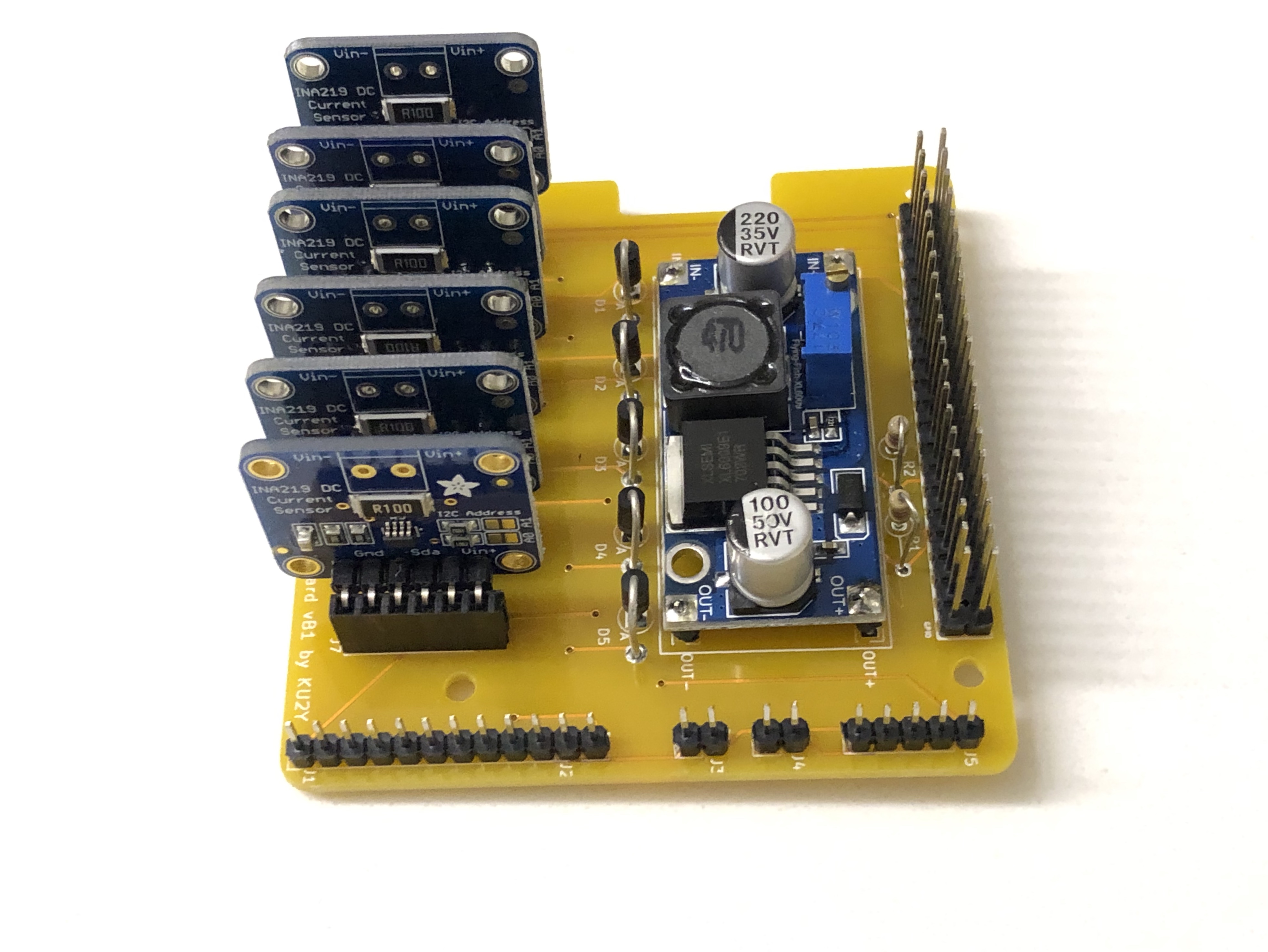
- Set the correct I2C bus address on the 6x INA219 boards by adding solder to jumpers to bridge A0 and A1 as needed. See instructions at https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-ina219-current-sensor-breakout/assembly (Note: do not use the pins and connectors that came with the INA219 board). Set the jumpers using this list:
- J7 X+ Board: Bus /dev/i2c-1 Address = 0x40 Offset = binary 00000 (no jumpers required)
- J8 Y+ Board: Bus /dev/i2c-1 Address = 0x41 Offset = binary 00001 (bridge A0)
- J9 Z+ Board: Bus /dev/i2c-1 Address = 0x44 Offset = binary 00100 (bridge A1)
- J10 Vbatt Board: Bus /dev/i2c-1 Address = 0x45 Offset = binary 00101 (bridge A0 and A1)
- J11 X- Board: Bus /dev/i2c-0 Address = 0x40 Offset = binary 00000 (no jumpers required)
- J12 Y- Board: Bus /dev/i2c-0 Address = 0x41 Offset = binary 00001 (bridge A0)
- Solder the 6 pin 90 degree headers into the boards so the pins face downward.
