What's New in ObsPy 1.0
ObsPy has been in development since 2008 and we now declare it stable enough to be called 1.0. It is a big release with significant internal changes, new features, stability enhancements, and much more to prepare ObsPy for future challenges and get rid of accumulated technical debt. This substantially increases the maturity and overall quality of ObsPy and also enhances it with quite a lot of new features.
This release contains contributions from 21 separate people. Thanks a bunch everyone! This would not have been possible without you!
We strongly encourage all users to update to the new version as it will effectively end support for the 0.10.x line (we will post a final source distribution-only 0.10.3 release soon). Please read at least the New Internal Structure section as it might necessitate changes on your side.
This document details significant new features and changes in ObsPy 1.0.0. It does not list all bug fixes and small improvements. The Full Changelog at the end is more comprehensive.
Documentation and resources for this version can (as always) be found at: https://docs.obspy.org
Aside from the occasional change and new feature, there never was any formal funding for ObsPy and it has been developed by enthusiastic volunteers. If you use ObsPy, please make sure to properly acknowledge us so we can justify investing time into it.
- Supported Systems
- Updating ObsPy
- New Internal Structure
- Support for New Data Formats
- New Clients
- Major improvements to PPSD class
- Signal Processing Improvements
- Changes in the TauP Implementation
- Other Notable Changes
- New Default Colormap
- Mass Downloader for FDSN Web Services
- New Fancy Event Plots
- Rewritten SAC Module
- Full Changelog
We officially support the following systems (meaning we test that they work with ObsPy; other versions - especially newer ones, might work, but we cannot guarantee that).
Python modules:
-
Python: 2.7, 3.3, 3.4, 3.5 (we dropped support for 2.6 but added support for 3.5) -
NumPy: 1.6 - 1.10 (minimum NumPy is now 1.6) -
SciPy: 0.9 - 0.17 (minimum SciPy is now 0.9) -
matplotlib: 1.1 - 1.5 -
basemap: 1.0.2 - 1.0.7
Supported Operating Systems (mostly 32bit and 64bit):
WindowsOSX-
Linux(tested with default packages on CentOS/RedHat 7, Debian 7 + 8, Fedora 22 + 23, openSUSE 13.2 + Leap 42.1, Ubuntu 12.04 + 14.04 + 15.10) -
Raspberry Pi(Raspbian Wheezy + Jessie)
Updating should be straight-forward. So depending on your installation do
# Anaconda Python Distribution
$ conda update -c obspy obspy# Generic Python
$ pip install -U obspy# Debian/Ubuntu
# add debs.obspy.org to your /etc/apt/sources.list first
$ apt-get update
$ apt-get upgrade python-obspy # and/or python3-obspyor whatever your package manager of choice needs to be told to update a package.
Over the years ObsPy has accumulated some cruft and technical debt. In this release we have massively restructured ObsPy to ease maintenance and to be able to tackle future challenges. A side effect of all these changes is that it might affect you - our users. We took great care to minimize these effects: Everything that worked with ObsPy 0.10.2 should still work with ObsPy 1.0.0 but you might get a lot of warnings. Please adjust your code until no more warnings are raised so it will work with future ObsPy versions..
ObsPy is now structured as follows:
-
obspy.clients: All modules retrieving data from the web or other resources. -
obspy.core: Core classes which are also restructured to yield smaller and more maintainable files. -
obspy.io: All modules reading and writing files in various formats. -
obspy.geodetics: Geographic utilities. -
obspy.realtime: Features for realtime seismogram analysis. -
obspy.signal: All signal processing functions and classes. -
obspy.taup: Theoretical arrival times using the tau-p method.
For example a script might yield the following output:
$ python some_obspy_script.py
/Users/lion/workspace/code/obspy/obspy/core/util/deprecation_helpers.py:57: ObsPyDeprecationWarning:
Function 'obspy.readEvents' is deprecated and will stop working with the next ObsPy version.
Please use 'obspy.read_events' instead.
/Users/lion/workspace/code/obspy/obspy/core/util/deprecation_helpers.py:68: ObsPyDeprecationWarning:
Module 'obspy.mseed' is deprecated and will stop working with the next ObsPy version.
Please import module 'obspy.io.mseed' instead.Thus you should change
-
obspy.readEvents()toobspy.read_events() -
obspy.mseedtoobspy.io.mseed
and your code will continue to work with future ObsPy versions.
