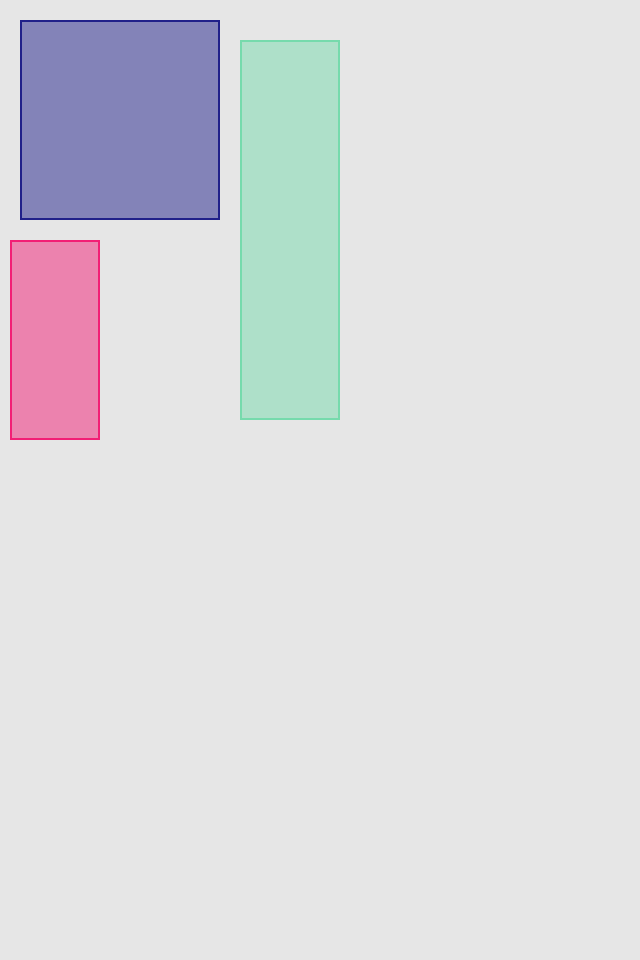
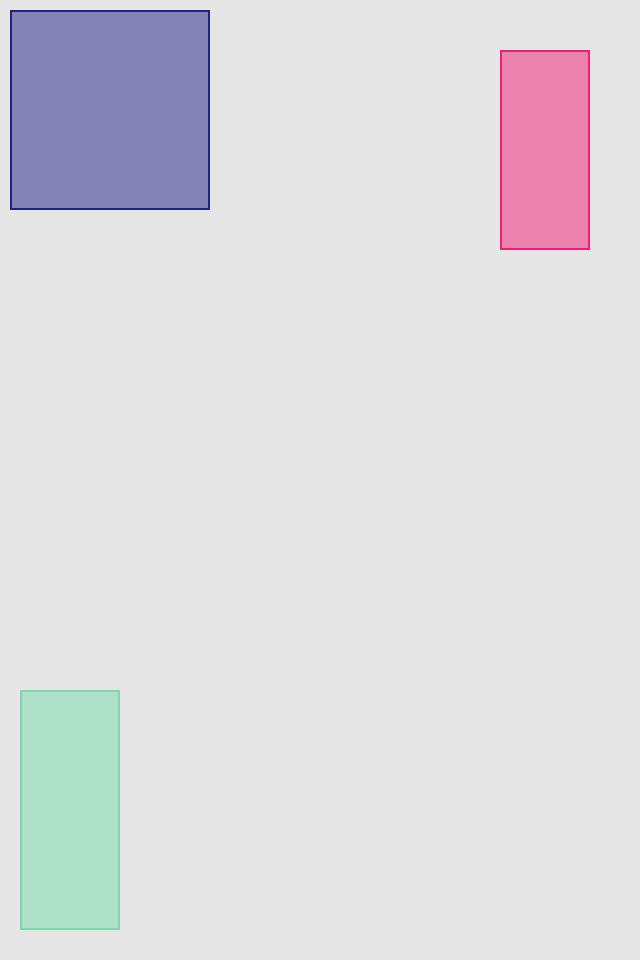
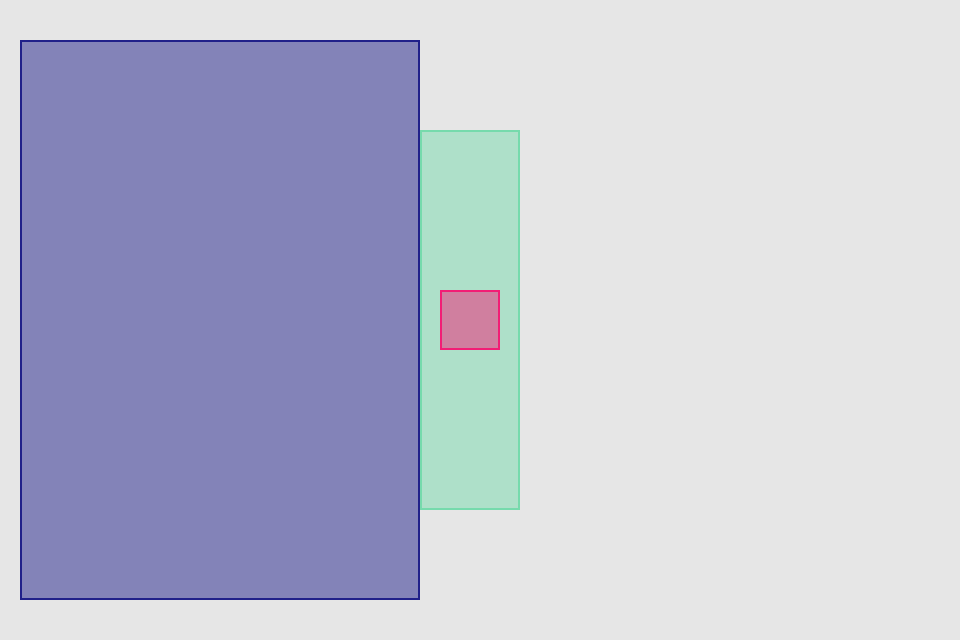
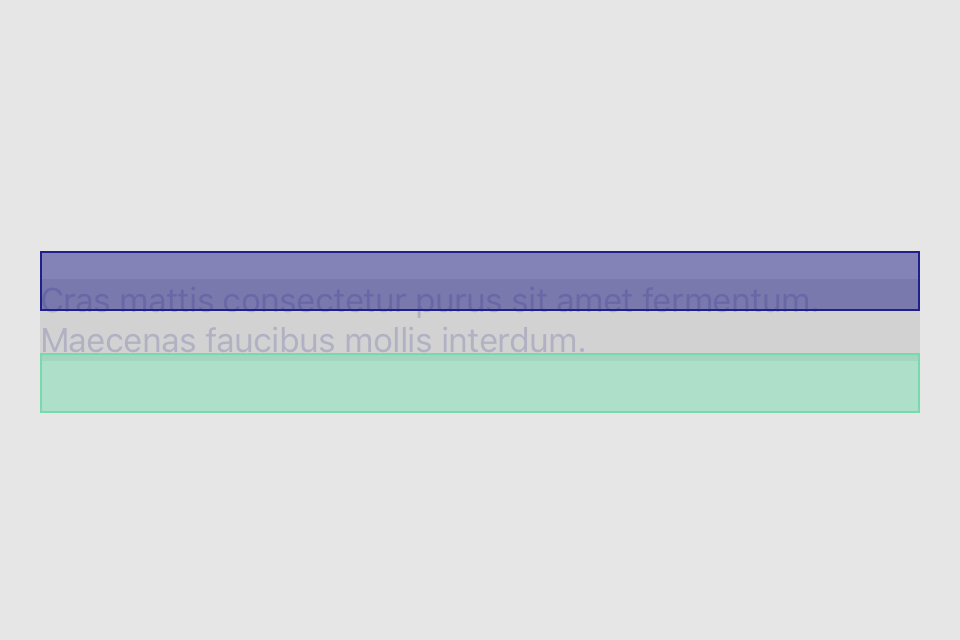
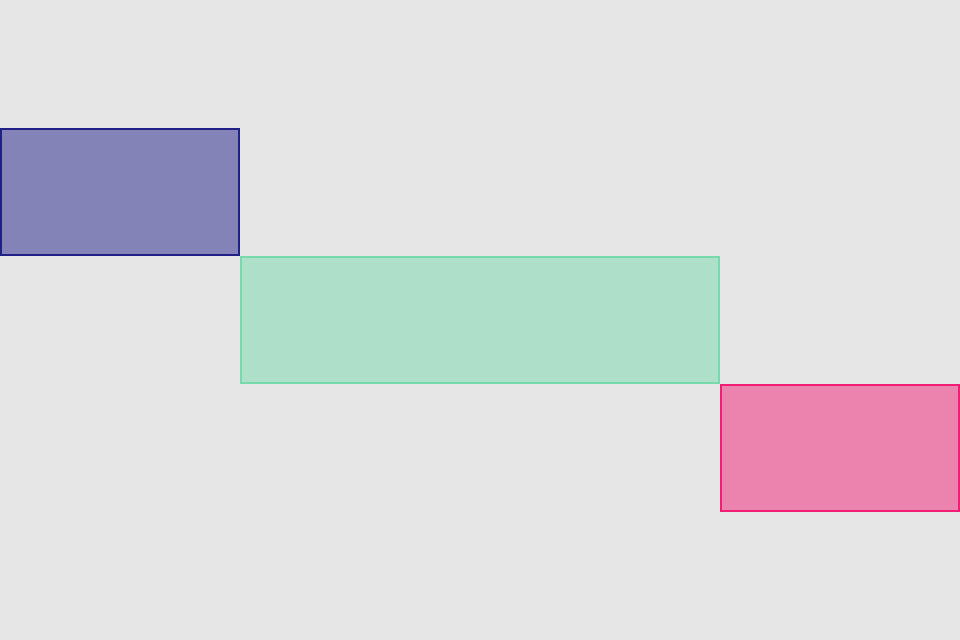
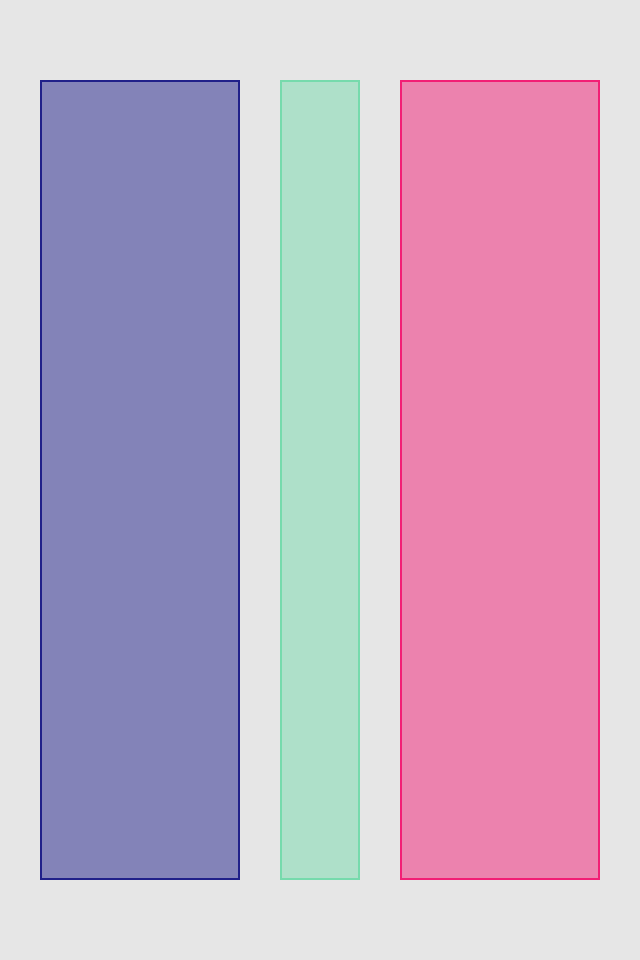
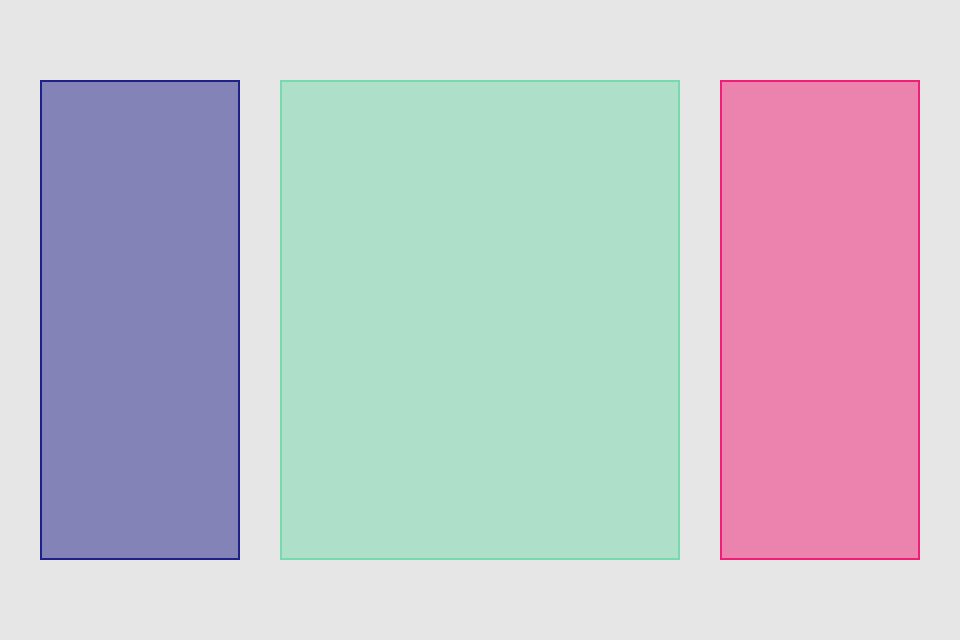
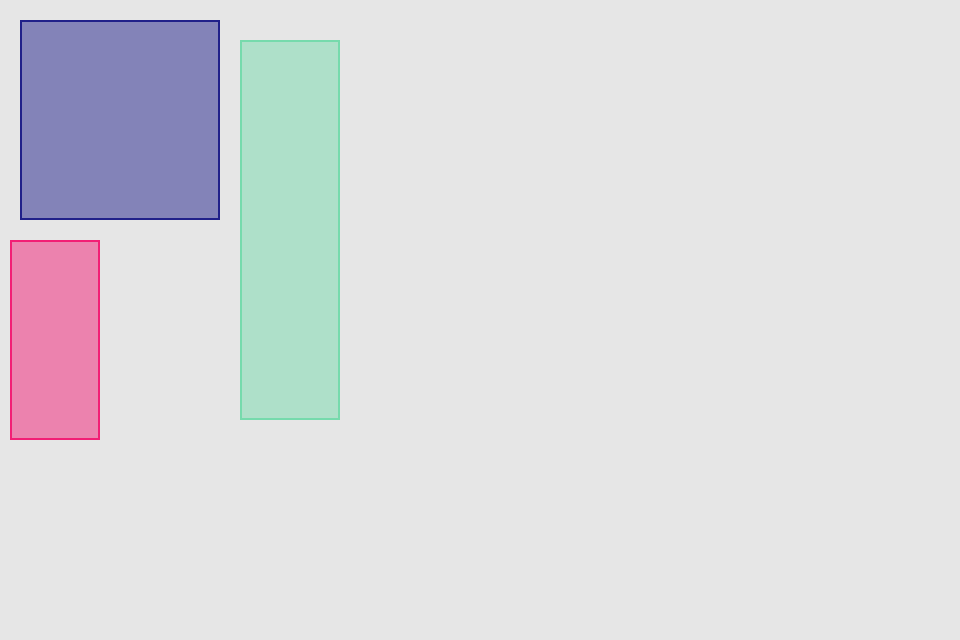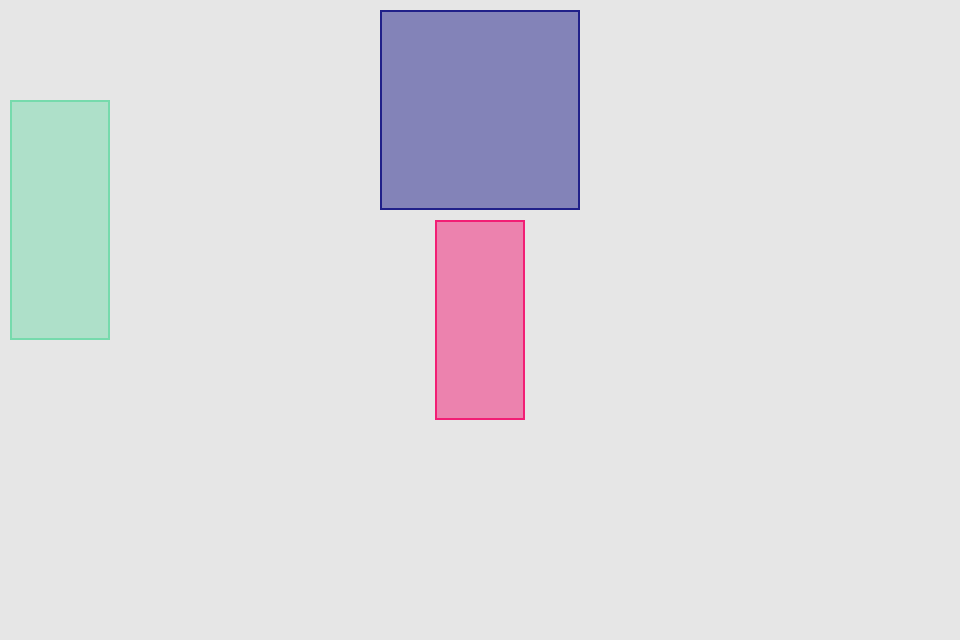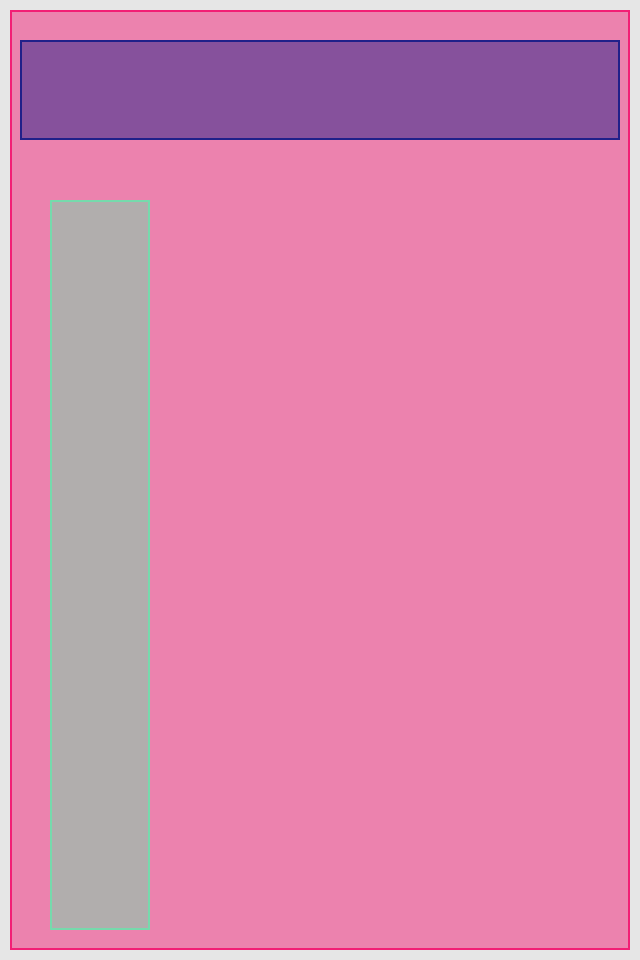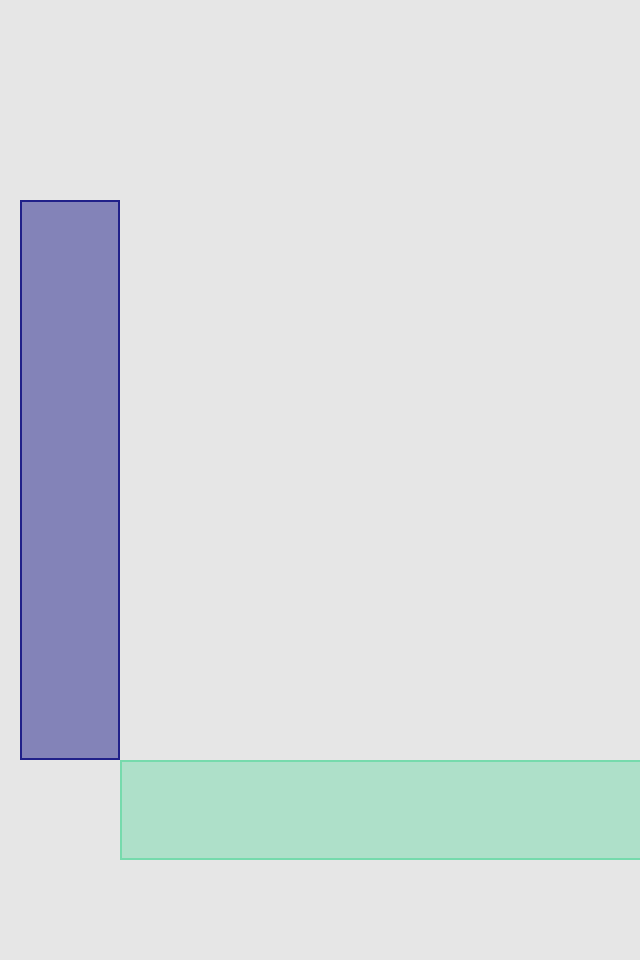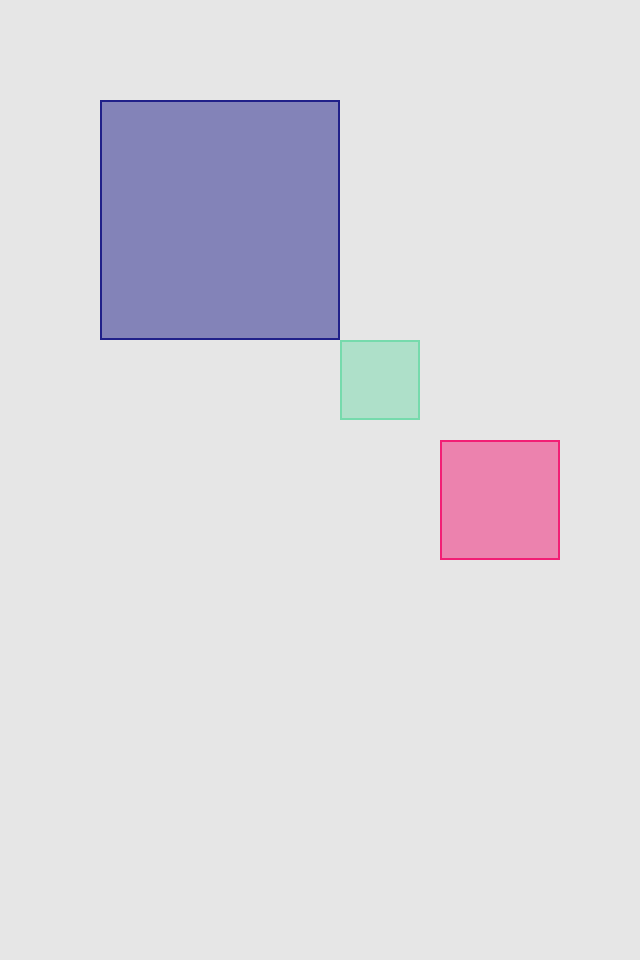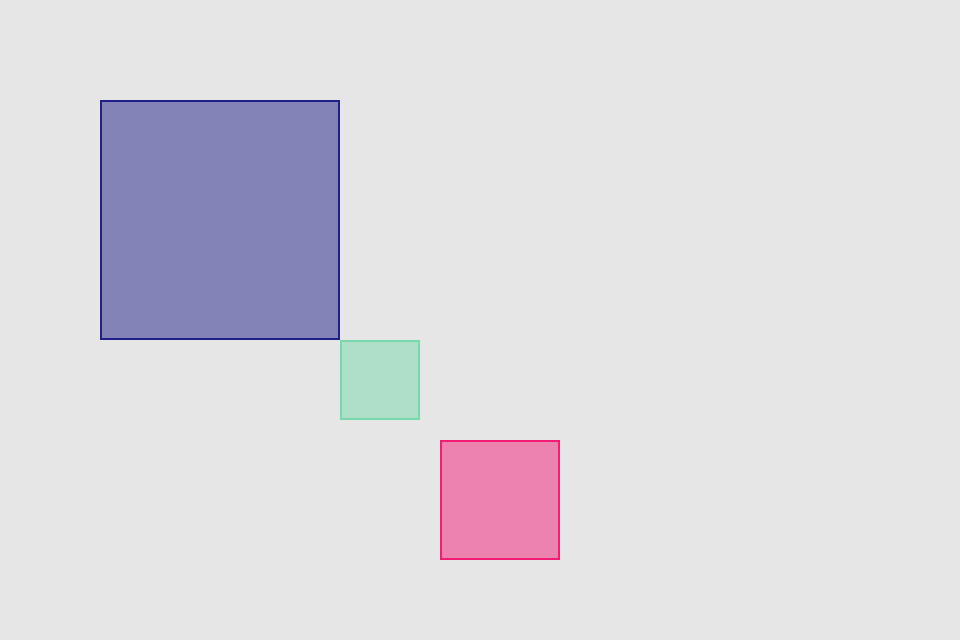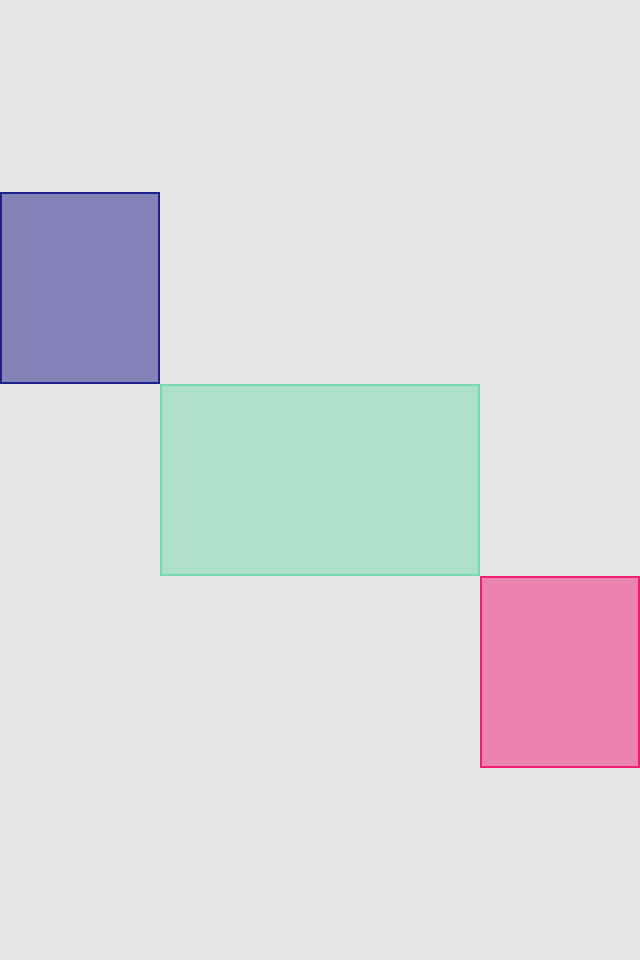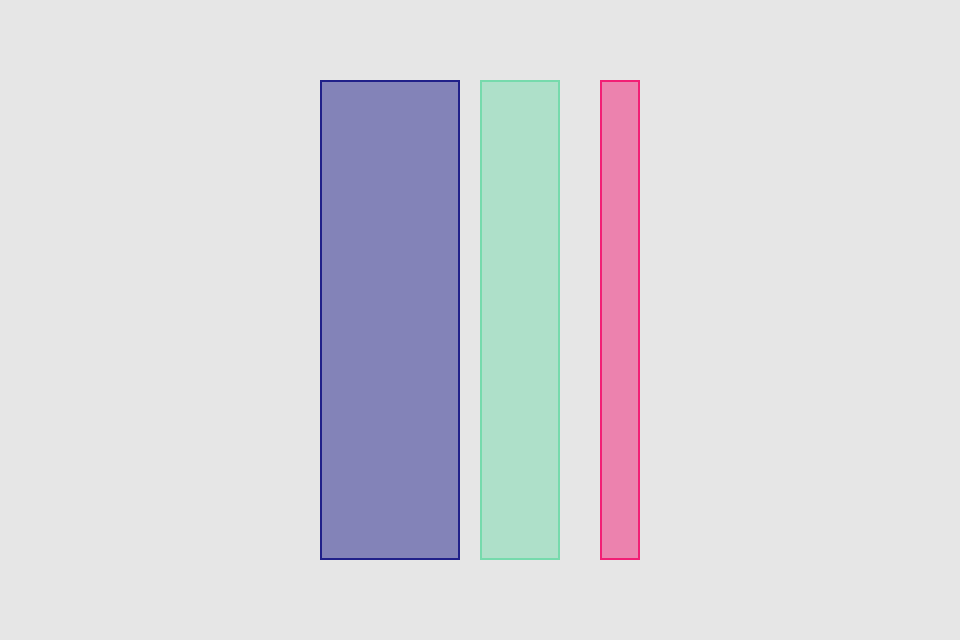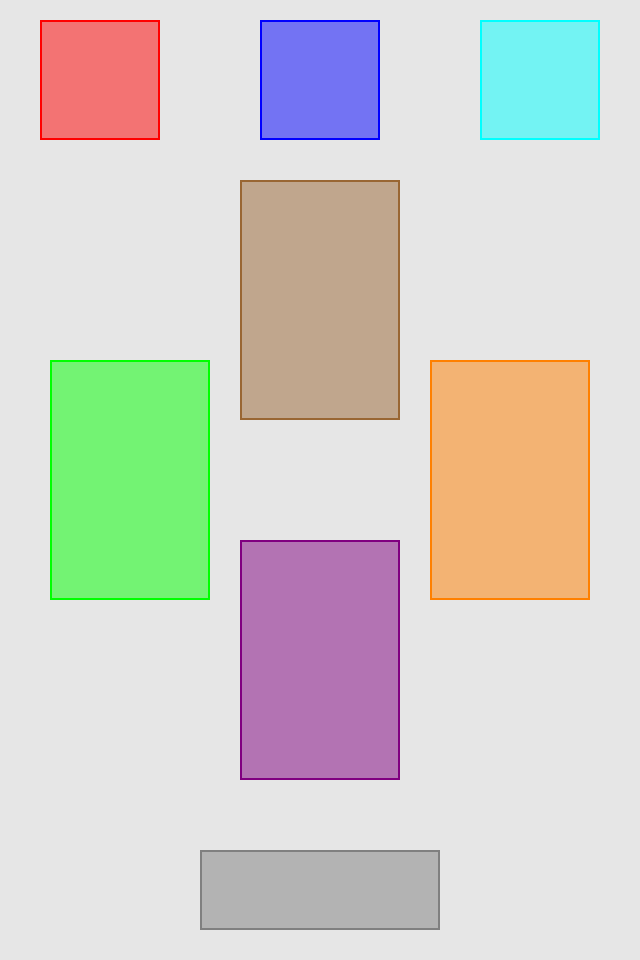set* operations directly put frame values
