## Environment Details
1.Branch Name : Dev-Migration
2.URL : https://dev.cclproducts.com
3.Database Used : CCLDEVDB
4.Purpose : DEVELOPMENT / DATA MIGRATION
Following are the technical details which are being used to develop the serverless web application.
### Software and Hardware List used in the project
| No | Software required |
| -------- | ------------------------------------|
| 1 | React JS, Go Lang |
| 2 | aws-lambda-go SDK |
| 3 | AWS Services |
The user interface is developed using React Js
The server side is developed using GoLang programming language
- AWS Cognito service is used to create application user pool configuration
- AWS Lambda functions are used to deploy the backend APIs with different endpoints.
- AWS API Gateway is used to authenticate and provide access to external clients to connect to the application.
- AWS S3 Bucket storage are the containers for data storage and configured website endpoint. Learn more @ http://ccpl-webapp.s3-website.ap-south-1.amazonaws.com
- Build code : env GOOS=linux go build -ldflags="-s -w" -o bin/fileName fileName.go
- Zip Build File : zip fileName.zip fileName
STEP 1 : Install the Go Programming Language NOTE: To run Go using AWS Lambda, you will need to compile any Go binaries on Amazon Linux to ensure compatibility. In your Amazon Linux environment, install Go with the following commands:
sudo yum -y update
sudo yum -y install go
Once installed, configure your $GOPATH environment variable. $GOPATH is used by Go to determine where dependencies are located. To set up $GOPATH, create a “go” folder in your home directory:
mkdir ~/go
STEP 2 : Create your Go Project Create a directory to house your Go project:
mkdir ~/go_helloworld cd ~/go_helloworld
Once the directory has been made, we can create our Go file. In order for this script to be “buildable” by Go, we need to source the dependancies of the script. As we only have one dependancy, we can get it using the following command:
go get "github.com/aws/aws-lambda-go/lambda"
This dependancy will be saved locally in the $GOPATH, so that it does not need to be downloaded again. Once done, we can next build the project. To build the Go binary, run:
go build helloworld.go Go will quietly create a binary file within the same directory. This is the file that Lambda will use to execute. Next, archive the file into a .zip for deployment to Lambda:
zip helloworld.zip helloworld STEP 3: Create an IAM Role for your Lambda function (Optional)
This is only necessary if you don’t already have an IAM Role created that grants Lambda the ability to assume it.
If we don’t already have an IAM role for Lambda, we’ll need to create one in order for the Lambda function to be able to log outputs to Cloudwatch. By default, it is required that Lambda functions have a valid IAM role configured.
Create a file called “lambda-trust-policy.json” and paste the contents of the cat statement into the file. Once done, use the following commands to create an IAM role for Lambda and attach some basic permissions to the role.
Once done, we should have a new IAM role created called “lambda-basic-execution”. We can use the same CLI to verify that the role was created by doing a GetRole command:
$ aws iam get-role --role-name lambda-basic-executio
STEP 4: Create your Lambda function (via CLI or AWS Console)
The ZIP file that we created in Step 2 can be used to deploy the Go program to Lambda. The name of the file “helloworld” will be used as the Lambda handler.
To create a function via the AWS CLI, you can use the following command:
aws lambda create-function
--function-name helloworld_go
--zip-file fileb://helloworld.zip
--handler helloworld
--runtime go1.x --role "arn:aws:iam::<YOUR_ACCOUNT_ID>:role/lambda-basic-execution"
Note that the above execution role needs to be set to a valid role that is assumable by Lambda. To invoke the function via the AWS CLI, you can use the following command:
aws lambda invoke
--function-name helloworld_go
--invocation-type "RequestResponse"
Response.txt
A new file called “response.txt” should be created in the directory. Reading the file, should contain “Hello from Go!”. This process can also be done via the Console by creating a Go Lambda function and uploading the ZIP as a deployment package.
To install the Gin package, you need to install Go and set your Go workspace first.
STEP 1: GO DOWNLOAD https://go.dev/dl/go1.17.5.windows-amd64.msi
STEP 2 : GO INTALL
1.Open the MSI file you downloaded and follow the prompts to install Go. By default, the installer will install Go to Program Files or Program Files (x86). You can change the location as needed. After installing, you will need to close and reopen any open command prompts so that changes to the environment made by the installer are reflected at the command prompt.
2.Verify that you've installed Go.
In Windows, click the Start menu. In the menu's search box, type cmd, then press the Enter key.
3.In the Command Prompt window that appears, type the following command: $ go version
4.Confirm that the command prints the installed version of Go.
