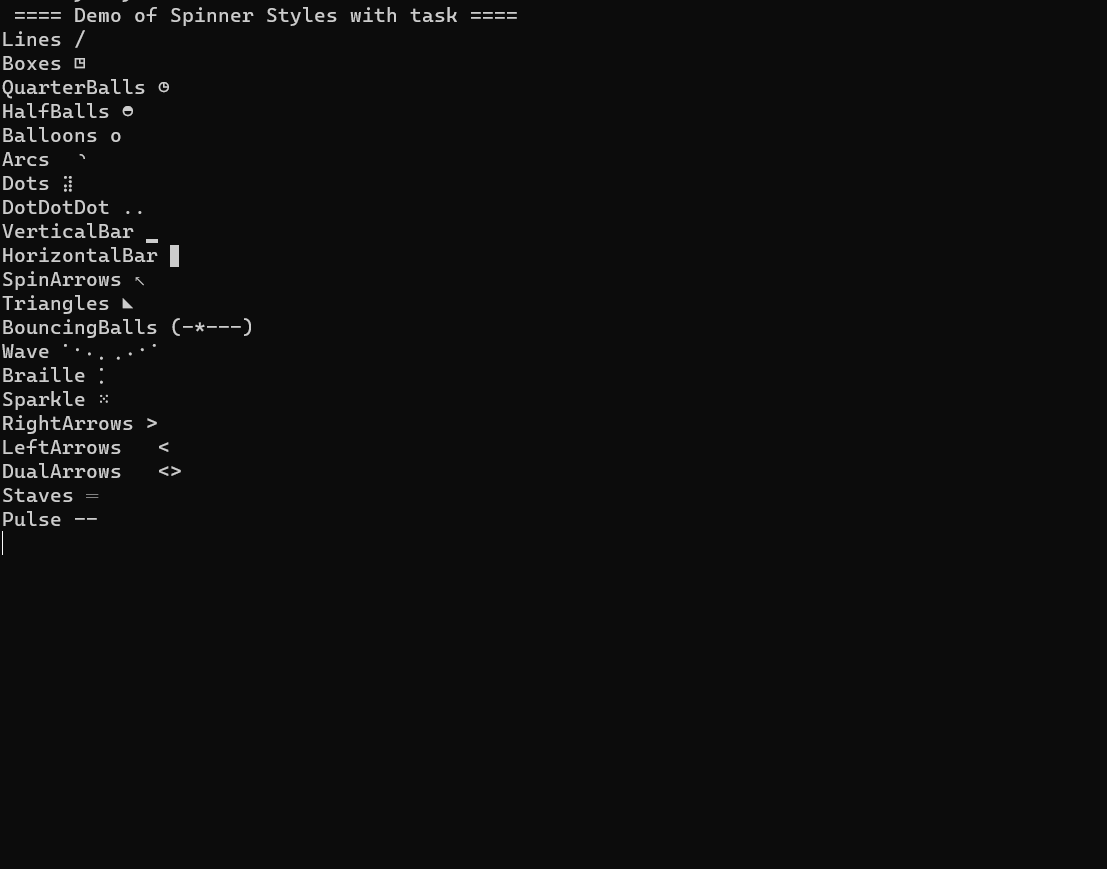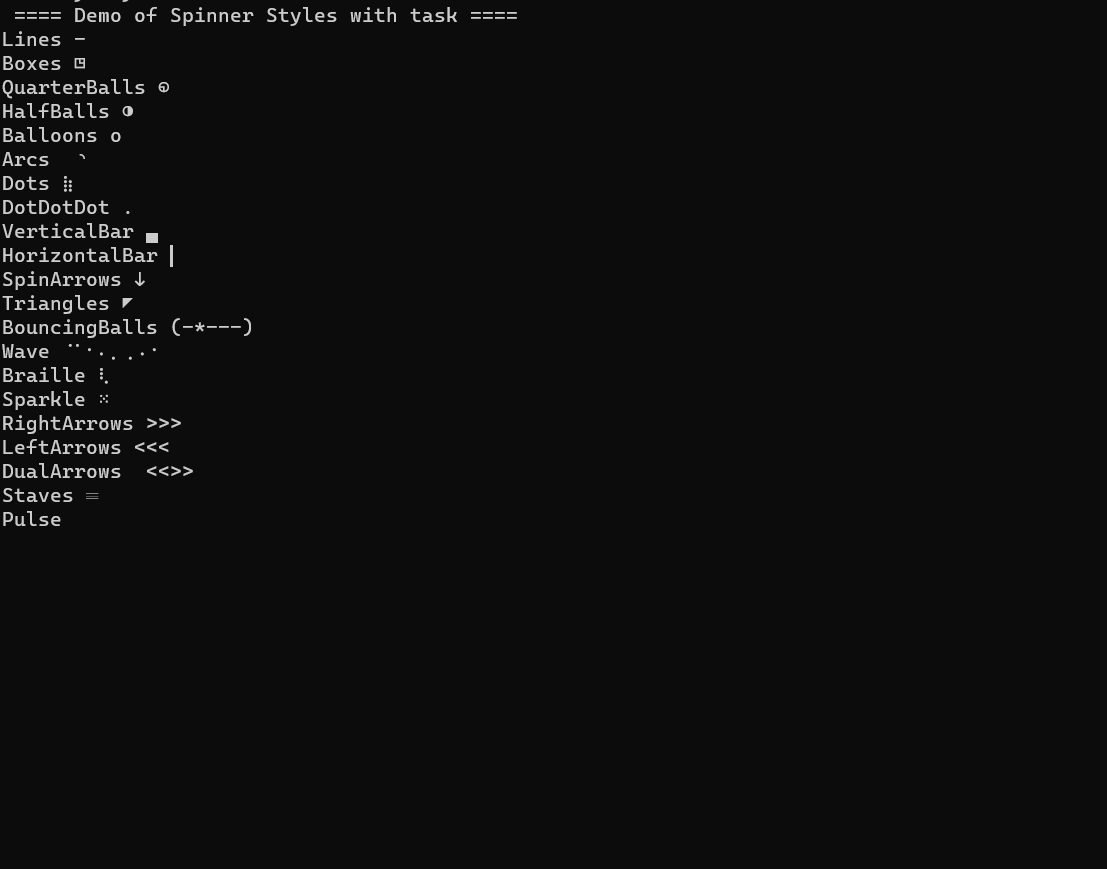