blueView.lx.set(x: 10, y: 10)
.set(width: 100, height: 100)
greenView.lx.set(x: 120, y: 20, width: 50, height: 190)
redView.lx.set(x: 5)
.set(y: 120)
.set(width: 45)
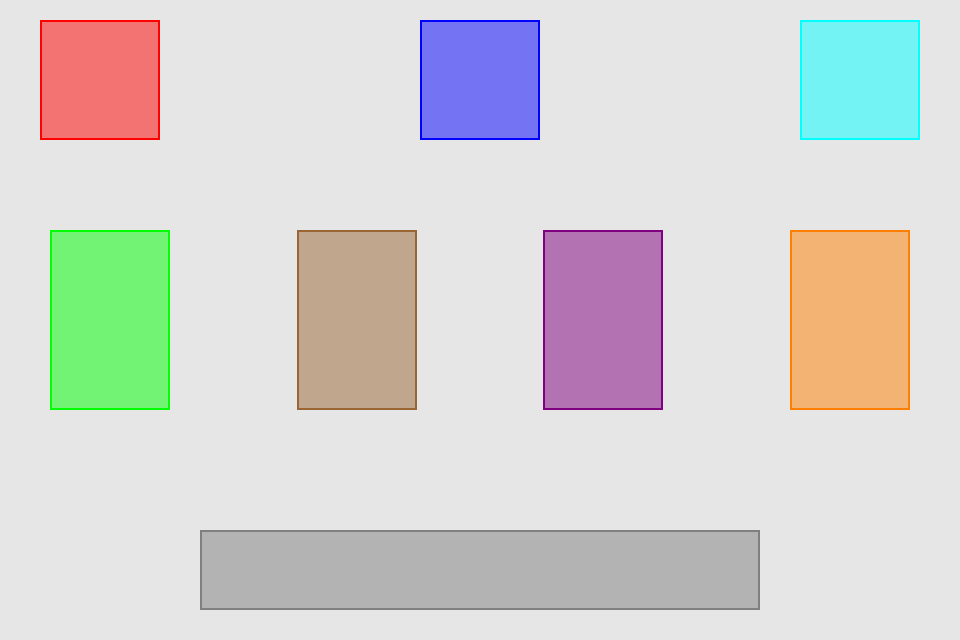
.set(height: 100)hcenter (horizontally), vcenter (vertically) and center (both) operations allows to center view in superview. Insets can be used to adjust center point (see green view, 100 pt from bottom). Size of view usually should be set with previous operations
blueView.lx.set(y: 5)
.set(width: 100, height: 100)
.hcenter()
greenView.lx.set(x: 5)
