本章使用到一个exit()函数,引用官方文档解释.
This chapter uses the exit() function which is explained in the official documentation
在Python中有4个不同的退出程序函数,exit(),quit(),os_exit()以及sys.exit()
There are 4 different exit program functions in Python exit() quit() os_exit() and sys.exit()
sys模块的exit函数,通过抛出一个SystemExit异常来尝试结束程序,Python代码可以捕获这个异常来进行一些程序退出前的清理工作,也可以不退出程序.sys.exit函数同样可以带一个参数来作为程序的退出码,默认是0
the exit function of the sys module tries to end the program by throwing a SystemExit exception Python code can catch this exception to perform some cleanup work before the program exits or it can not exit the program The sys.exit function can also take a parameter as Exit code of the program default is 0
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from sys import exit
# 导入sys中的exit模块
# Import the exit module in sys
def gold_room():
print ("This room is full of gold. How much do you take ?")
# 提示用户输入信息,如果用户输入除0或1以外的数字,则调用dead函数结束执行
# Prompt the user for information If the user enters a number other that 0 or 1 the dead function is called to end execution
choice = input (">")
if "0" in choice or "1" in choice :
how_much = int(input (">"))
else :
# 调用dead函数
# Call the dead function
dead ("Man, learn to type a number.")
if how_much < 50 :
print ("Nice ,you're not greedy ,you win!")
# 调用exit模块直接退出当前程序
# Call the exit module to exit the current program directly
exit(0)
else :
# 调用dead函数
# Call the dead function
dead ("You greedy bastard")
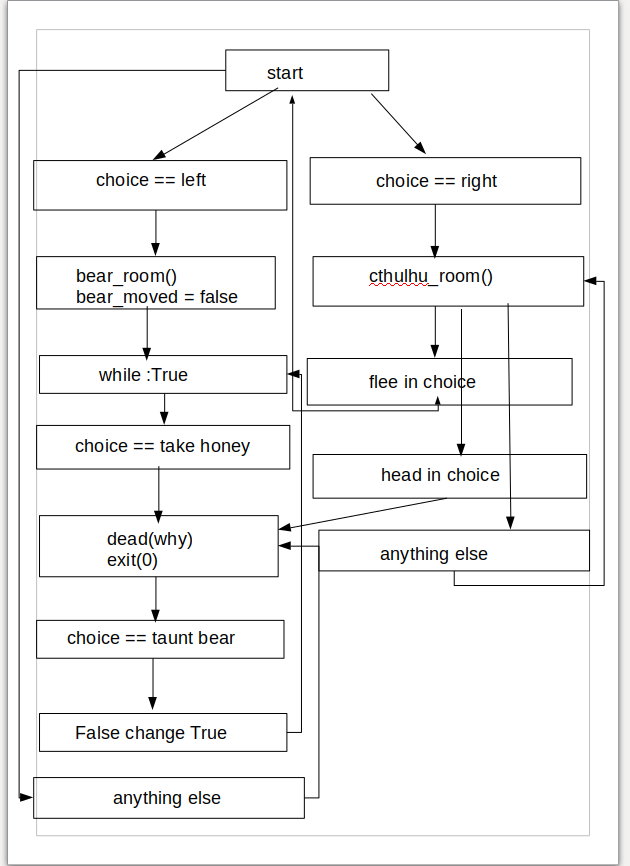
def bear_room():
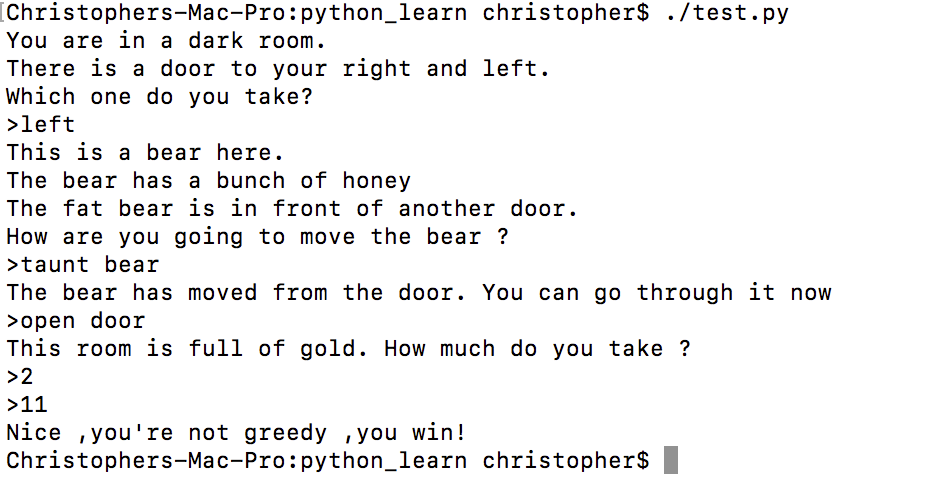
print ('This is a bear here.')