- Cut two 40 pin female headers into 1x 5 pin (J6), 6x 6 pin (J7, J8, J9, J10, J11, J12). See https://www.instructables.com/id/How-to-cut-pin-headers/ for good tips on how to sacrifice one pin to ensure the cut header has full stregth.
Solder J7-J12 onto the board.
- Test fit the INA219 boards vertically into connectors J7 through J12, but do not leave them plugged in.
Materials:
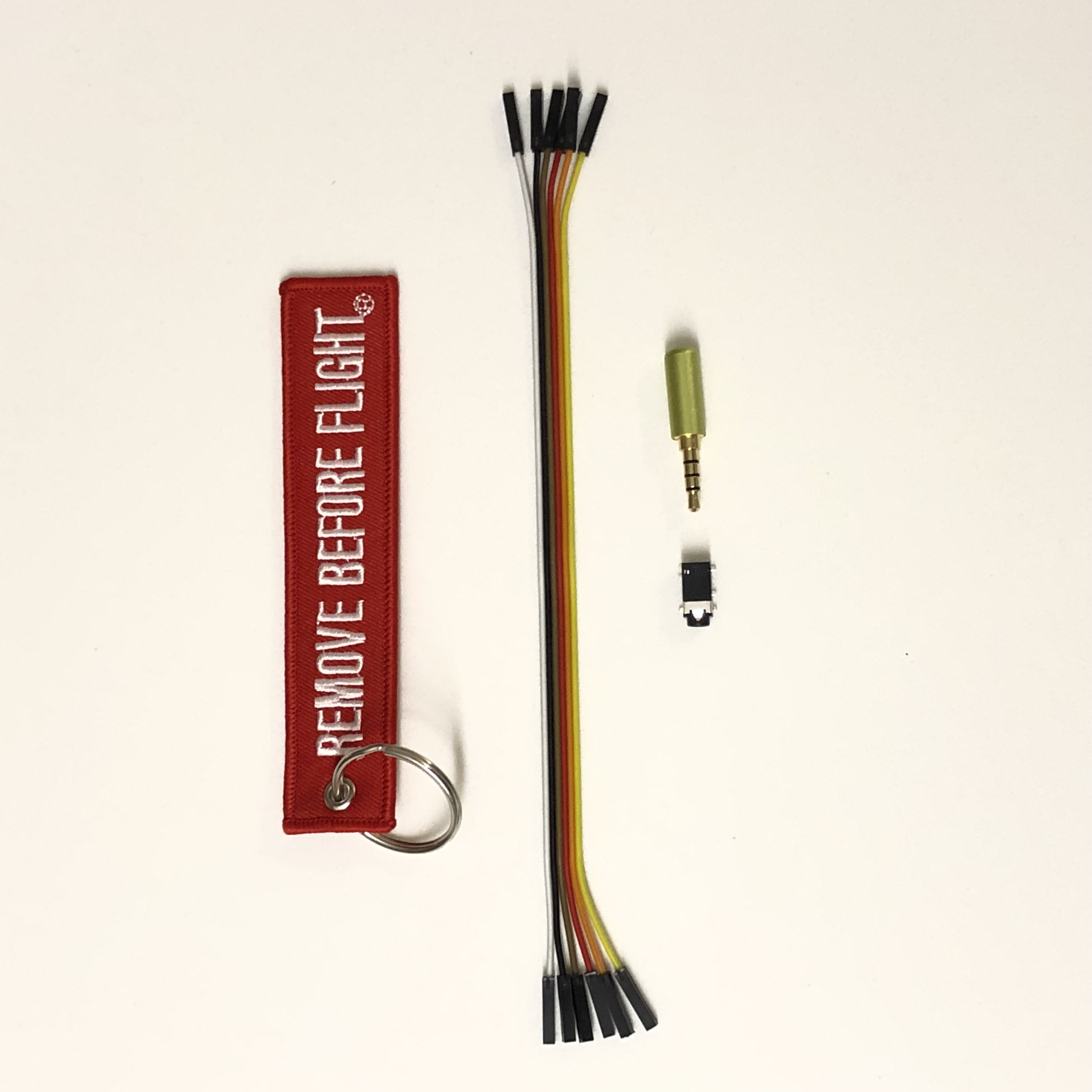
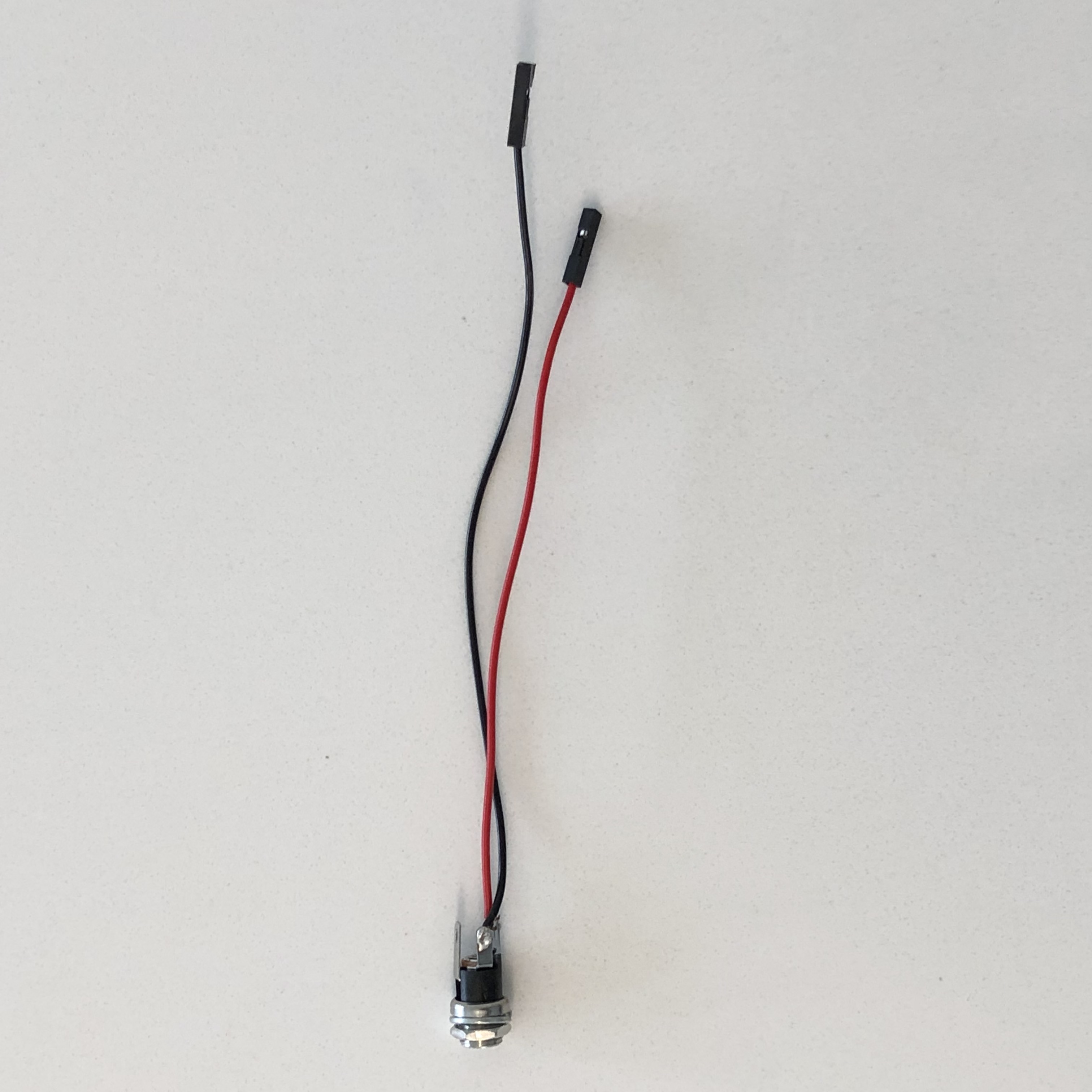
- 1x 3.5mm TRS female audio jack with 2 switches
- 1x 3.5mm TRS male plug
- 5x female jumper wires (keep attached together if possible)
- 1x Remove Before Flight keyring
Steps:
- Plug female ends of jumper wires into J5 connector and measure length for position of RBF switch. Cut to length and trim wires
- Solder onto 3.5mm audio jack per schematic
- Remove screw cover on male TRS plug and drill hole through for mounting RBF tag or other handle
- From jumper wire remains, cut a jumper wire short enough to stay inside the cover of the male jack to connect pins 3 and 1 (center to outer conductors). Solder jumper wire and put cover back on
- Attach Remove Before Flight keyring through the hole in the cover, taking care not to hit the jumper or connector.