.set(width: 50, height: 120)
.vcenter(topInset: 0, bottomInset: 100)
redView.lx.set(width: 45, height: 100)
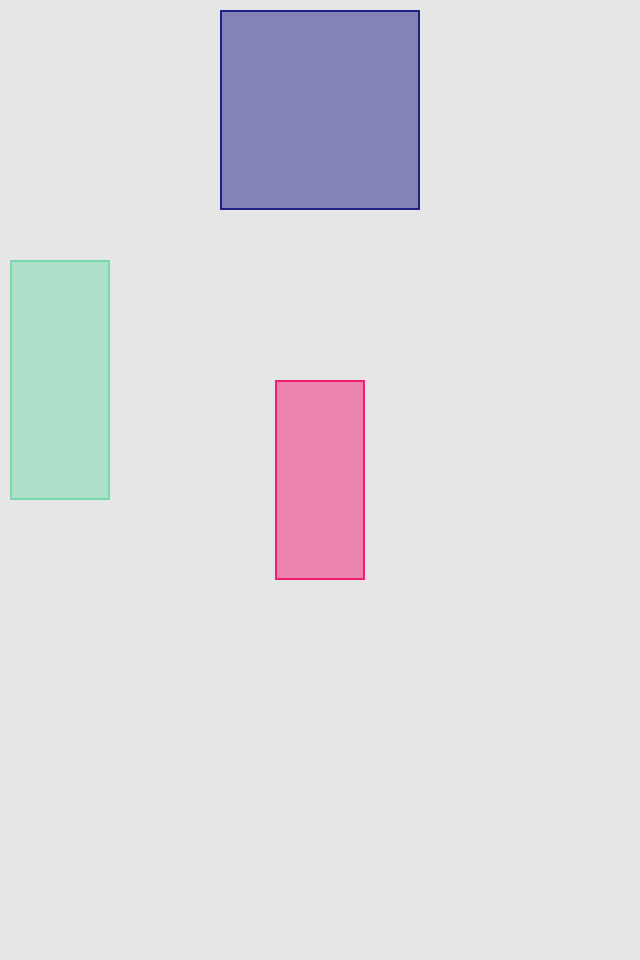
.center()hfill (horizontally), vfill (vertically) and fill (both) operations make view to fill its superview. Insets can be used to control how much space to be left unfilled from the superview edges
redView.lx.fill(inset: 5)
blueView.lx.set(y: 20)
.set(height: 50)
.hfill(inset: 10)
greenView.lx.set(x: 25)
.set(width: 50)
.vfill(topInset: 100, bottomInset: 15)align* operations allow to put view relatively to edges of superview. Inset value can be used to set distance to edge. Size of view usually should be set with previous operations.
blueView.lx.set(width: 100, height: 100)
.alignLeft(5)
.alignTop(5)
greenView.lx.set(width: 50, height: 120)
.alignLeft(10)
.alignBottom(15)
redView.lx.set(width: 45, height: 100)
.alignRight(25)
.alignTop(25)sizeToFit operation fits view in defined box using -sizeThatFits: method. Box (width and height) can be defined using different options. .value option sets exact value for box. Result size will be equal or less than it.
icon.lx.sizeToFit(width: .value(100), height: .value(100))
.alignTop(10)
.hcenter()
label.lx.sizeToFit(width: .value(100), height: .value(100))
.center()
title.lx.sizeToFit(width: .value(100), height: .value(100))
.alignBottom(10)
.hcenter().max option sets infinite value for fitting box. Result size will be most comfortable for view to display content. WARNING: multiline labels are comfortable with single line, don't use .max for width
icon.lx.sizeToFitMax() //same as view.lx.sizeToFit(width: .Max, height: .Max)
.alignTop(10)
.hcenter()
label.lx.sizeToFit(width: .max, height: .max)
.center()
title.lx.sizeToFit(width: .max, height: .max)
.alignBottom(10)
.hcenter().current option sets value for box with current frame's width or height.
