@[TOC](基于java swing的TCP数据传输)
一不小心在维基上抄太多了,最近在练英语,瞎翻译容易上瘾,见谅。。。。
还是先从维基百科上抄一段。然后练练自己的英语翻译
The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) is one of the main protocols of the Internet protocol suite. It originated in the initial network implementation in which it complemented the Internet Protocol (IP). Therefore, the entire suite is commonly referred to as TCP/IP. TCP provides reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of a stream of octets (bytes) between applications running on hosts communicating via an IP network. Major internet applications such as the World Wide Web, email, remote administration, and file transfer rely on TCP, which is part of the Transport Layer of the TCP/IP suite. SSL/TLS often runs on top of TCP. TCP is connection-oriented, and a connection between client and server is established (passive open) before data can be sent. Three-way handshake (active open), retransmission, and error-detection adds to reliability but lengthens latency. Applications that do not require reliable data stream service may use the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), which provides a connectionless datagram service that prioritizes time over reliability. TCP employs network congestion avoidance. However, there are vulnerabilities to TCP including denial of service, connection hijacking, TCP veto, and reset attack. For network security, monitoring, and debugging, TCP traffic can be intercepted and logged with a packet sniffer. Though TCP is a complex protocol, its basic operation has not changed significantly since its first specification. TCP is still dominantly used for the web, i.e. for the HTTP protocol, and later HTTP/2, while not used by latest standard HTTP/3.
传输控制协议(TCP)是主要的网络协议簇中的一个协议。它在开始的网络操作中是用来补充网际协议(IP)的。因此,整个协议簇通常被叫做TCP/IP。对于在主机上运行的可以由IP协议通信的网络应用,TCP提供可靠的、有序的和可检错的==字节流==传输。像一些主要的网络应用,万维网、email、远程管理、文件传输都依赖于TCP协议。因此它也是TCP/IP簇传输层的的一部分。SSL(加密套接字协议层)/TLS(安全传输层协议)通常是运行于TCP协议之上的。 TCP是==面向连接==的,在数据传输之前,服务器和客服端之间的连接必须建立。它还加有==三次握手==、重传和错误检测的机制用来保证可靠性,但是会增加延迟时间。不需要可靠的数据流服务的应用通常使用用户数据报协议(UDP),它提供了一种及时性优与可靠性的无连接的数据报服务。TCP可以避免网络拥堵。但是在网络安全、监听和调试方面有些漏洞。TCP的流量可以被截获也可以被包嗅探器记录。 尽管TCP是一个复杂的协议,但是自从它的第一个规范出来以后,它的基本操作没有什么大的更改。TCP协议仍然在web中占有主导地位,也就是它用在HTTP协议,后来用在HTTP/2,但是没有用在最新的HTTP/3。 自己也不是专学计算机网络的,所以其实对TCP了解的也并不算太深,也就是大概知道它是怎么回事吧。它传输时加的头,各个字节代表什么的,想要知道的话可以网上查一下就好。
A network socket is an internal endpoint for sending or receiving data within a node on a computer network. Concretely, it is a representation of this endpoint in networking software (protocol stack), such as an entry in a table (listing communication protocol, destination, status, etc.), and is a form of system resource. The term socket is analogous to physical female connectors, communication between two nodes through a channel being visualized as a cable with two male connectors plugging into sockets at each node. Similarly, the term port (another term for a female connector) is used for external endpoints at a node, and the term socket is also used for an internal endpoint of local inter-process communication (IPC) (not over a network). However, the analogy is limited, as network communication need not be one-to-one or have a dedicated communication channel.