ObsPy gained support for a few new data formats. They can be read by just using the normal obspy.read(), obspy.read_events(), and obspy.read_inventory() functions.
-
Support for additional waveform data formats:
- Read support for the ASCII format for waveforms from the K-NET and KiK-net strong-motion seismograph networks. See documentation.
-
Support for additional event data formats:
- CMTSOLUTION files used by many waveform solvers. See documentation.
- ESRI shapefile write support, useful in GIS applications. See documentation.
- Google Earth KML output. See documentation.
-
Support for additional station data format:
- The FDSN web service station text format can now be read. See documentation.
- Read support for the NIED's moment tensor TEXT format. See documentation.
- ESRI shapefile write support, useful in GIS applications. See documentation.
- Google Earth KML output. See documentation.
- Read support for SeisComP3 inventory files. See documentation.
With 1.0.0 ObsPy gained support for a couple of new local and remote data sources.
-
SDS file system structure: The
obspy.clients.filesystemmodule has a client to read data from SDS directory structure (or organize your own data in an SDS structure). Very useful for observatories. See documentation -
Syngine: The
obspy.clients.synginemodules grants access to the IRIS Syngine service. See documentation. - The old, deprecated
obspy.neriesclient has been removed. The same data can be accessed with theobspy.clients.fdsnclient.
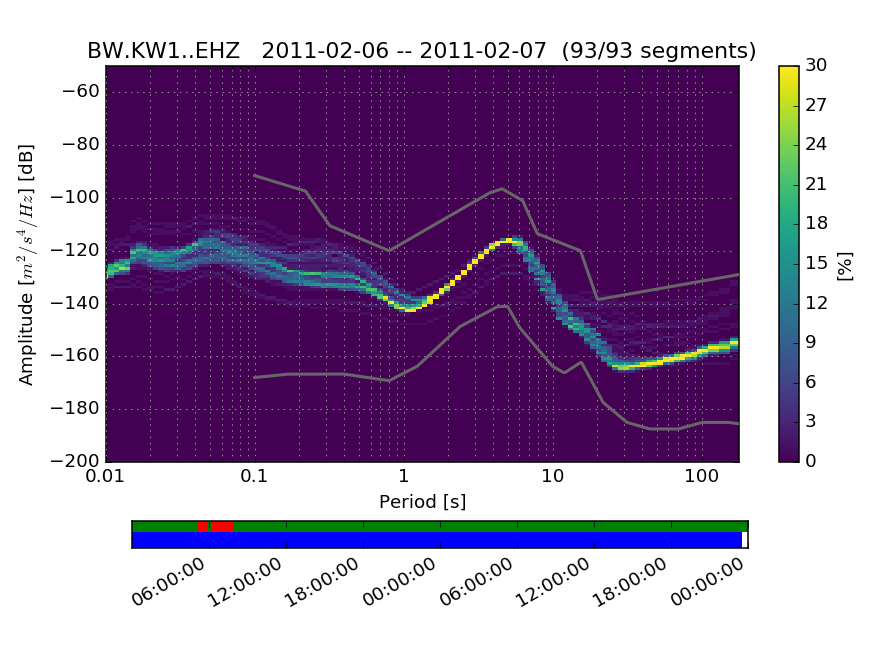
The PPSD class has seen some major improvements and changes since the last stable release:
- The Algorithm for power spectral density computation has been improved, affecting data especially at the long-period band (noise was generally overestimated at high periods)
-
PPSDnow stores the psd for each individual time segment, so after processing all data, arbitrary stacks (e.g. by time span, day of time, day of year, ...) are possible now (seePPSD.calculate_histogram) - Metadata can now be provided to
PPSDduring initialization in any kind of format supported by ObsPy (StationXML, dataless SEED, RESP, ...) - Instrument response calculations now take into account the full response (i.e. not only poles and zeros and overall sensitivity)
- Storing/loading data processed in a
PPSDinstance is now working without problems across dependency versions by using numpy'snpzbinary format, and savedPPSDdata from multiple files can be combined (seePPSD.save_npz(),PPSD.load_npz()andPPSD.add_npz()) - Default colormap for PPSD is now
viridis, seePPSD.plot()documentation how to use PQLX style colormap, x-Axis can now be switched to frequency in the plot - Bin width and smoothing width in the histogram can now be controlled during
PPSDinitialization, also period limits for binning can be explicitly specified, so that computations across data on different sampling rates can share the same histogram layout
See full Changelog for all details and links to corresponding GitHub issues with full discussion.