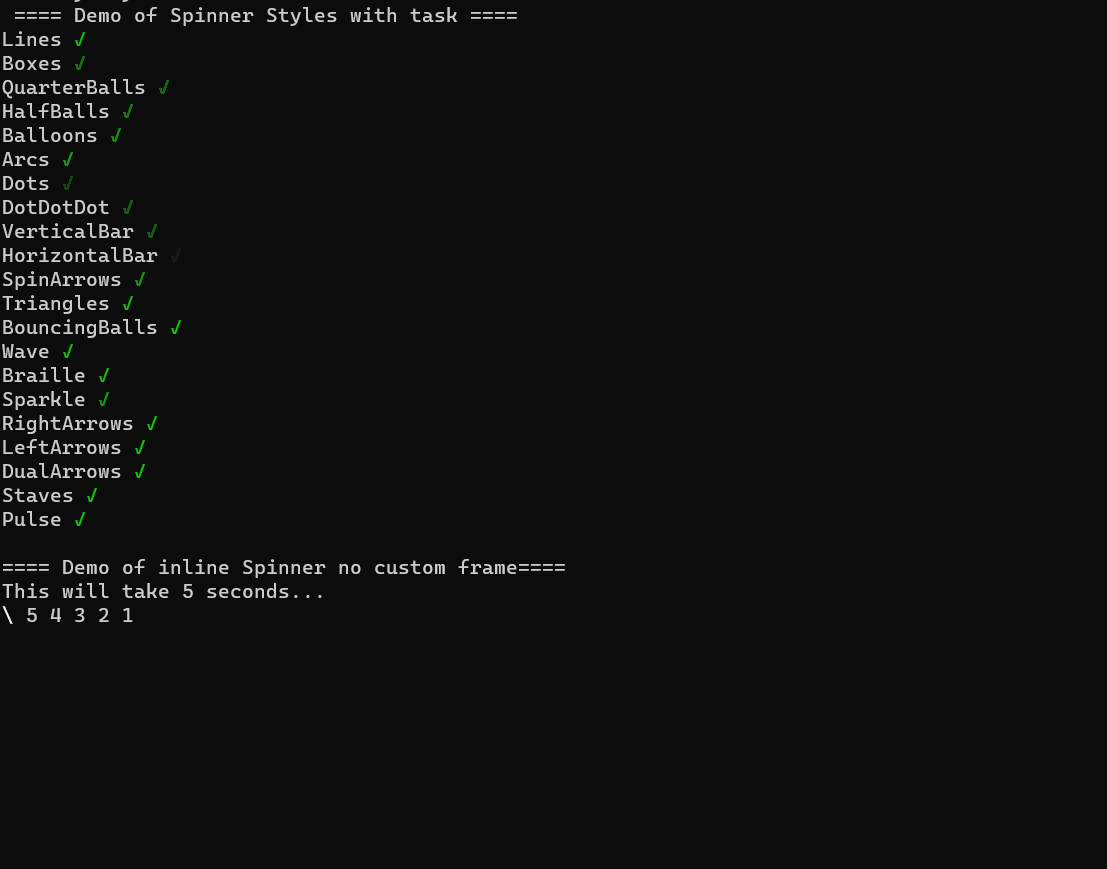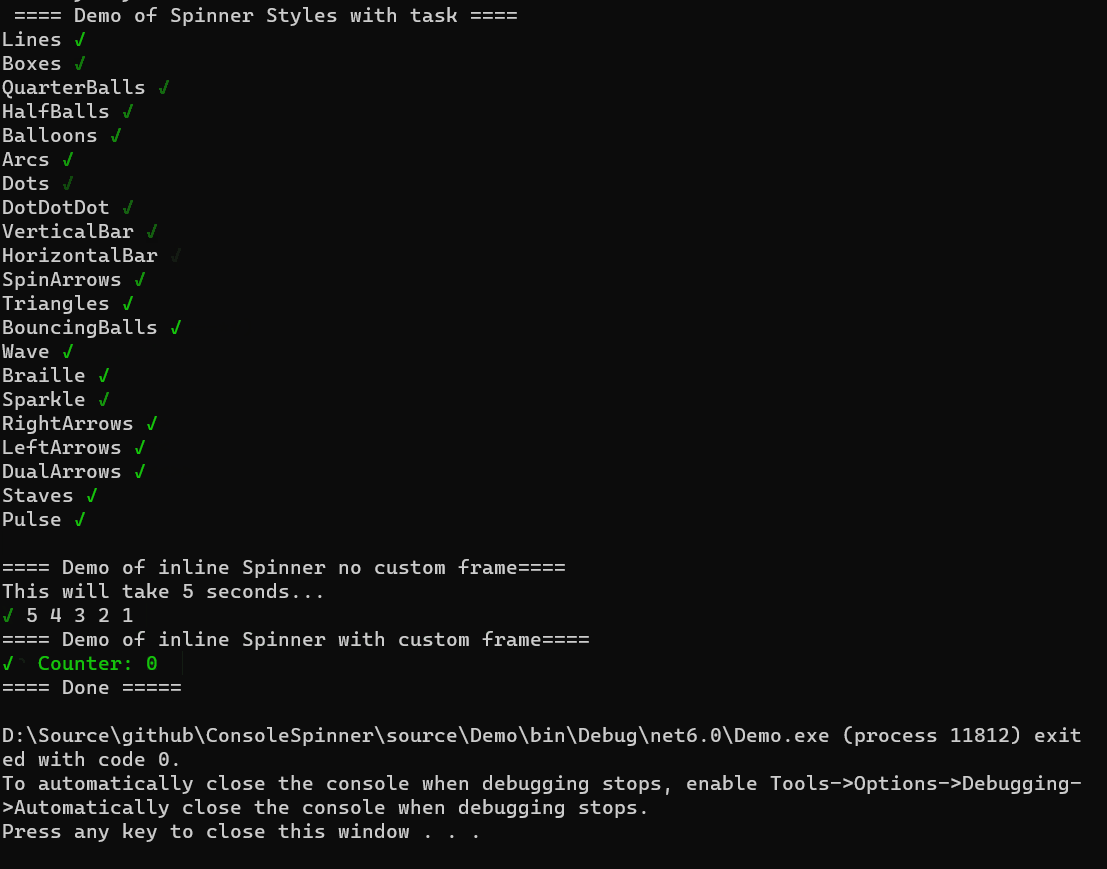
This library is a simple console spinner for .NET Core Console applications. It can be used for synchronous blocks of code or async tasks.