网络套接字是在计算机网络节点中用来发送或者接受数据的内部端点。具体来说,它代表了网络上运行的软件的这个端点(协议栈),就像表中的一个条目(这表中列出了通信的协议、终点、状态等等),它也是系统资源的一种形式。 套接字和现实中的两个母头插口之间的通信比较像,==它利用一个两端都公头的的电缆,通过将两个公头分别插入两个母头来实现通信。== 相似地,端口在网络节点中被用来和外部的端口交流,套接字也可以用来和内部之间的进程通信(不通过网络)。然而,这个必须也有些不恰当,因为网络通信并不需要一对一或者说不需要专门的信道。
A process can refer to a socket using a socket descriptor, a type of handle. A process first requests that the protocol stack create a socket, and the stack returns a descriptor to the process so it can identify the socket. The process then passes the descriptor back to the protocol stack when it wishes to send or receive data using this socket. Unlike ports, sockets are specific to one node; they are local resources and cannot be referred to directly by other nodes. Further, sockets are not necessarily associated with a persistent connection (channel) for communication between two nodes, nor is there necessarily some single other endpoint. For example, a datagram socket can be used for connectionless communication, and a multicast socket can be used to send to multiple nodes. However, in practice for internet communication, sockets are generally used to connect to a specific endpoint and often with a persistent connection.
开始一个进程先需要协议栈创建一个套接字,然后套接字返回给这个进程一个可以识别这个套接字的描述符。当进程想要通过这个套接字发送或者接受数据时,进程就将这个描述符返回给协议栈。和端口不同,每个节点的套接字都不同,它们是本地资源,不可以直接被其他节点引用。另外,套接字不需要用一个持久的连接来进行两个节点之间的通信,也不需要其他的一些单一端点。例如,一个数据包套接字可以进行一个无连接的通信,一个multicast套接字可以给多个节点发送消息。然而,在现实的网络通信中,套接字通常用来连接一个特定的端点,也经常是用持久的连接
A protocol stack, today usually provided by the operating system (rather than as a separate library, for instance), is a set of services that allow processes to communicate over a network using the protocols that the stack implements. The operating system forwards the payload of incoming IP packets to the corresponding application by extracting the socket address information from the IP and transport protocol headers and stripping the headers from the application data.
现在的协议栈一般是由操作系统提供(而不是分离的库),它是允许一系列服务的集合,这些服务允许进程通过实现了栈的协议在网络中通信。通过从IP和传输协议头里提取套接字的地址信息并把消息头从引用数据里剥离出来,操作系统将传来的IP包的有效数据传给相关的应用。
The application programming interface (API) that programs use to communicate with the protocol stack, using network sockets, is called a socket API. Development of application programs that utilize this API is called socket programming or network programming. Internet socket APIs are usually based on the Berkeley sockets standard. In the Berkeley sockets standard, sockets are a form of file descriptor, due to the Unix philosophy that "everything is a file", and the analogies between sockets and files. Both have functions to read, write, open, and close. In practice the differences strain the analogy, and different interfaces (send and receive) are used on a socket. In inter-process communication, each end generally has its own socket.
利用网络套接字用来与协议栈进行通信的应用程序接口(API)被叫做socke API。而利用这个API编程的应用开发叫做套接字编程或者网络编程。因特网套接字API一般是基于伯克利套接字标准的。在伯克利套接字标准中,套接字以一种文件描述符的形式存在,这是因为Unix的哲学是万物皆文件。套接字也可以类比文件这样。它们都有用来读写、打开、关闭的函数。而在实际中,这个类比可能也不太贴切,因为许多不同的接口(接受和发送)都会在一个套接字上使用。在内部进程之间通信时,通常每个进程都会有一个它自己的套接字。
In the standard Internet protocols TCP and UDP, a socket address is the combination of an IP address and a port number, much like one end of a telephone connection is the combination of a phone number and a particular extension. Sockets need not have a source address, for example, for only sending data, but if a program binds a socket to a source address, the socket can be used to receive data sent to that address. Based on this address, Internet sockets deliver incoming data packets to the appropriate application process. Socket often refers specifically to an internet socket or TCP socket. An internet socket is minimally characterized by the following: (1) local socket address, consisting of the local IP address and (for TCP and UDP, but not IP) a port number (2) protocol: A transport protocol, e.g., TCP, UDP, raw IP. This means that (local or remote) endpoints with TCP port 53 and UDP port 53 are distinct sockets, while IP does not have ports. (3)A socket that has been connected to another socket, e.g., during the establishment of a TCP connection, also has a remote socket address.