icon.lx.set(size: CGSize(width: 200, height: 200))
.sizeToFit(width: .current, height: .current)
.alignTop(10)
.hcenter()
label.lx.hfill(leftInset: 20, rightInset: 20)
.sizeToFit() //same as view.lx.sizeToFit(width: .Current, height: .Current)
.center()
title.lx.hfill(leftInset: 20, rightInset: 20)
.sizeToFit(width: .current, height: .current)
.alignBottom(10)
.hcenter().keepCurrent options sets value for box with current frame's width or height, but result size will be still equal to those original frame values. This is usefull to layout multiline labels. First you need to set somehow label width, and then call something like label.lx.sizeToFit(width: .keepCurrent, height: .max).
icon.lx.set(size: CGSize(width: 200, height: 200))
.sizeToFit(width: .keepCurrent, height: .max)
.alignTop(10)
.hcenter()
label.lx.hfill(leftInset: 20, rightInset: 20)
.sizeToFit(width: .keepCurrent, height: .max)
.center()
title.lx.hfill(leftInset: 20, rightInset: 20)
.sizeToFit(width: .keepCurrent, height: .max)
.alignBottom(10)
.hcenter()sizeToFit operation also can have min, max or both constraints to limit resulted width/height.
label.lx.sizeToFitMax(widthConstraint: .max(100), heightConstraint: .min(300))
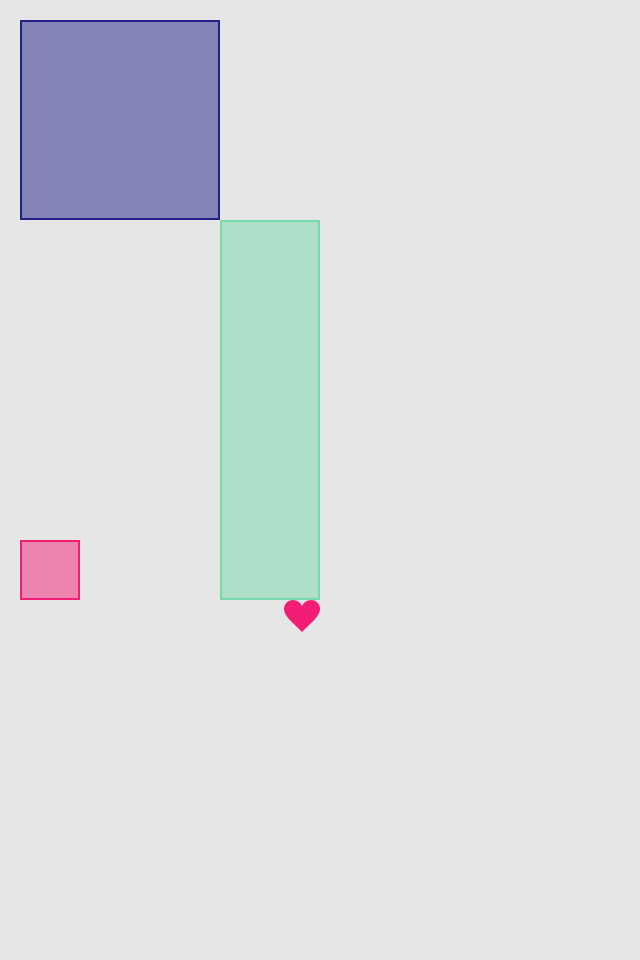
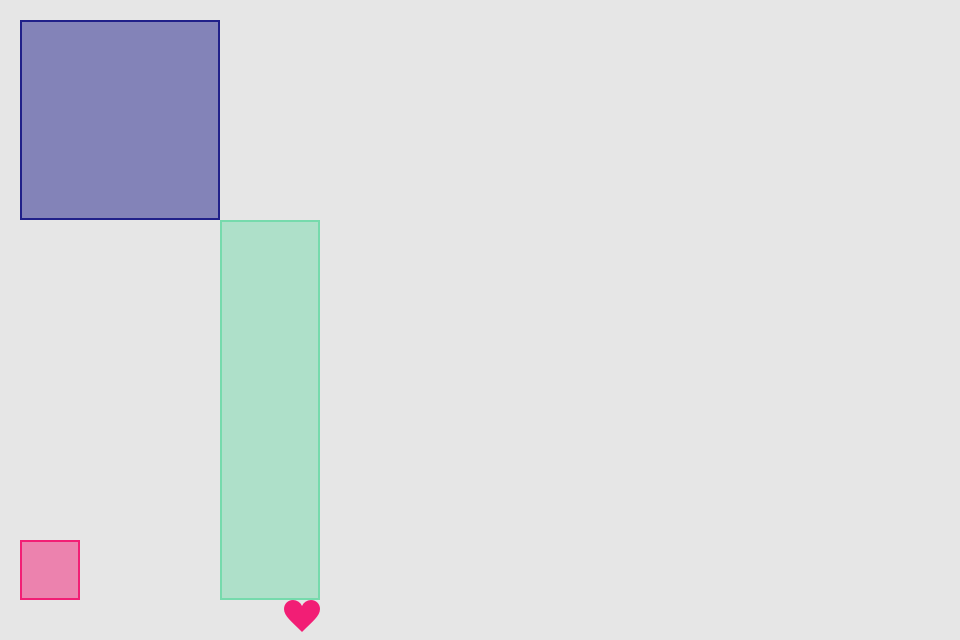
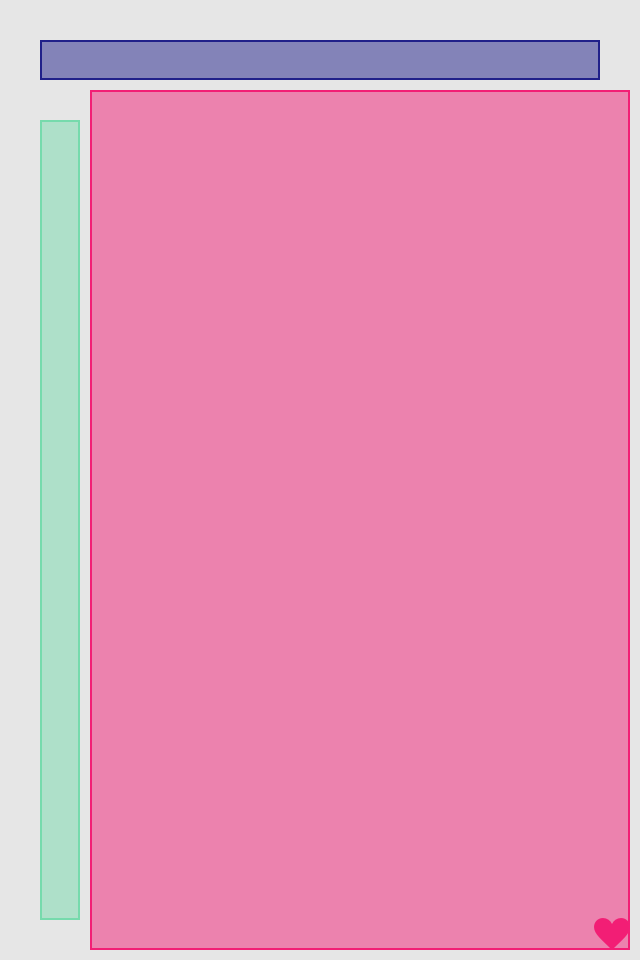
.center()Follow operation makes one view's anchor to be the same with others view anchor (+/- inset). Anchors can be horizontal or vertical, and can be followed only with the anchors of same type. Anchor can follow anchors of other views at the same level of hierarchy, or parent anchors
blueView.lx.set(x: 10, y: 10)
.set(width: 100, height: 100)
greenView.lx.set(width: 50, height: 190)
greenView.lx.leftAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.rightAnchor)
greenView.lx.topAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.bottomAnchor)
redView.lx.set(width: 30, height: 30)
redView.lx.leftAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.leftAnchor)
redView.lx.bottomAnchor.follow(greenView.lx.bottomAnchor)
heartView.lx.topAnchor.follow(greenView.lx.bottomAnchor)
heartView.lx.rightAnchor.follow(greenView.lx.rightAnchor)There are not only edge anchors, but also center anchors
blueView.lx.set(x: 10, y: 10)
.set(width: 200)
.vfill(inset: 20)
greenView.lx.set(width: 50, height: 190)
greenView.lx.leftAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.rightAnchor)
greenView.lx.vcenterAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.vcenterAnchor)
redView.lx.set(width: 30, height: 30)
redView.lx.hcenterAnchor.follow(greenView.lx.hcenterAnchor)
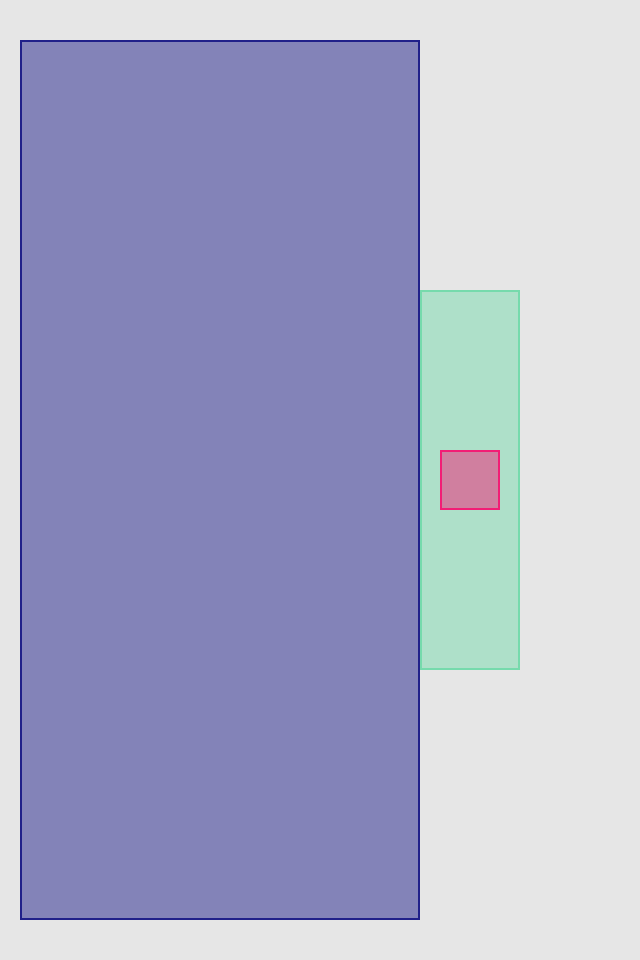
redView.lx.vcenterAnchor.follow(greenView.lx.vcenterAnchor)There are also size anchors
blueView.lx.set(x: 10)
.set(width: 50)