- New
Trace/Stream.slide()method to ease the implementation of windows algorithms. See documentation. - New
Trace/Stream.remove_sensitivity()method to only apply a constant factor but not remove the full response. See documentation. - Much more stable Butterworth filters! Really worth a try - higher order and narrower filters are now stable. See here for some more details.
- Sinc based reconstruction filter. This is essentially an almost optimal resampling filter and in many cases you should use it as it has the best results. See documentation and here for more details.
- Higher order detrending methods. See documentation here and here.
- Now supports the
ndvelocity model files as an input. - Added geographic methods to calculate ray paths and pierce points on geographic bodies. See the documentation for more details: The
get_travel_time_geo(),get_pierce_points_geo(), andget_ray_paths_geo()methods are new. - Support for buried receivers.
- In general more accurate and faster calculations.
- We now ship with a bunch more velocity models:
1066a,1066b,ak135,ak135f,ak135f_no_mud,herrin,iasp91,jb,prem,pwdk,sp6
-
obspy.clients.fdsn
- Can now also download the text representations of stations and events, which are much smaller, though less flexible.
- Downloads a gzipped response if possible.
-
obspy.imaging
- Now also supports
cartopyas an alternative tobasemap. Will be used if installed and requested.
- Now also supports
Where possible, ObsPy now uses a much superior default colormap. Long story short, the main features of the new colormap is being perceptually uniform, both in color and greyscale and being friendly to people with different kinds of color blindness. Fret not - you can always revert to the old colormaps if you want to, but first watch this very informative and entertaining video or read this blog post for the reasoning behind the change. Scientists should care about how their data are visualized, so it's well worth a watch/read!
ObsPy now contains a module to download and integrate data from any number of FDSN web services at once. Users only have to describe the geographic domain and what they want to download and it does it for them. If you routinely download data - check it out: https://docs.obspy.org/packages/autogen/obspy.clients.fdsn.mass_downloader.html
The following picture shows a possible domain restriction to only download data from within Germany:

If an event has moment tensors it can now be plotted in some fancy ways:
from obspy import read_events
cat = read_events("/path/to/CMTSOLUTION")
ev = cat[0]
ev.plot()
If you have mayavi installed you can even get interactive three dimensional radiation patterns:
ev.plot(kind="mayavi")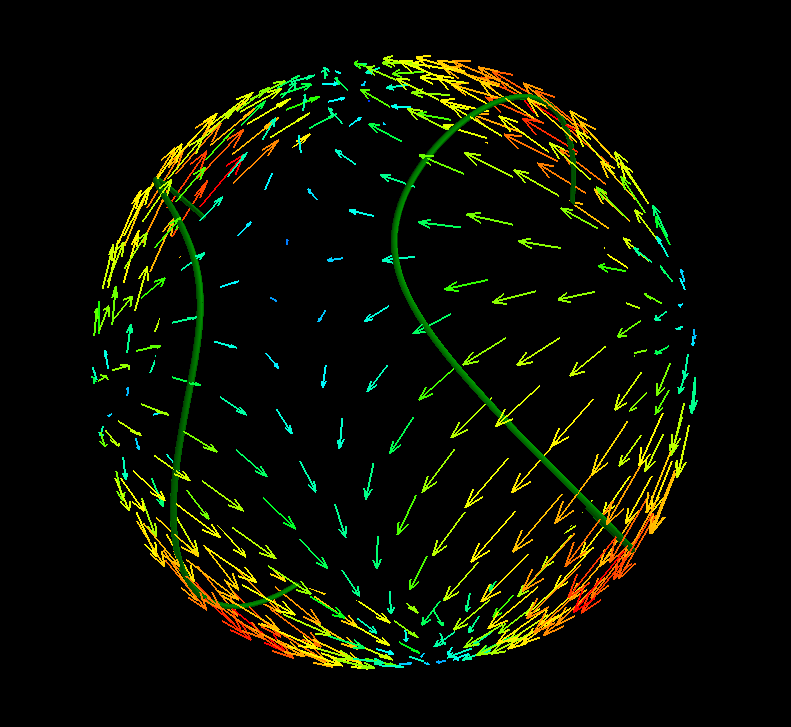
The ObsPy SAC plugin has been rewritten, resulting in two changes in obspy.read and Stream/Trace.write using SAC files, and significant changes in the lower-level handling.