在标准的因特网TCP和UDP协议里,==一个套接字的地址是IP地址和端口号的结合,== 很像电话连接时的用的是电话号码和分机号码的组合。套接字不需要源地址,例如,仅仅发数据时就是这样,但是如果一个套接字绑定了一个源地址,那么这个套接字就可以用来接受向这个源地址发的数据。基于这个地址,英特网套接字将此刻收到的数据打包到正确的进程中。套接字经常是特别用来指英特网套接字或者TCP套接字。一个因特网套接字可以被简单的描述如下: (1)本地套接字地址,由本地IP地址(对TCP和UDP,但不是IP)和端口号组成。 (2)协议:一种传输协议,例如,TCP,UDP,raw IP,==这意味着端点的TCP端口号53和UDP端口号53是两个不同的端口==,而IP没有端口。 (3)一个已经被另一个端口连接的端口,例如建立了TCP连接的端口,还会有一个远程套接字地址。
下面参见了这位兄弟的博客的一点内容 在TCP和UDP同属于传输层,共同架设在IP层(网络层)之上。而IP层主要负责的是在节点之间(End to End)的数据包传送,这里的节点是一台网络设备,比如计算机。因为IP层只负责把数据送到节点,而不能区分上面的不同应用,所以TCP和UDP协议在其基础上加入了端口的信息,端口于是标识的是一个节点上的一个应用。除了增加端口信息,UPD协议基本就没有对IP层的数据进行任何的处理了。而TCP协议还加入了更加复杂的传输控制,比如滑动的数据发送窗口(Slice Window),以及接收确认和重发机制,以达到数据的可靠传送。不管应用层看到的是怎样一个稳定的TCP数据流,下面传送的都是一个个的IP数据包,需要由TCP协议来进行数据重组。 TCP/IP只是一个协议栈,就像操作系统的运行机制一样,必须要具体实现,同时还要提供对外的操作接口。就像操作系统会提供标准的编程接口,比如Win32编程接口一样,TCP/IP也必须对外提供编程接口,这就是Socket编程接口 ==阐述了TCP/IP和Socket的关系==
这个。。。估计得等一个我精力旺盛的日子了,也可以单独写一个。
下面是实现后的gif。和我最开始的想法基本差不多吧。写两个程序,一个为服务器端一个为客户端。要先运行服务器端,在运行客户端,实现后就是这样的两个窗口:
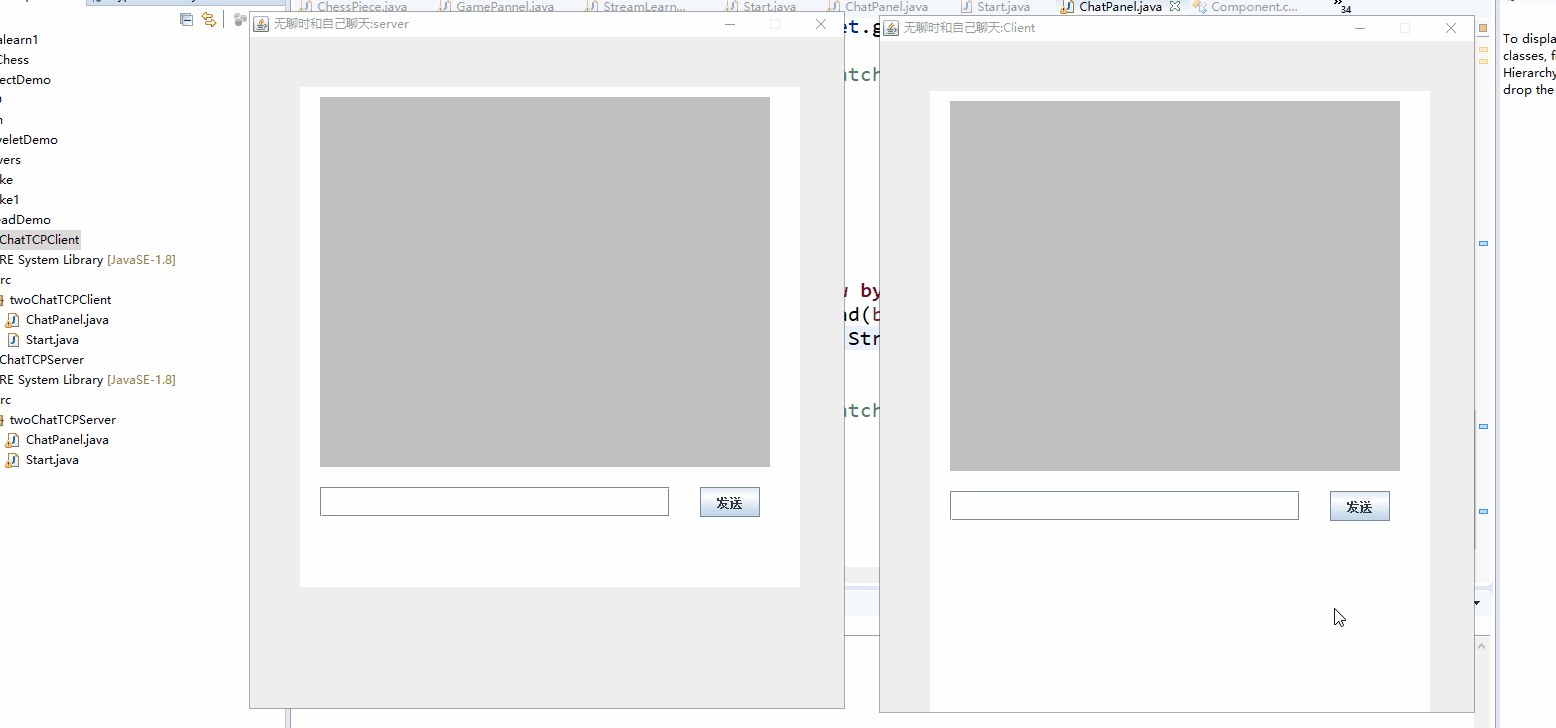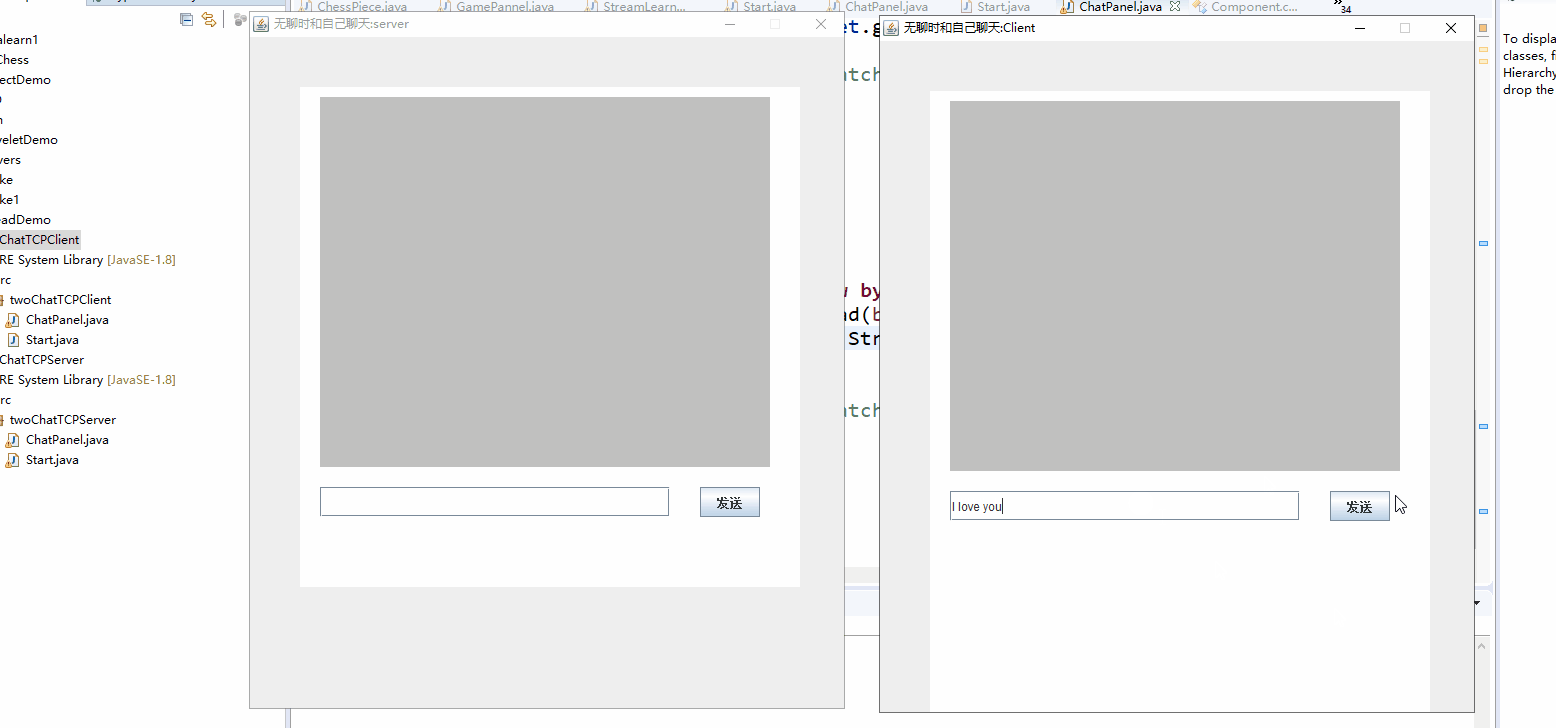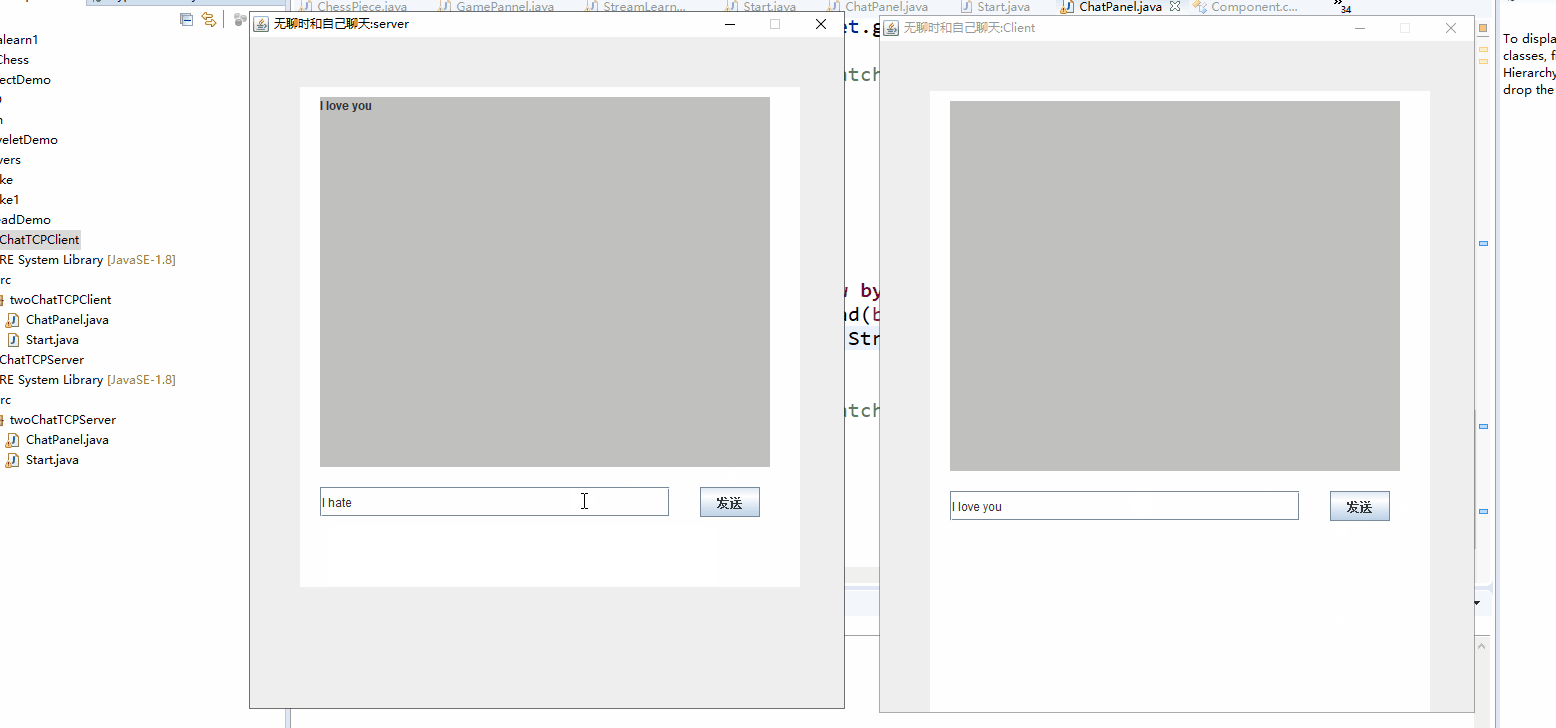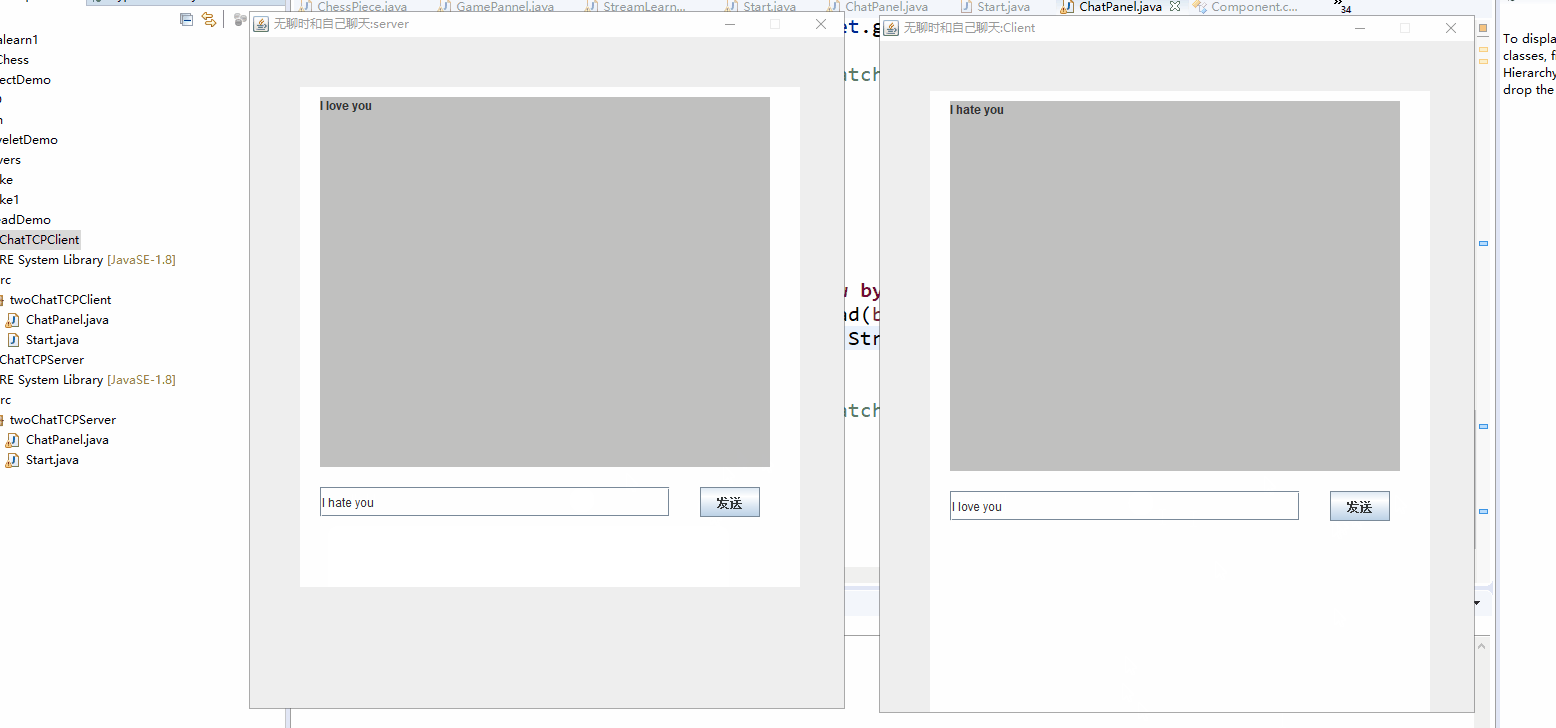