STEP 3: Open a Terminal or Command prompt and Create a Directory anywhere and Open this Directory with any Text Editor(Visual Studio Code) Now create a Mode file inside your newly created Directory with the following Command: $ go mod init root Now Create your root module name using $ touch root.go
STEP 4: Then you can use the below Go command in the browser $ go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
Paste the command given below $ go get -u github.com/gin-gonic/gin
In the cmd and hit enter , Which downloads the Necessary Files
STEP 5: Write the code in the terminal in the root Module and Save the file Use this URL http://localhost:8080 and go to the browser and use this URL and must Run the Web Server using $ run . in the terminal Now go to the browser and reload the URL and you will see the message
WHAT IS GOLANG ? Go language is a statically typed, compiled programming language designed at Google by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson.Go is syntactically similar to C, but with memory safety, garbage collection, structural typing, and CSP-style concurrency.
GOLANG SETUP FOR WINDOWS :
1.GO DOWNLOAD : Click the button below to download the Go installer. https://go.dev/dl/go1.17.5.windows-amd64.msi
-
GO INSTALL:
-
Open the MSI file you downloaded and follow the prompts to install Go. By default, the installer will install Go to Program Files or Program Files. You can change the location as needed. After installing, you will need to close and reopen any open command prompts so that changes to the environment made by the installer are reflected at the command prompt.
2.Verify that you've installed Go.
1.In Windows, click the Start menu. 2.In the menu's search box, type cmd, then press the Enter key. 3.In the Command Prompt window that appears, type the following command: $ go version
The output after entering go version should look like this:
4.Confirm that the command prints the installed version of Go.
3.CREATING YOUR GO WORKPLACE:
First, confirm your Go binaries: go to your computer’s Control Panel, then to System and Security > System > Advanced system settings, and on the left-hand pane click the Advanced tab. Then click on Environmental Variables on the bottom-right-hand side. Ensure Path under System Variables has the “C:\Go\bin” variable in it. Then create your Go work-space. This will be in a separate and new folder from where the Go installation files are saved. For example, your G installation files were saved under the path C:\Go and you are creating your Go work-space under C:\Projects\Go
In your new Go work-space folder, set up three new folders:
4 . CREATE THE GOPATH ENVIRONMENT VARIABLE:
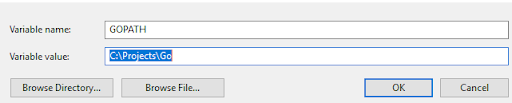
Create the GOPATH variable and reference your newly-created Go work-space. Go back to your Control Panel and navigate to System and then Environmental Variables. Then under System Variables click on New.
Next to Variable Name, enter “GOPATH,” and next to Variable Value enter “C:\Projects\Go”
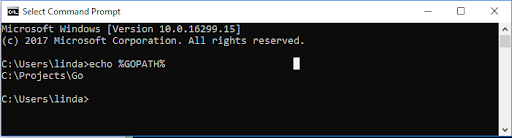
To check that your path has been set correctly, enter “echo %GOPATH%” on the command line.
5 . TEST AND ENSURE:
Now you’re ready to verify that all is working correctly by opening the command line and typing:
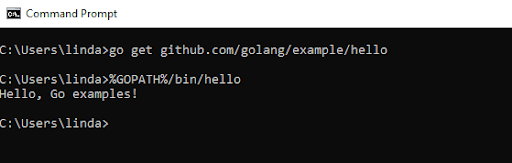
go get github.com/golang/example/hello
Wait for the code to be entirely implemented (this could take a few seconds), then enter in the following in the command line:
%GOPATH%/bin/hello
If the installation was successful, you should get the following return message:
“Hello, Go examples!”
-
Get started with Hello, World. Open a command prompt and cd to your home directory. On Windows:
cd %HOMEPATH%
2.Create a hello directory for your first Go source code. For example, use the following commands:
mkdir hello
cd hello
3.Enable dependency tracking for your code.
When your code imports packages contained in other modules, you manage those dependencies through your code's own module. That module is defined by a go.mod file that tracks the modules that provide those packages. That go.mod file stays with your code, including in your source code repository. To enable dependency tracking for your code by creating a go.mod file, run the go mod init command, giving it the name of the module your code will be in. The name is the module's module path. In actual development, the module path will typically be the repository location where your source code will be kept. For example, the module path might be github.com/mymodule. If you plan to publish your module for others to use, the module path must be a location from which Go tools can download your module. For more about naming a module with a module path, see Managing dependencies. For the purposes of this tutorial, just use example/hello. $ go mod init example/hello go: creating new go.mod: module example/hello
4.In your text editor, create a file hello.go in which to write your code.
- Write the code into your hello.go file and save the file.
6.Run your code to see the greeting. $ go run . Hello, World! The go run command is one of many go commands you'll use to get things done with Go. Use the following command to get a list of the others: $ go help