Changes in obspy.read, obspy.write
- The new SAC module will preserve the original
iztypeand reference time (if found inTrace.stats.sac) during writing, thus also preserving any existing relative time headers (e.g. travel-time picks). This better supports round-trip SAC file processing. The previous SAC module generally producediztype = ibSAC files without checking the previous headeriztype, which had the possibility of producing invalid relative time headers. -
obspy.readdoes not put unset SAC headers intotrace.stats.sacunlessdebug_headers=Trueis set. This is a change in default behavior.
SACTrace replaces SacIO
The recommended way of reading and writing SAC files is still using obspy.read and obspy.write, but users of obspy.sac.SacIO will need to be aware of changes. The old obspy.sac.sacio has be rewritten and recycled into a new obspy.io.sac subpackage, and the old SacIO class is replaced by the SACTrace class, which provides a simplified I/O interface and more flexible reference time and relative-time header handling.
The previous SacIO I/O methods, ReadSacFile, ReadSacHeader, ReadSacXY, ReadSacXYHeader, WriteSacBinary, WriteSacHeader, and WriteSacXY are replaced by just two methods: SACTrace.read and SACTrace.write. Reading and writing of header-only vs. full-file, ASCII vs. binary, and big vs little-endian byte order are controlled by keywords in these two methods. Additionally, producing a SACTrace instance from a file does not require initializing an empty class instance first, as was required by SacIO.
from obspy.io.sac import SACTrace
# read from a binary file
sac = SACTrace.read(filename)
# read or write header only
sac = SACTrace.read(filename, headonly=True)
sac.write(filename, headonly=True)
# read from an ASCII file, write a big-endian binary SAC file
sac = SACTrace.read(filename, ascii=True)
sac.write(filename, byteorder='big')The new SACTrace class also has more flexible reference time and relative time header handling. In SACTrace, the SAC reference time (a combination of nzyear, nzjday, nzhour, nzmin, nzsec, and nzmsec) can be accessed and manipulated through the SACTrace.reftime attribute (property), which is a UTCDateTime instance. The reference time (or any of the relative time headers) can be modified by adding/subtracting seconds, or by setting it to a new UTCDateTime instance entirely. Any changes to reftime will be reflected in the "nz" time headers, and will trigger corresponding changes in the relative time headers a, e, f, t0-t9 such that they stay correctly referenced in absolute time.
sac = SACTrace(nzyear=2000, nzjday=1, nzhour=0, nzmin=0, nzsec=0, nzmsec=0,
t1=23.5, data=numpy.arange(100))
sac.reftime, sac.b, sac.e, sac.t1
# (2000-01-01T00:00:00.000000Z, 0.0, 99.0, 23.5)
# Move reference time by relative seconds, relative time headers are preserved.
sac.reftime -= 2.5
sac.reftime, sac.b, sac.e, sac.t1
# (1999-12-31T23:59:57.500000Z, 2.5, 101.5, 26.0)
# Set reference time to new absolute time, relative time headers are preserved.
sac.reftime = UTCDateTime(2000, 1, 1, 0, 2, 0, 0)
sac.reftime, sac.b, sac.e, sac.t1
# (2000-01-01T00:02:00.000000Z, -120.0, -21.0, -96.5)Additionally, manually changing the iztype header will similarly preserve the absolute referencing of relative time headers.
1.0.0 also contains all fixes from 0.10.3 which will be released right afterwards as a source distribution only (for special purposes; no binary packages provided).
1.0.0:
- General:
* Requirements have been increased to reflect latest distributions:
* Removed support for Python 2.6.
* Added support for Python 3.5.
* matplotlib >= 1.1.0 is now required.
* numpy >= 1.6.1 is now required
* scipy >= 0.9.0 is now required
* Reorganized the submodule structure. We provide a deprecation path so the
old imports will continue to work for one ObsPy version.
* Consistent naming scheme across the code base. This results in some
functions having different names. Most things that worked with ObsPy 0.10
will continue to work with this version, but starting with the next
version they will fail. Pay attention to the deprecation warnings.
* Support for additional waveform data formats:
- Read support for the ASCII format for waveforms from the K-NET and
KiK-net strong-motion seismograph networks.
* Support for additional event data formats:
- CMTSOLUTION files used by many waveform solvers.
- ESRI shapefile write support, useful in GIS applications (see #1066)
- Google Earth KML output.
* Support for additional station data format:
- The FDSN web service station text format can now be read.