- 点按钮发消息的话可以设置按钮的监听事件,在事件处理函数中来发送消息。
- 接收消息并显示的话,因为这是一个一直持续的过程,不会停止。所以肯定需要一个一直循环的程序来接受消息。当然最好不要main()里面加一个一直不会结束的循环,那我们可以开启一个子线程嘛,在子线程里一直收消息,并把它显示到JLabel上。
服务器端就是有两个类,一个是Start,一个是ChatPanel。
下面是Start类,省略了import和package。就是建了一个JFrame,并将chatPanel的实例添加了进去。并设置了它们基础的设置。注意的地方是最好要自己设置一下布局为null的,不然组件会乱跑的,甚至不会出现。因为默认是上下左右中的布局。
public class Start {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
JFrame frame = new JFrame("无聊时和自己聊天:server");
frame.setBounds(100, 100, 600, 700);
frame.setResizable(false);
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
Container container = frame.getContentPane();
container.setLayout(null);
ChatPanel chatSeverPanel = new ChatPanel();
container.add(chatSeverPanel);
chatSeverPanel.setBounds(50, 50, 500, 500);//这里如果不设置长宽,就不会显示,因为默认长宽为0,0.
}
}看代码的乍一看有点小长哈。稍微分析一下。
- 前面是对一些属性的声明,因为后面会在按钮的点击事件和子线程里都会用到,所以就放在class前面啦。
- 再就是chatPanel的构造函数,里面是对chatPanel的一些设置,背景啊、可见性、布局啊。还有一个
init()方法。 - 下面就是
init()方法的具体内容啦,里面又有layoutInit()方法netInit()方法,它们的具体实现在下面。最后还有new Thread(this,"ThreadServer").start();就是开启子线程啦,关于Thread构造函数还是想有时间好好看一下,这里它的参数this,好像是指定子线程的入口程序是这个类里面的run()函数,ThreadServer是这个线程的名字吧。 - 再下面是
