A RobotWar - inspired programming game
jobotwar builds upon the concept of the classic Robot War programming game. See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/RobotWar for information on the classic game.
The game takes place on a plane of 640x480 pixels, where up to twelve robots are fighting each other. Test your programming skills using either jobotwar's new state-based programming language, or a language that is very close to the one used by the classic Robot War game.
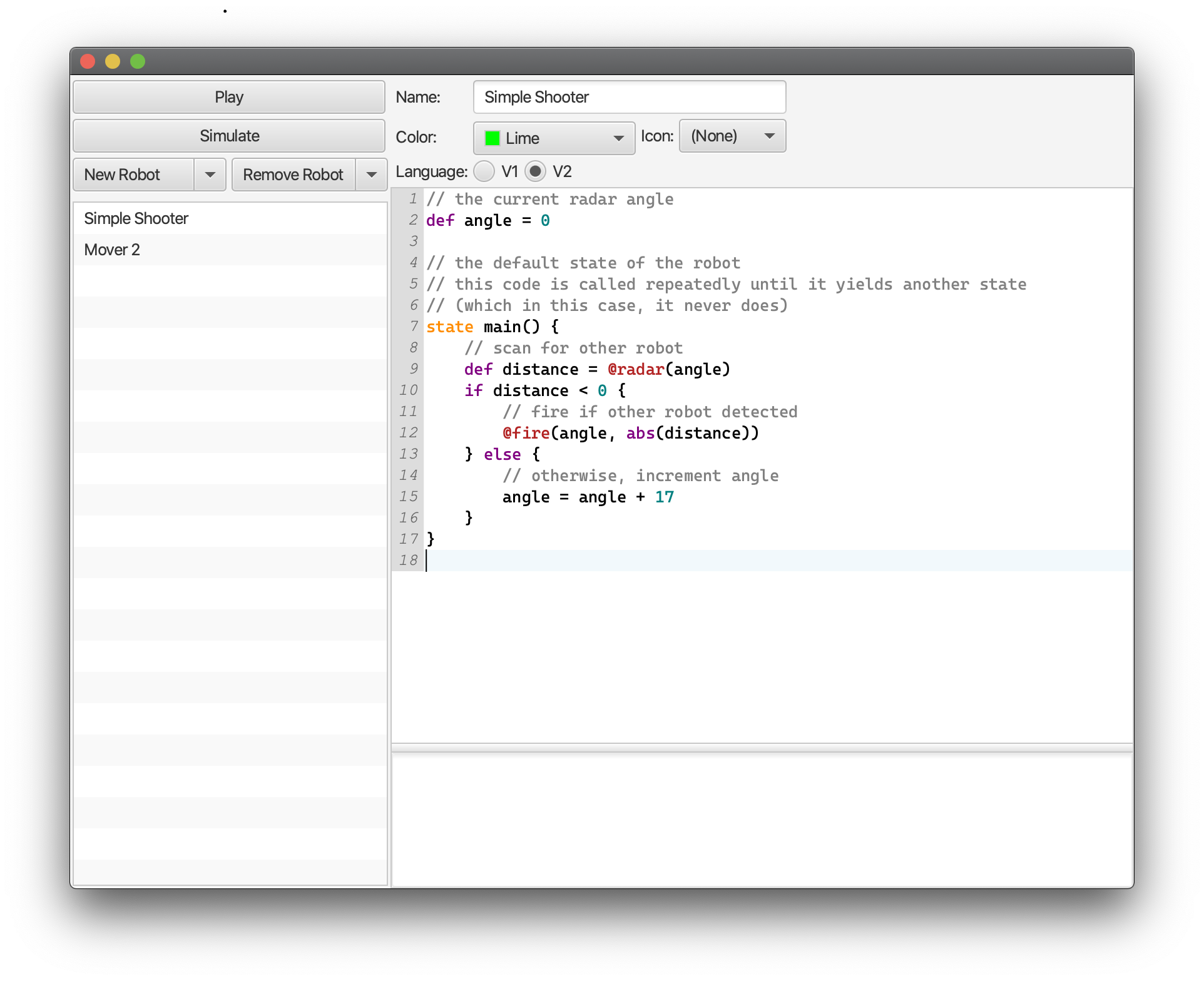
This screenshot shows jobotwar's V2 language:
And here is some game play footage:
The game includes implementations of classic Robot Wars and crobots programs like Mover, Shooter and Corner, plus it adds many fresh designs as samples.