- Test switch while unplugged from PCB using DMM set to Ohms or continuity:
- With the plug in, there is a short circuit between pins 4 and 5. There is an open circuit between pins 1 and 2, and pins 3 and 4.
- With the plug out, there is a short circuit between pins 1 and 2, and between pins 3 and 4. There is an open circuit between pins 4 and 5.
- Mount switch on CubeSat frame on top but do not plug into J5 yet.
Materials:
- 1x Barrel power connector 5.5mm x 2.1mm female
- 2x Female jumper wires
Steps:
- Plug female jumper wires into connector J3. Measure and cut length based on barrel connector mount position on frame
- Solder wires to connector.
- Connect center of barrel connector to J3 pin 1. Connect outer conductor of barrel connector to J3 pin 2. Leave unplugged.
Materials:
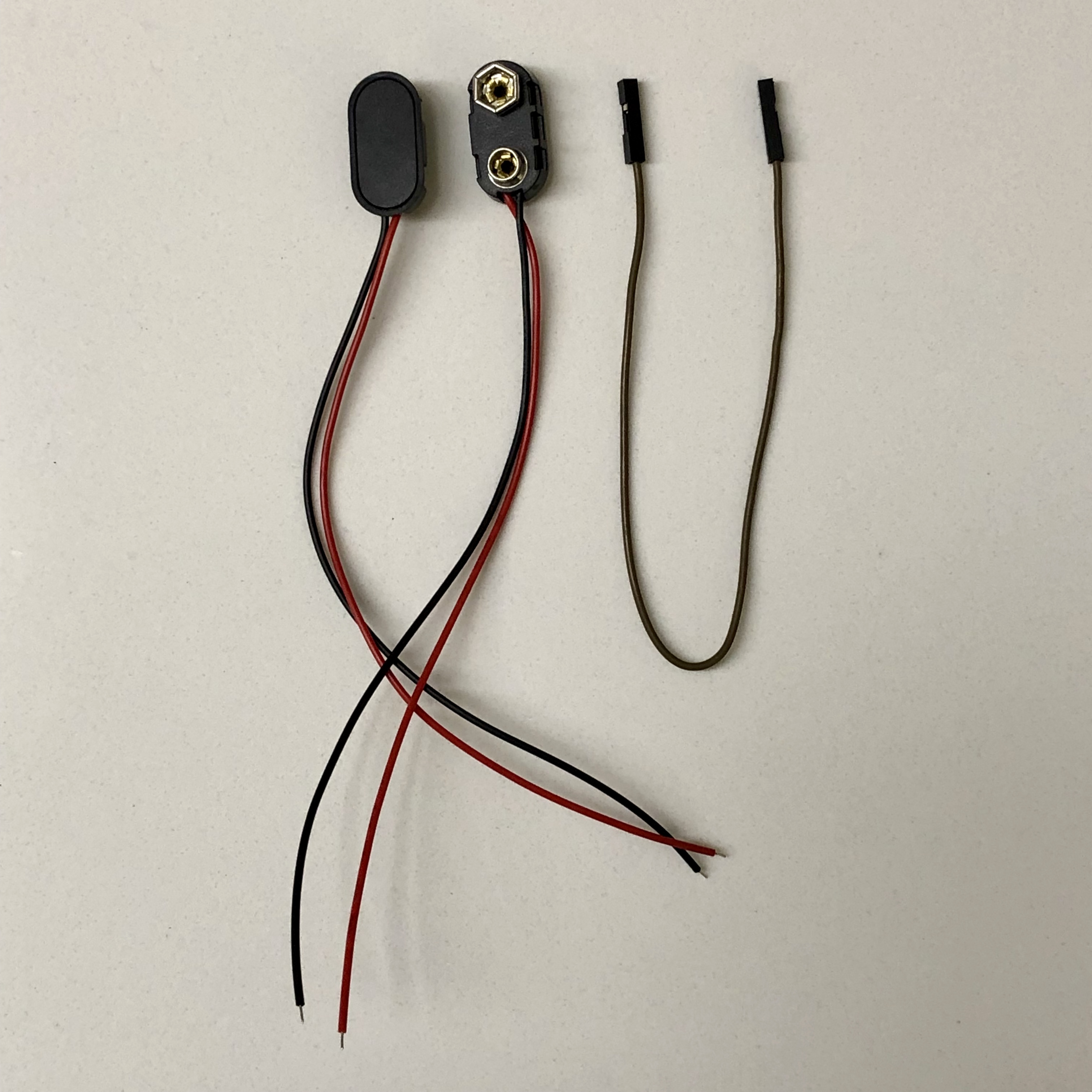
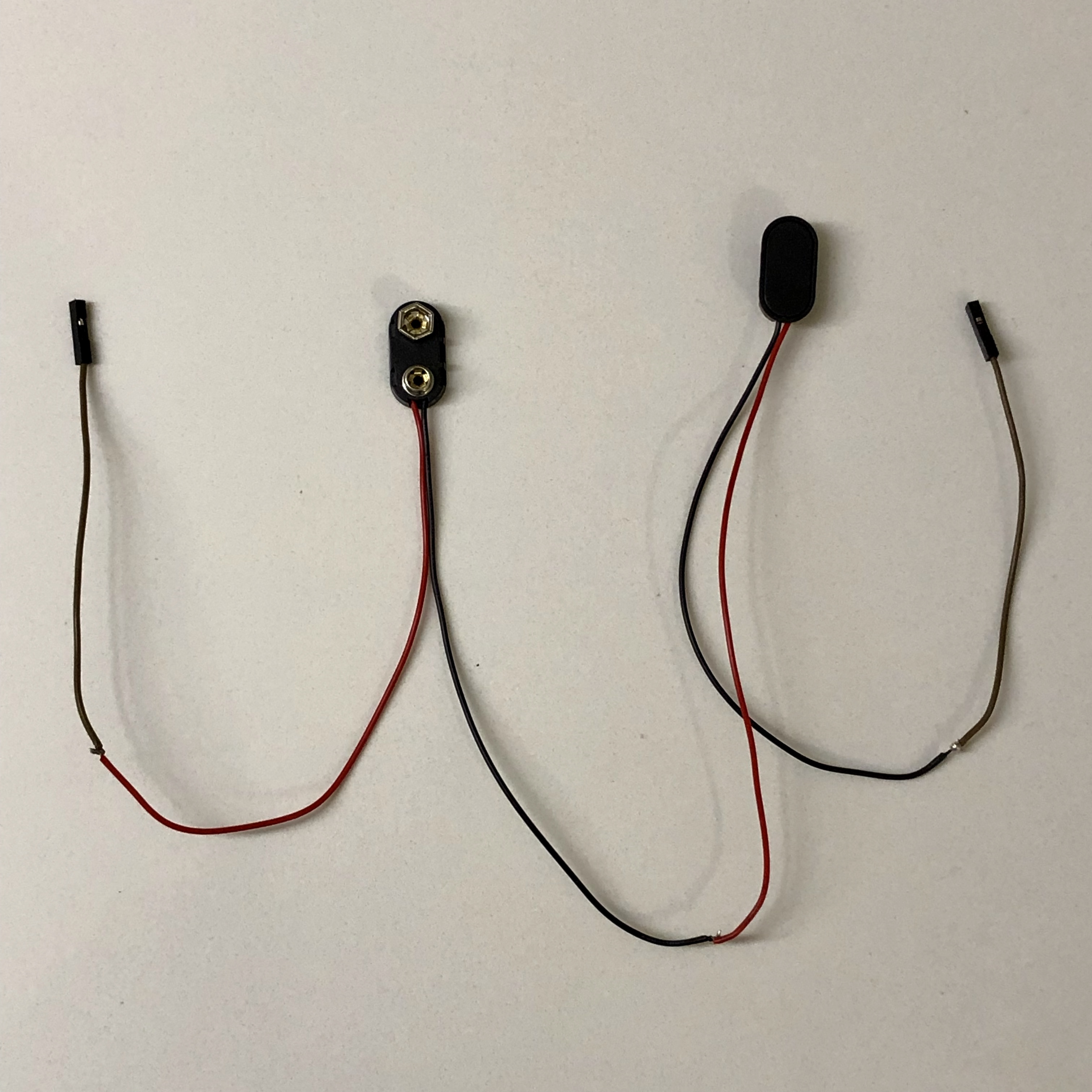
- 2x 9V snap connector wires
- 1x female to female jumper
Steps:
- Cut jumper wire in half. Solder one half of the jumper wire to a positive lead of one 9V connector (red lead) and solder the other half to the negative lead of the other 9V connector (black lead)
- Solder the other ends of the two 9V connectors together (black to red leads).
