Given a string containing digits from
2-9inclusive, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent.A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below. Note that 1 does not map to any letters.
Example:
Input: "23" Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
代码:
class Solution(object):
def letterCombinations(self, digits):
"""
:type digits: str
:rtype: List[str]
"""
letterMap = [" ","","abc","def","ghi","jkl","mno","pqrs","tuv","wxyz"]
res = []
def findCombination(digits, index, s):
if index == len(digits):
res.append(s)
return
ch = digits[index]
ch_letters = letterMap[ord(ch)-ord('0')]
for i in range(len(ch_letters)):
findCombination(digits, index+1, s+ch_letters[i])
return
if digits == "":
return []
findCombination(digits, 0, "")
return resGiven n pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
For example, given n = 3, a solution set is:
[ "((()))", "(()())", "(())()", "()(())", "()()()" ]
思路:
- 要么加左括号,要么加右括号
- 递归终止:右括号个数已经等于n,证明n对括号已经匹配组合完成,把
cur_str添加到res中,直接return. - 加左括号的条件:当左括号个数小于n。
- 加右括号的条件:当右括号的个数小于左括号。
class Solution(object):
def generateParenthesis(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[str]
"""
res = []
def dfs(cur_str, res, n, lp, rp):#lp: 左括号个数, rp: 右括号个数
if rp == n:
res.append(cur_str)
return
if lp < n:
# add '('
dfs(cur_str+"(", res, n, lp+1, rp)
if rp < lp:
# only the num of ')'< '(', we can add ')'
dfs(cur_str+")", res, n, lp, rp+1)
dfs("",res,n,0,0)
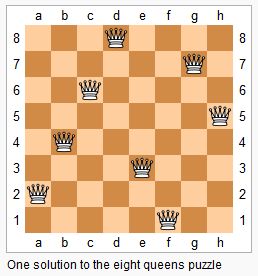
return resThe n-queens puzzle is the problem of placing n queens on an n×n chessboard such that no two queens attack each other.
Given an integer n, return all distinct solutions to the n-queens puzzle.
Each solution contains a distinct board configuration of the n-queens' placement, where
'Q'and'.'both indicate a queen and an empty space respectively.
参考:回溯算法详解
code:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> res;
vector<vector<string>> solveNQueens(int n) {
vector<string> board(n, string(n,'.'));
backtrack(board, 0);
return res;
}
void backtrack(vector<string>& board, int row){
// 触发结束条件
if (row == board.size()){
res.push_back(board);
return;
}
int n = board[row].size();
for (int col = 0; col < n; col++){
if (!isValid(board, row, col))
continue;
board[row][col] = 'Q';
backtrack(board, row+1);
board[row][col] = '.';
}
}
// check if conflict
bool isValid(vector<string>& board, int row, int col){
int N = board.size();
// check column first
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
if (board[i][col] == 'Q')
return false;
}
// check 右上方
for (int i = row - 1, j = col + 1; i>=0 && j<N; i--, j++) {
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
return false;
}
// check 左上方
for (int i = row - 1, j = col - 1; i>=0 && j>=0; i--, j--){
if (board[i][j] == 'Q')
return false;
}
return true;
}
};给定一个Distinct的数组求全排列
Given a collection of distinct integers, return all possible permutations.
Example:
Input: [1,2,3] Output: [ [1,2,3], [1,3,2], [2,1,3], [2,3,1], [3,1,2], [3,2,1] ]
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
LinkedList<Integer> route = new LinkedList<>();
backtrack(nums, route);
return res;
}
public void backtrack(int[] nums, LinkedList<Integer> route) {
if (route.size() == nums.length) {
res.add(new LinkedList(route));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (route.contains(nums[i]))
continue;
route.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums, route);
route.removeLast();
}
}
}给定一个有重复的数组求全排列
Given a collection of numbers that might contain duplicates, return all possible unique permutations.
Example:
Input: [1,1,2] Output: [ [1,1,2], [1,2,1], [2,1,1] ]
- 先要对数组排序,目的是为了处理duplicate number
- 设置 visited[] 记录访问情况
- 回溯中的if条件有二:
- visited[i] == true
- 当前数字不是数组(排序后)中第一位,且前一个数字未被访问(因为回溯会在每次循环时,对 visited[i] 先 true 后 false,如果当前数字与它前一个相同,且未被访问,例如 [1, 1, 2],当第一次进行循环时,先对第一个1进行遍历,包括它在内的三个数字会被依次访问且添加到路径中,此时第一个1的循环结束时,来到 res.add() 的操作,return 后再对第二个1重复跟第一个1一样的操作,但需要注意的是,每次回溯都会进到for循环的 i = 0 的地方,也就是每次回溯都会经过第一个1,如何保证不会重复添加?这里体现了 visited 的作用,最外层的循环只有三个数,1,1,2,第一个1走完所有的分支后,它的visited就从 true 变成了 false,所以第二个1开始走,发现前一个1的 visited 是 false 的时候,就说明前一个是重复的数,不需要添加。可以画递归树来理解!
class Solution {
private List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums); // first sort nums;
LinkedList<Integer> route = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[nums.length];
backtrack(nums, visited, route);
return res;
}
private void backtrack(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, LinkedList<Integer> route) {
if (route.size() == nums.length) {
res.add(new LinkedList<>(route));
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (visited[i] == true)
continue;
if (i > 0 && visited[i - 1] == false && nums[i] == nums[i - 1]) {
// meet duplicate number
continue;
}
visited[i] = true;
route.add(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums, visited, route);
visited[i] = false;
route.removeLast();
}
}
}https://leetcode.com/problems/iterator-for-combination/
Design an Iterator class, which has:
- A constructor that takes a string
charactersof sorted distinct lowercase English letters and a numbercombinationLengthas arguments.- A function next() that returns the next combination of length
combinationLengthin lexicographical order.- A function hasNext() that returns
Trueif and only if there exists a next combination.Example:
CombinationIterator iterator = new CombinationIterator("abc", 2); // creates the iterator. iterator.next(); // returns "ab" iterator.hasNext(); // returns true iterator.next(); // returns "ac" iterator.hasNext(); // returns true iterator.next(); // returns "bc" iterator.hasNext(); // returns false
class CombinationIterator:
def __init__(self, characters: str, combinationLength: int):
self.combinations = []
def backtrack(combination, i):
if len(combination) == combinationLength:
self.combinations.append(combination)
elif len(combination) < combinationLength:
for j in range(i + 1, len(characters)):
backtrack(combination + characters[j], j)
for i in range(len(characters)):
backtrack(characters[i], i)
def next(self) -> str:
return self.combinations.pop(0)
def hasNext(self) -> bool:
if self.combinations:
return True
return False