- Read support for the NIED's moment tensor TEXT format (see #1125)
- Google Earth KML output.
- Read support for SeisComP3 inventory files.
- obspy.core:
* New method for generating sliding windows from Stream/Trace windows.
(see #860)
* Stream/Trace.slice() now has the optional `nearest_sample` argument from
Stream/Trace.trim().
* Trace.remove_response() now has `plot` option to show/output a plot of all
individual steps of instrument response removal in frequency domain
(see #1116).
* New method Stream/Trace.remove_sensitivity() to remove instrument
sensitivity
* Fix incorrect parsing of some non-ISO8601 date/time strings. (see #1215)
* Added plotting method to Event (customizable subplots from a selection
of map, beachball and farfield radiation plots, see #1192)
- obspy.clients.fdsn:
* Replace FDSN webservice shortcut `NERIES` with `EMSC` and deprecate the
`NERIES` shortcut, will be removed in a future release (see #1146).
* Now requests gzipped data for the XML files. Much smaller files!
* The station service can now also be used to download files in the text
format. This has limited information but is much faster.
* New mass downloader to assist in downloading data across a large number
of FDSN web services.
* Catch invalid URLs when initialising Client and avoid confusing error
messages (see #1162)
- obspy.clients.filesystem.sds:
* New client to read data from local SDS directory structure (see #1135).
* Command line script `obspy-sds-report` to generate html page with
information on latency, data availability percentage and number of gaps
for a local SDS archive (see #1202)
- obspy.clients.neries:
* Removed the dedicated client. Data can still be accessed by using the FDSN
client.
- obspy.clients.syngine:
* New client for the IRIS Syngine service to retrieve custom synthetic
seismograms.
- obspy.imaging:
* Experimental support for Cartopy when plotting maps. Use the `method`
argument to functions that plot maps to select between Basemap or Cartopy.
* New default colormap for all plots. A backport of the new viridis colormap
from matplotlib is available for those using older matplotlib releases.
* Added plotting routines for farfield radiation patterns of moment tensors
- obspy.io.kml:
* New module for Google KML output of Inventory and Catalog objects
(e.g. for use in Google Earth)
- obspy.io.mseed:
* Upgrade to libmseed 2.16
- obspy.io.seiscomp.sc3ml:
* New module reading SeisComP3 inventory files to ObsPy inventory objects
(see #1182).
- obspy.io.shapefile:
* New module for ESRI shapefile write support (see #1066)
- obspy.io.stationtxt:
* New module reading the FDSN station files.
- obspy.signal:
* Switch to second-order sections for filters; backported from SciPy 0.16.0
(see #1028)
* New Lanczos interpolation/resampling (see #1101)
* Higher order detrending methods (see #1173)
* PPSD (see #931, #1108, #1130, #1187):
- Algorithm for PSD computation was improved, especially affecting results
at long periods (for detailed discussion see #931 and #1108).
- Keywords `paz` and `parser` were removed in favor of new keyword
`metadata`. PPSD now accepts `metadata` in a much wider range
of formats:
* Inventory objects (e.g. from StationXML or from FDSN webservice)
* obspy.io.xseed Parser objects (e.g. from dataless SEED file)
* filename of a RESP file
* dictionary with poles and zeros information (like in
prior versions)
Most old codes should still work, issuing a deprecation warning, but
old code that specifies *both* `paz` and `parser` keywords will raise
an exception.
- Whenever possible (i.e. when using for `metadata` an Inventory,
a Parser or a RESP file), response calculation now takes into account
the full response (all stages) as opposed to only using the poles and
zeros response stage (as was done in previous versions when using a
Parser object). When using a poles and zeros dictionary response
calculation is unchanged (as no information on other stages is
available, of course).
- PPSD now stores the psd for each time segment that gets processed,
instead of only storing the stacked histogram. That way, differing
custom stacks with various selection criteria (e.g. time of day, by
weekday, etc.) can now be made from the same processed data
(see #1130).
- New save/load mechanism using numpy .npz binary format that circumvents
some problems with the old pickle mechanism:
`PPSD.save_npz()` and `PPSD.load_npz()` (and `PPSD.add_npz()` to add
data from additional npz files)
- Change default colormap to new obspy default sequential colormap
(matplotlibs new viridis colormap). The old PQLX colormap is provided by
`obspy.imaging.cm.pqlx` and can be used with
`PPSD.plot(..., cmap=...)`.