.vfill(inset: 100)
greenView.lx.heightAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.widthAnchor)
greenView.lx.widthAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.heightAnchor)
greenView.lx.leftAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.rightAnchor)
greenView.lx.topAnchor.follow(blueView.lx.bottomAnchor)firstBaselineAnchor/lastBaselineAnchor anchors are special. Only Baselinable views have it. For the moment only UILabel is conforming this protocol
label.lx.hfill(inset: 20)
.sizeToFit(width: .keepCurrent, height: .max)
.center()
blueView.lx.set(height: 30)
.hfill(inset: 20)
greenView.lx.set(height: 30)
.hfill(inset: 20)
blueView.lx.bottomAnchor.follow(label.lx.firstBaselineAnchor)
greenView.lx.topAnchor.follow(label.lx.lastBaselineAnchor)hput and vput operations successively layout views in superview in horizontal or vertical direction using intentions. Fix intention means that view size will take exact value, either directly defined or current one
self.lx.hput(
Fix(50),
Fix(blueView, 120),
Fix(greenView, 40),
Fix(10),
Fix(redView, 60)
)
self.lx.vput(
Fix(50),
Fix(blueView, 120),
Fix(greenView, 40),
Fix(10),
Fix(redView, 60)
)hput and vput operations successively layout views in superview in horizontal or vertical direction using intentions. Flex intention means that view size will take value based weight of flex value. Flex operates only with free space left after Fix intentions
self.lx.hput(
Flex(blueView, 0.5),
Flex(greenView, 1.0),
Flex(redView, 0.5)
)
self.lx.vput(
Flex(),
Flex(blueView),
Flex(greenView),
Flex(redView),
Flex()
)Biggest power comes when we combine Fix and Flex intentions
self.lx.hput(
Fix(20),
Fix(blueView, 100),
Fix(20),
Flex(greenView),
Fix(20),
Fix(redView, 100),
Fix(20)
)
blueView.lx.vfill(inset: 40)
greenView.lx.vfill(inset: 40)
redView.lx.vfill(inset: 40)It is really to easy to center bunch of views all together
self.lx.hput(
Flex(),
Fix(blueView, 70),
Fix(10),
Fix(greenView, 40),
Fix(20),
Fix(redView, 20),
Flex()
)
blueView.lx.vfill(inset: 40)
greenView.lx.vfill(inset: 40)
redView.lx.vfill(inset: 40)Single intention can be defined for several views, all calculations are doing for first one, and others use this result as is
self.lx.hput(
Flex(),
Fix(blueView, 70),
Fix(10),
Fix(greenView, 40),
Fix(20),
Fix(redView, 20),
Flex()
)
self.lx.vput(
Fix(40),
Flex([blueView, greenView, redView]),
Fix(40)
)Elegant way to layout views in grid using just one hput and one vput
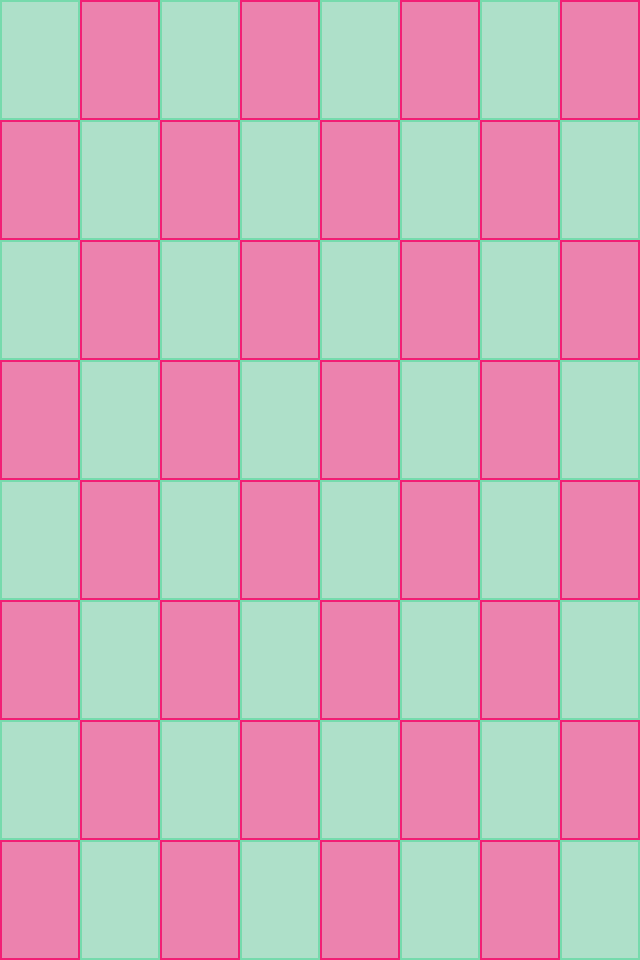
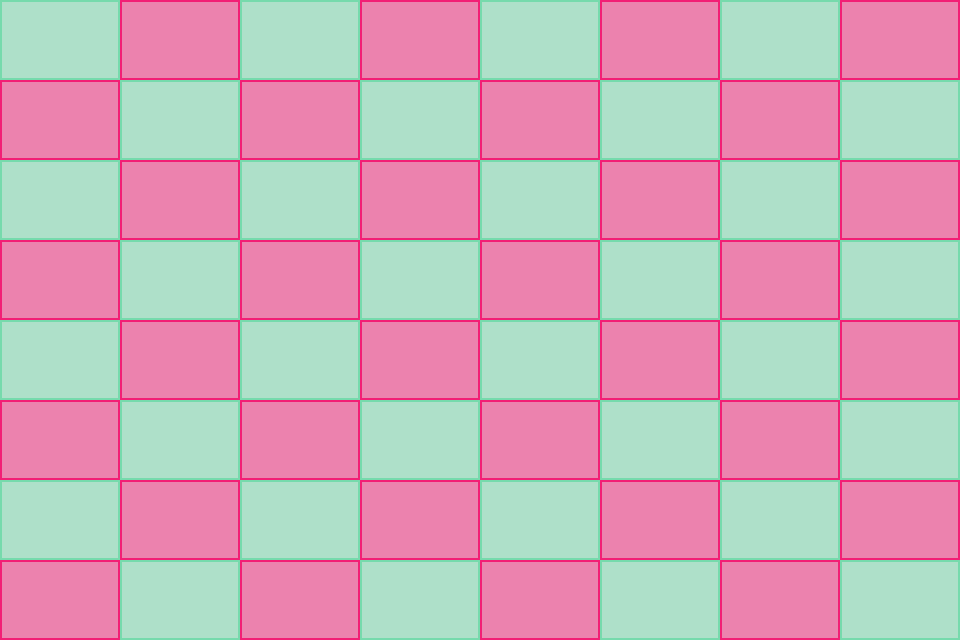
func putCols() {
var r = [PutIntention]()
for i in 0..<8 {
var row = [Layoutable]()
for j in 0..<8 {
row.append(views[i*8 + j])
}
r.append(Flex(row))
}
self.lx.hput(r)
}
func putRows() {
var r = [PutIntention]()
for i in 0..<8 {
var col = [Layoutable]()