- Plug jumper wire into J2 with the positive lead of the connector into pin 1, and the negative lead of the connector plugged into pin 2 of J2.
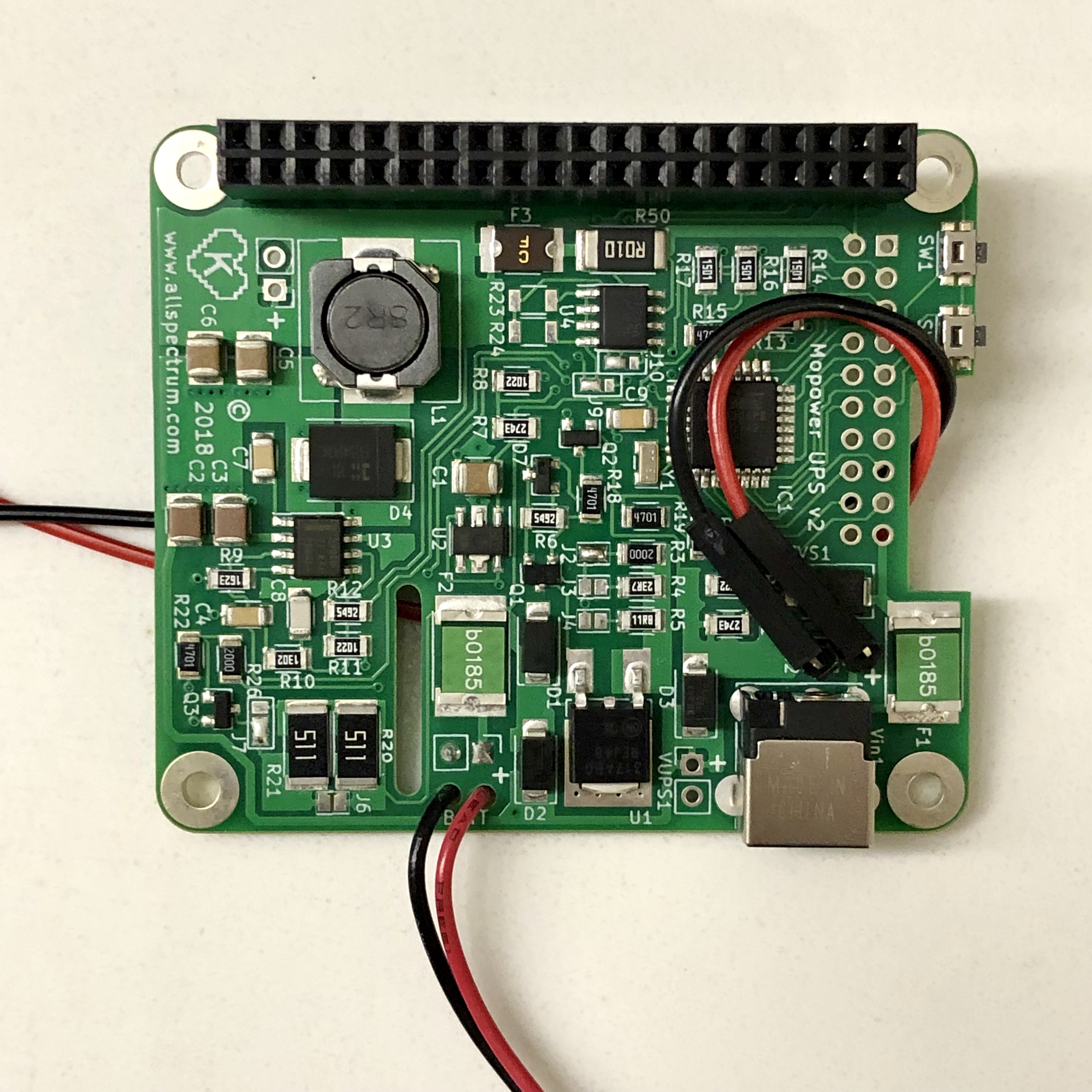
- Plug the NiMH battery into the connector that the positive lead is wired to the header connector. Plug the connector from the MoPower UPS V2 board into the other connector. CHECK!