layoutInit()方法的实现,添加了JButton、JLabel、JTextFiled,以及对它们的设置。其中在设置JLabel的颜色是,要首先将它设置成不透明的,不然不行额。另外一个重要的操作就是在JButton里实现了发送数据的操作,这里设置监听事件时采用了匿名的内部类。在里面的处理函数中就是String sendData = textF.getText();和outputStreamServer.write(sendData.getBytes());,一个是从TextFiled读数据,一个是通过流传输数据,里面涉及了字符字节的转换。还有下面这个常识: 在java的编程中,对于按钮button可以有.addActionListener,也可以有.addMouseListener区别:.addActionListener:一般事件,仅侦听鼠标左键的单击事件,右键单击无效,仅在按钮为enable可用状态下生效.addMouseListener:可以监听鼠标按下、松开、离开、进入、点击,反正里面会有5个监听鼠标动作细节的方法。 - 下面是
netInit()方法,用来new SeverSock类和得到用来传输相应输入输出的流。要抛出异常额。 - 最后就是子线程了,里面就是通过流将客户端传来的数据存到
byteData[]中。然后用Jlabel的.setText()方法将数据显示出来,这里可以通过利用String的构造函数将字节转换为字符。ok,结束~
public class ChatPanel extends JPanel implements Runnable{
JLabel chatView;
OutputStream outputStreamServer;
Socket acceptSocket;
InputStream inputStreamServer;
ServerSocket serSocket;
ChatPanel() {
this.setBackground(Color.white);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setLayout(null);
init();
}
public void init() {
layoutInit();
netInit();