- new option `PPSD.plot(..., cumulative=True)` for a cumulative plot of
the histogram, i.e. a non-exceedence percentage visualization, similar
to the `percentile` option.
- x axis in `PPSD.plot()` can be switched to frequency in Hz with
`PPSD.plot(..., xaxis_frequency=True)` (see #1130)
- changes to special handling of rotational: now handled by kwarg
`special_handling="ringlaser"` (kwarg `is_rotational_data` is
deprecated, see #916)
- special handling option for hydrophone data (no differentiation, see
#916)
- bin width on frequency axis can now be controlled using
`PPSD(..., frequency_bin_width_octaves=...)` (in fractions of octaves,
default is the old fixed setting of 1/8 octaves as in PQLX)
- obspy.taup
* Added support for nd file format for input velocity models. Allows for
named discontinuities at arbitrary depths allowing for less Earth like
models (see #1147).
* Added three methods (`get_travel_times_geo()`, `get_pierce_points_geo()`
and `get_ray_paths_geo()`) to `TauPyModel` to handle station and
event location data as latitude and longitude, instead of the source to
station distance in degrees. In addition `get_ray_paths_geo()` and
`get_pierce_points_geo()` decorate the returned pierce points and ray
paths with the latitude and longitude of each point. Some functionality
needs the `geographiclib` module to be installed. (See #1164.)
* ObsPy now ships with a bunch of new velocity models in addition to the
existing ones: `prem`, `sp6`, `1066a,b`, `herrin` (See #1196).
* Add support for buried receivers (see #1103.)
* Port more accurate calculation of ray parameter from Java. The effect is
stronger for longer phases, but also corrects issues with shorter body and
surface waves (see #986.)
* Fix incorrect branch splitting which also caused issues for extremely
shallow phases (see #1057.)
* Proper cache for model splits resulting in much faster calculations if
the source depth is repeatedly the same (see #1248).
0.10.3:
- obspy.core:
* Fix reading of multiple catalog files using globs (see #1065).
* Fixed a bug when using
`Trace.remove_response(..., water_level=None)`.
With that setting that is supposed to not use any water level
stabilization in the inversion of the instrument response
spectrum actually the instrument response was never inverted and
thus instead of a deconvolution a convolution was performed
(see #1104).
* Fixing floating point precision/rounding issue with UTCDateTime when
initializing with floating point seconds, i.e. with microseconds,
that could lead to microseconds being off by 1 microsecond
(see #1096)
* Correct gap/overlap time returned by Stream.get_gaps() and printed
by Stream.print_gaps() which was incorrect by one time the sampling
interval (see #1151)
* Stream.get_gaps(): return overlaps specified in units of samples
as negative integers (see #1151)
- obspy.fdsn:
* More detailed error messages on failing requests (see #1079)
* Follows redirects for POST requests (see #1143)
- obspy.imaging:
* fix some bugs in `obspy-scan` (see #1138)
- obspy.mseed:
* Blockette 100 is now only written for Traces that need it. Previously
it was written or not for all Traces, depending on whether the last
Trace needed it or not. (see #1069)
* Fixed a bug that prevented microsecond accuracy for times before 1970
(see #1102).
* Updated to libmseed 2.17.
- obspy.signal:
* Bug fixed within rotate.rotate2zne(). Additionally it can now also
perform the inverse rotation (see #1061).
* Bug fixed in triggering. When using option `max_len_delete` and a trigger
occurred right before the end of data, one trigger was potentially lost
(see #1145 for details).
- obspy.station:
* Plotting responses across multiple channels is more robust now in
presence of some strange channels (e.g. with zero sampling rate,
happens e.g. for state of health channels, see #1115)
* ObsPy no longer assumes that the StationXML namespace is the default
namespace (see #1060).
* Checking if a file is a StationXML file is less rigorous (and much
faster) now (not checking strict validity against xsd schema but
only looking for a FDSNStationXML root element, see #1114).
This means that `read_inventory()` without explicitly specified
format will correctly detect more files as StationXML that have very
slight breaches of the schema but still can be interpreted as
StationXML.
* fix saving `xcorrPickCorrection()` results to an image file (see #1154)
- obspy.taup:
* Calculating arrival times for surface waves now works (see #1055)
* Calculating arrivals for underside reflections now works (see #1089)
- obspy.y:
* correct misspelled name of a Y specific header field (see #1127)
- obspy.zmap
* Add support for time values with sub-second precision (see #1093)