- Verify Pi boots and runs from the battery.
Materials:
- 6x solar panels
- 12x female to female jumper wires
- 1x mounting square, foam
Steps:
- Cut off one end of each of the female to female jumper wires. Solder two to each solar panel, using a different color for the positive (+) and negative (-) connections.
- Cut mounting square into small squares, and use one each corner to mount solar panels on the frame of the CubeSat Simulator. You may need to drill holes for the wires to go through.
Materials:
- 1x red female to female jumper wire
- 1x black female to female jumper wire
Steps:
- Plug red female to female jumper wire into J4 pin 1
- Plug black female to female jumper wire into J4 pin 2
-
Plug Pi Zero W board into this board. Power up Pi and make sure Pi works fine. Check J6 for 3.3V (pin 2 to pin 3) and 5V supply (pin 1 to pin 3). On J7-J12, check pins 6 to 5 for 3.3V. Shutdown the Pi.
-
Plug in INA219 boards to J7 - J12 and power up the Pi. Run
i2cdetect -y 1command on Pi. You should see each INA219 Board you have plugged in (40, 41, and 44, and 45 for J7, J8, J9, and J10):
. . 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: 40 41 -- -- 44 45 -- -- -- -- 4a -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
(If you have the Current Sensor module included in the MoPower UPS V2 board, you will also see it at 4a as well). If not, check A0 and A1 jumpers and soldering of the missing board. If i2cdetect -y 1 returns all dashes, did you bend two of the GPIO connector pins (pins 3 and 5) on the MoPower UPS board so that when you plug the Digital Transceiver board into it, they do not make contact? Run i2cdetect -y 0 command on Pi.
. . 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 0a 0b 0c 0d 0e 0f
00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
40: 40 41 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
50: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
70: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
You should see the other INA219 Board you have plugged in (40 and 41 for J11 and J12). If not, check A0 and A1 jumpers and soldering of the missing board.
- Run the Sensor only software on the Pi:
python ~/CubeSatSim/python/telem.py
You should see results for all the boards. Plug in an illuminated solar panel into J1 for X+ (pin 1 to + and pin 2 to -) and rerun the Sensor only software - you should see the X+ voltage (open circuit voltage of the solar panel), and current (approximately zero) and power (approximately zero). Repeat for Y+, Z+, X-, and Y- (if you have them) (pins 3 and 4, pins 5 and 6, pins 7 and 8, and pins 9 and 10).
-
With one or more illuminated solar panels plugged into J1, you should read a voltage on J5, pin 1, of slightly less than your open circuit solar panel voltage, depending on the light level. With the RBF pin out, plug in the RBF switch connector to J5. You should measure a voltage on J4 pins 1 to 2 - this is the output of the boost converter module. Shutdown the Pi and unplug it from the GPIO connector.
-
With the Pi not plugged in, you can adjust the trimpot on the boost converter U1 so that the voltage on J4 pins 1 to 2 reads around 15V when at least one solar panel is in full illumination. It may take a few turns. Put the RBF pin back in, and the voltage on J4 pins 1 to 2 should drop to zero.
-
With the RBF pin plugged in, plug in the DC in barrel power cable into J3. With a DC power pack plugged in, you should read around 15V on J4 pin 1 to 2.
-
On the MoPower UPS V2 board, solder two 90 degree male headers into the Vin2 + and - holes. Mount the headers on the top side of the PCB (same side as the chips and components) and angle them towards the GPIO connector.