new Thread(this,"ThreadServer").start();//开启子线程,套接字接受数据的在子线程里实现。
}
//布局初始化,及按钮的响应事件
public void layoutInit() {
JButton btSend = new JButton("发送");
JTextField textF = new JTextField();
chatView = new JLabel();
this.add(btSend);
this.add(textF);
this.add(chatView);
btSend.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {//按钮点击事件发送消息
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent var1) {
String sendData = textF.getText();
try {
outputStreamServer.write(sendData.getBytes());//将sendData通过流写出
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}//想server传输数据
}
});
btSend.setBounds(400, 400, 60, 30);
textF.setBounds(20,400,350,30);
chatView.setBounds(20, 10, 450, 370);
chatView.setOpaque(true);//设置颜色时,必须先把它设置成不透明的
chatView.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
chatView.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);
}
public void netInit() {
try {
serSocket = new ServerSocket(9999);
acceptSocket = serSocket.accept();
inputStreamServer = acceptSocket.getInputStream();
outputStreamServer = acceptSocket.getOutputStream();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//接受客户端数据的子线程
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
byte byteData[] = new byte[1024];
inputStreamServer.read(byteData);
chatView.setText(new String(byteData));
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}程序与服务端差不多,start类是完全一样的,ChatPanel类有些小区别,但也是在button的事件处理函数中发送,在子线程中接受。
public class ChatPanel extends JPanel implements Runnable{
JLabel chatView;
JTextField textF;
JButton btSend;
OutputStream outputStreamClient;
Socket cliSocket ;
InputStream inputStreamClient;
ChatPanel() {
this.setBackground(Color.white);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setLayout(null);
init();
}
public void init() {
layoutInit();
netInit();
new Thread(this,"ThreadClient").start();;//开启子线程,套接字的在子线程的实现。
}
public void layoutInit() {
btSend = new JButton("发送");
btSend.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {//按钮点击事件
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent var1) {
String sendData = textF.getText();
try {
outputStreamClient.write(sendData.getBytes());//将sendData写出