for j in 0..<8 {
col.append(views[i + j*8])
}
r.append(Flex(col))
}
self.lx.vput(r)
}
putCols()
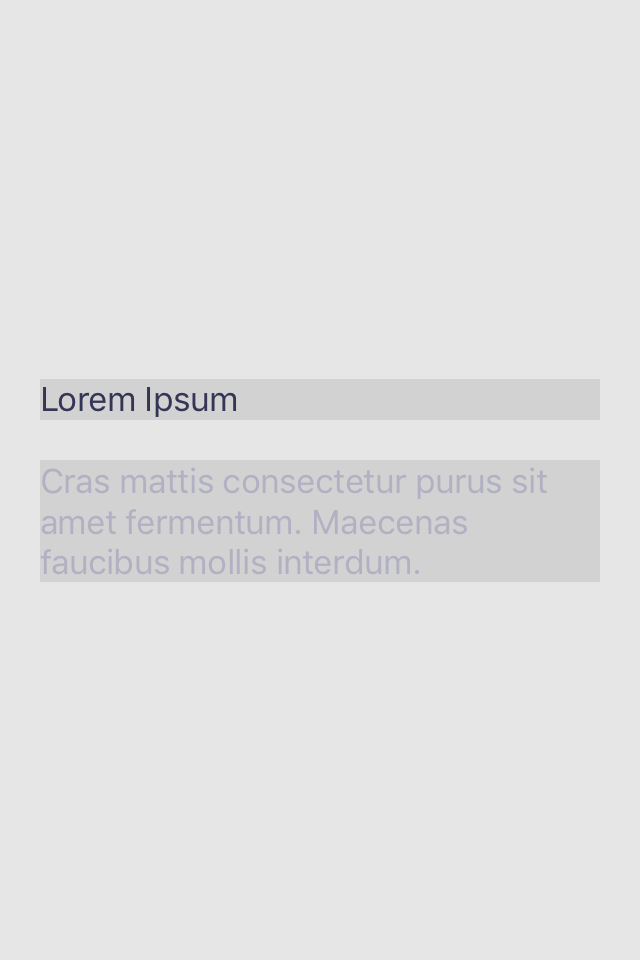
putRows()hfillvfit is used to fill width and size to fit height for both labels. vput is used to center group of labels
titleLabel.lx.hfillvfit(inset: 20)
detailsLabel.lx.hfillvfit(inset: 20)
self.lx.vput(
Flex(),
Fix(titleLabel),
Fix(20),
Fix(detailsLabel),
Flex()
)AL Battle
let topSize = CGSize(width: 60, height: 60)
let topPadding: CGFloat = 10
let topLeftRightPadding: CGFloat = 20
topView1.lx.set(size: topSize)
.alignTop(topPadding)
topView2.lx.set(size: topSize)
.alignTop(topPadding)
topView3.lx.set(size: topSize)
.alignTop(topPadding)
lx.hput(
Fix(topLeftRightPadding),
Fix(topView1),
Flex(),
Fix(topView2),
Flex(),
Fix(topView3),
Fix(topLeftRightPadding)
)
let cardSize = bounds.width < bounds.height ? CGSize(width: 80, height: 120) : CGSize(width: 60, height: 90)
let cardLeftRightPadding: CGFloat = 25
cardView1.lx.set(size: cardSize)
cardView2.lx.set(size: cardSize)
cardView3.lx.set(size: cardSize)
cardView4.lx.set(size: cardSize)
if bounds.width < bounds.height {
cardView1.lx.vcenter()
cardView2.lx.vcenter()
lx.hput(
Fix(cardLeftRightPadding),
Fix(cardView1),
Flex(),
Fix(cardView2),
Fix(cardLeftRightPadding)
)
cardView3.lx.hcenter()
cardView4.lx.hcenter()
lx.vput(
Flex(),
Fix(cardView3),
Fix(60),
Fix(cardView4),
Flex()
)
} else {
cardView1.lx.vcenter()
cardView2.lx.vcenter()
cardView3.lx.vcenter()
cardView4.lx.vcenter()
lx.hput(
Fix(cardLeftRightPadding),
Fix(cardView1),
Flex(),
Fix(cardView3),
Flex(),
Fix(cardView4),
Flex(),
Fix(cardView2),
Fix(cardLeftRightPadding)
)
}
bottomView.lx.set(height: 40)
.hfill(inset: 100)
.alignBottom(15)Derivative from put operation. Accepts only Fix. Modifies parent frame to wrap childs. Method to perform selfsizing.
let maxLabelsWidth: CGFloat = 250
title.lx.sizeToFit(width: .value(maxLabelsWidth), height: .max)
details.lx.sizeToFit(width: .value(maxLabelsWidth), height: .max)
container.lx.hwrap(
Fix(10),
Fix([title, details], .max), //fixing for view with greatest width
Fix(10)
)
container.lx.vwrap(
Fix(10),
Fix(title),
Fix(10),
Fix(details),
Fix(10)
)
container.lx.center()Viewport can be defined using anchors of any childview, or nil anchor if using superview edges
blueView.lx.hfill(inset: 20)
self.lx.vput(
Fix(20),
Fix(blueView, 20),
Fix(20),
Flex(greenView),
Fix(20)
)
greenView.lx.alignLeft(20)
.set(width: 20)
self.lx.inViewport(topAnchor: blueView.lx.bottomAnchor.insettedBy(5), leftAnchor: greenView.lx.rightAnchor.insettedBy(5), bottomAnchor: self.lx.bottomAnchor.insettedBy(-5), rightAnchor: self.lx.rightAnchor.insettedBy(-5)) {
redView.lx.fill()
heartView.lx.bottomAnchor.follow(self.lx.bottomAnchor)
heartView.lx.rightAnchor.follow(self.lx.rightAnchor)
}