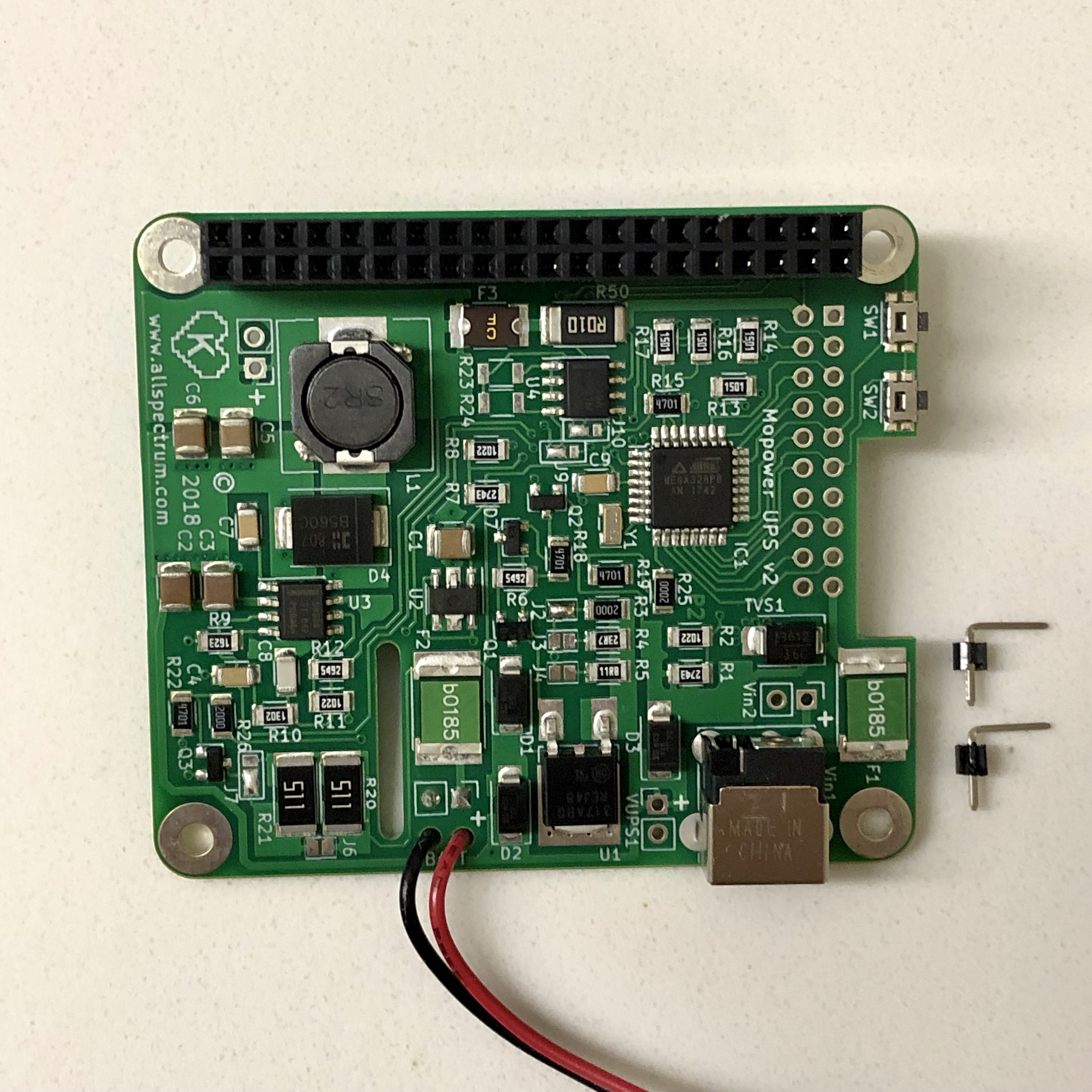
If a DC power pack is plugged into the MoPower board, unplug it. Use the red and black pair of female to female jumper wires to connect the Vin2+ to J4 pin 1 (red), and Vin2 - to J4 pin 2 (black). With the RBF pin inserted and the Pi powered up, plug the power pack into the barrel connector on the PCB and verify using the Sensor only software that the battery pack is charging ().
-
With the RBF pin removed and the solar panels covered or unplugged, note the current and power supplied by the battery. Illuminate one or more solar panels and verify using the Sensor only software that the battery current and power is lower.
-
On the Pi, run the ./radioafsk application and note the telemetry. Vary the illumination level and position, and you should see that reflected in the telemetry.
-
Place the Sim on the turntable in front of the halogen lamp and switch on to lowest rotation rate. Capture the telemetry and analyze using the spreadsheet. You should be able to calculate the rotation rate of the Sim based on the period of the solar panel current waveforms.