print ("The bear has a bunch of honey")
print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.")
print ("How are you going to move the bear ?")
# 定义一个布尔变量
# Define a Boolean variable
bear_moved = False
while True:
# 注意此处使用死循环,如果没有手动终止该循环,则该循环会一直运行
# Note that an endless loop is used here If the loop is not manually terminated the loop will always run
choice = input(">")
if choice == "take honey" :
dead ("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.")
elif choice == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved :
# 进入此判断后会将bear_moved的值修正为True
# After entering this judment the value of bear_moved will be corrected to True
print ("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now")
bear_moved = True
elif choice == "taunt bear" and bear_moved :
# 要想进入此判断,首先需要将bear_moved的值修正为True
# To enter this judment you first need to modify the value of bear_moved to True
# 调用dead方法进行输出
# Call the dead method for output
dead ("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.")
elif choice == "open door" and bear_moved :
# 在将bear_moved修正为True后调用gold_room方法
# Call the gold_room method after fixing bear_moved to True
gold_room()
else :
print ("I got no idea what that means.")
def cthulhu_room():
"""输出提示信息,并等待用户输入,根据用户输入结果进入某一个方法体内"""
""" Output prompt information wait for user input and enter a certain method body based on the user input"""
print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.")
print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.")
print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?")
choice = input (">")
if "flee" in choice :
# 调用start函数
# Call start function
start()
elif "head" in choice :
# 调用dead函数
# Call the dead function
dead ("Well what was tasty")
else :
# 调用自身函数
# Call own function
cthulhu_room()
def dead(why):
"""将接收到的值进行打印输出后调用exit函数进行退出当前程序"""
"""After printing the received value call the exit function to exit the current program"""
print (why,"Good job!")
exit(0)
def start():
"""在进入本方法后,输出提示信息,并等待用户输入,根据用户输入结果进入其中某一个方法体内"""
"""After entering this method output prompt information and wait for user input and enter one of the method bodies according to the result of user input"""
print ("You are in a dark room.")
print ("There is a door to your right and left.")
print ("Which one do you take? ")
choice = input(">")
if choice == "left" :
# 调用bear_room函数
# Call the bear_room function
bear_room()
elif choice == "right" :
# 调用cthulhu_room函数
# Call cthulhu_room function
cthulhu_room()
else :
dead ("You stumble around the room unuil you starve.")
# 从这里开始执行脚本
# Execute script from here
start()
实际结果:
无
无
结果:
在python中会将所有接受到的值默认转换为字符串类型,如果需要特定的类型,手动进行转换即可。
Reset all received values in python and convert them to concatenated types If you need a specific type you can convert it manually
判断用户输入是否为数字可以使用str.isdigit()函数
To determine whether the user input is a number, you can use the str.isdigit() function
在该脚本中需要注意的是,类型不同无法进行比较,所以第二次判断用户输入时直接使用int来进行转换限定类型。
It should be noted in this script that different types cannot be compared so the second time to determine the user input directly uses int to convert the restricted type
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from sys import exit
# 导入sys中的exit模块
# Import the exit module in sys
def gold_room():
print ("This room is full of gold. How much do you take ?")