The game is written in Java 13, using ANTLR and JavaFX.
Here are some code samples to get started with programming robots:
// robot 'Bumblebee'
// main is the default state. programs start in this state
state main() {
// randomly choose a new destination
def destX = @random(40, 600)
def destY = @random(40, 440)
// print the new destination
@log(destX)
@log(destY)
// set the speed
@speed(destX - @x(), destY - @y())
// and change state to 'move'
yield move(destX, destY)
}
// the moving state. yields as soon as the destination has been reached.
state move(destX, destY) {
// calculate distance from destination
def dx = destX - @x()
def dy = destY - @y()
if sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy) < 40 {
// if distance if less than 40 pixels, change state to 'main'
yield main()
}
}
As you can see, the jobotwar language is state based. You define states by declaring code blocks, which are then executed repeatedly by the jobotwar runtime. You change to another state by using the keyword yield.
States can receive arguments, which cannot be changed while the program remains in this state (see destX and destY in the preceding sample).
Functions prefixed with @ are robot methods, which manipulate or monitor the controlled robot.
| Read | Write | Description |
|---|---|---|
@x() |
- | Gets the current x-position of the robot |
@y() |
- | Gets the current y-position of the robot |
@speedX() |
@speedX(value) |
Gets or sets the speed in x-direction in the range -500 to +500 |
@speedY() |
@speedY(value) |
Gets or sets the speed in y-direction in the range -500 to +500 |
| - | @speed(x, y) |
Sets the speed in x-direction and in y-direction |
| - | @log(value) |
Writes value to the program's log console |
@fire() |
@fire(angle, distance) |
Gets the state of the robot's gun (0 if ready) or fires a shot into direction angle to explode in the given distance |
@radar() |
@radar(angle) |
Gets the result of the last radar scan or sends a radar beam into direction angle and returns the result: Either the distance to a wall or the negative distance to a robot. See the sample below. |
@random() |
- | Gets a random floating point value between 0 and 1 |
@random(max) |
- | Gets a random floating point value between 0 and max |
@random(min, max) |
- | Gets a random floating point value between min and max. |
@damage() |
- | Gets the current health state of the robot in the range 0 to 100, where 0 means dead |
// robot 'Shooter'
// serves as radar sample
def angle
state main() {
def distance = @radar(angle)
if distance < 0 {
// robot hit
@fire(angle, abs(distance))
} else {
// wall hit
angle = angle + 17
}
}
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
abs(v) |
The absolute value of v | |
tan(v) |
The tangens of v. v is in degrees | |
sin(v) |
The sine of v. v is in degrees | |
cos(v) |
The cosine of v. v is in degrees | |
atan(v) |
The arc tangens of v in degrees | |
asin(v) |
The arc sine of v in degrees | |
acos(v) |
The arc cosine of v in degrees | |
sqrt(v) |
The square root of v | |
trunc(v) |
The integer part of v, e.g. | trunc(12.5) == 12 // true |
sign(v) |
The signum of v (-1, 0 or 1) | |
min(a, b) |
The smaller value of a and b | |
max(a, b) |
The greater value of a and b | |
hypot(x, y) |
The square root of the sum of x squared and y squared | |
atan2(x, y) |
The arc tangens of y divided by x |
The only supported data type is 64bit floating point.
The syntax is similar to Go: blocks require braces, semicolons and parenthesis are optional.
Use def to declare variables or functions, state to declare states.
The supported control flow mechanisms include if else and the while loop. return returns a value from a function, yield returns from a state, changing to a new state.
To go further, have a look at the samples: https://github.com/smackem/jobotwar/tree/master/src/site
All .jobot files in this folder can be loaded into the game.