The library adds a new helper function ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner(). This function returns an IDisposable that will display the spinner until it is disposed,
or you can pass in a task and it will display the spinner until the task is complete.
This allows the spinner to be used in two ways, with long running synchronous code or with async tasks.
With synchronous code you can simply wrap the code in a using statement and the spinner will be displayed until the code block is complete.
using(_ = ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner())
{
// long running non-task based code
}With async tasks you simply pass the task into ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner() and it will animate the spinner until the task is complete.
var task = Task.Delay(delay);
lock (Console.Out)
{
ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner(task);
Console.WriteLine();
}You can control the behavior of the spinner by passing in a SpinnerOptions object to ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner().
You can pass in a different animation style by passing in the Options to ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner().
using(_ = ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner(new SpinnerOptions() { Animation = Animations.Args }))
{
// long running non-task based code
}Predefined animations are: The spinner can be displayed in the following styles:
| Style | Description |
|---|---|
| Animations.Lines | Displays a line spinner |
| Animations.Dots | Displays a dot spinner |
| Animations.Boxes | Displays a box spinner |
| Animations.Arrows | Displays an arrow spinner |
| Animations.VerticalBars | Displays a vertical bar spinner |
| Animations.HorizontalBars | Displays a horizontal bar spinner |
| Animations.Triangles | Displays a triangle spinner |
| Animations.QuarterBalls | Displays a quarter ball spinner |
| Animations.HalfBalls | Displays a half ball spinner |
| Animations.Balloons | Displays a balloon spinner |
| Animations.Arcs | Displays an arc spinner |
| Animations.BouncingBalls | Displays a bouncing ball spinner |
| Animations.Wave | Displays a wave spinner |
| Animations.Braille | Displays a braille spinner |
You can also defined your own animations by passing in a array of equal width strings. The animation will cycle through the strings.
using(var _ = ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner(new SpinnerOptions() { Animation= new [] { "` ", "`` ", "```", " ``", " `", " "}))
{
...long running code..
}The options.Theme is an array of ConsoleColors which will be used for each frame. The spinner will cycle through the colors.
using(_ = ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner(new SpinnerOptions() { Theme = Themes.RedWhiteBlue }))
{
// long running non-task based code
}Delay controls how many ms between each frame of the animation. The default is 100ms.
These options all you to define the string for success, failure, and the color for each.
You can customize the spinner by passing in a CustomFrame function. The custom frame function takes in the current frame, and a boolean for whether the task is done or not. It returns a string that represents the frame.
Arguments are
- frame - the current frame of the animation
- done - a boolean indicating whether the task is done or not Return:
- A formatted string representing the frame.
NOTE: The width of the output and position of the frame in the output needs to be consistent for the animation to look correct.
i = 10;
using (var _ = ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner(new SpinnerOptions() { CustomFrame: (frame, done) => $"{frame} Counter: {i} " }))
{
for (; i > 0; i--)
{
// simulate doing stuff...
await Task.Delay(1000);
}
}This allows you to have the spinner act like a progress bar.
The animation is asynchronously using Console.SetPosition to position the cursor to the location of the animation so that it can change it.
While there are active spinners you should put a lock(Console.Out) around any Console output API call, preventing any background animations from interacting with the current cursor position.
Example:
using (var _ = ConsoleEx.WriteSpinner())
{
...long running code..
// lock writing to the console while a spinner is potentially running
lock(Console.Out)
Console.Write(...);
...long running code..
}