# 提示用户输入信息,如果用户输入除0或1以外的数字,则调用dead函数结束执行
# Prompt the user for information If the user input is not a number , call the dead function to end execution
choice = input (">")
if str.isdigit(choice) == True :
how_much = int(input (">"))
else :
# 调用dead函数
# Call the dead function
dead ("Man, learn to type a number.")
# 将接收到的值在此处进行判断,如果是数字并且小于50,则继续执行,否则直接调用dead函数进行退出
# The received value is judged here ,If it is a number and is less than 50 continue to execute otherwise call the dead function directly to exit
if how_much < 50 :
print ("Nice ,you're not greedy ,you win!")
# 调用exit模块直接退出当前程序
# Call the exit module to exit the current program directly
exit(0)
else :
# 调用dead函数
# Call the dead function
dead ("You greedy bastard")
def bear_room():
print ('This is a bear here.')
print ("The bear has a bunch of honey")
print ("The fat bear is in front of another door.")
print ("How are you going to move the bear ?")
# 定义一个布尔变量
# Define a Boolean variable
bear_moved = False
while True:
# 注意此处使用死循环,如果没有手动终止该循环,则该循环会一直运行
# Note that an endless loop is used here If the loop is not manually terminated the loop will always run
choice = input(">")
if choice == "take honey" :
dead ("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.")
elif choice == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved :
# 进入此判断后会将bear_moved的值修正为True
# After entering this judment the value of bear_moved will be corrected to True
print ("The bear has moved from the door. You can go through it now")
bear_moved = True
elif choice == "taunt bear" and bear_moved :
# 要想进入此判断,首先需要将bear_moved的值修正为True
# To enter this judment you first need to modify the value of bear_moved to True
# 调用dead方法进行输出
# Call the dead method for output
dead ("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.")
elif choice == "open door" and bear_moved :
# 在将bear_moved修正为True后调用gold_room方法
# Call the gold_room method after fixing bear_moved to True
gold_room()
else :
print ("I got no idea what that means.")
def cthulhu_room():
"""输出提示信息,并等待用户输入,根据用户输入结果进入某一个方法体内"""
""" Output prompt information wait for user input and enter a certain method body based on the user input"""
print ("Here you see the great evil Cthulhu.")
print ("He, it, whatever stares at you and you go insane.")
print ("Do you flee for your life or eat your head?")
choice = input (">")
if "flee" in choice :
# 调用start函数
# Call start function
start()
elif "head" in choice :
# 调用dead函数
# Call the dead function
dead ("Well what was tasty")
else :
# 调用自身函数
# Call own function
cthulhu_room()
def dead(why):
"""将接收到的值进行打印输出后调用exit函数进行退出当前程序"""
"""After printing the received value call the exit function to exit the current program"""
print (why,"Good job!")
exit(0)
def start():
"""在进入本方法后,输出提示信息,并等待用户输入,根据用户输入结果进入其中某一个方法体内"""
"""After entering this method output prompt information and wait for user input and enter one of the method bodies according to the result of user input"""
print ("You are in a dark room.")
print ("There is a door to your right and left.")
print ("Which one do you take? ")
choice = input(">")
if choice == "left" :
# 调用bear_room函数
# Call the bear_room function
bear_room()
elif choice == "right" :
# 调用cthulhu_room函数
# Call cthulhu_room function
cthulhu_room()
else :
dead ("You stumble around the room unuil you starve.")
# 从这里开始执行脚本
# Execute script from here
start()
结果:
str.isalnum() 所有字符都是数字或者字母
str.isalpha() 所有字符都是字母
str.isdigit() 所有字符都是数字
str.islower() 所有字符都是小写
str.isupper() 所有字符都是大写
str.istitle() 所有单词都是首字母大写,像标题
str.isspace() 所有字符都是空白字符、\t、\n、\r