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}//想server传输数据
}
});
textF = new JTextField();
chatView = new JLabel();
this.add(btSend);
this.add(textF);
this.add(chatView);
btSend.setBounds(400, 400, 60, 30);
textF.setBounds(20,400,350,30);
chatView.setBounds(20, 10, 450, 370);
chatView.setOpaque(true);//设置颜色时,必须先把它设置成不透明的
chatView.setBackground(Color.lightGray);
chatView.setVerticalAlignment(SwingConstants.TOP);;
}
public void netInit() {
try {
InetAddress serverIP = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");//得到服务器的IP,这里是本机
int port = 9999;
cliSocket =new Socket(serverIP,port);
outputStreamClient = cliSocket.getOutputStream();
inputStreamClient = cliSocket.getInputStream();
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
byte byteData[] = new byte[1024];
inputStreamClient.read(byteData);
chatView.setText(new String(byteData));
}
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
}这里总结说一下,IP和Socket连接,端口什么的。首先需要服务器先启动,因为它监听来自客户端的请求。服务端创建套接字时,只需要端口号,因为就是在本机这里创建TCP服务啊,IP肯定是本机IP。如果有客户端说要和服务端建立连接的话,客户端需要知道服务器端的IP地址,这里用的本机地址127.0.0.1,(一方面没有两个电脑,另一个是网络上更复杂。。但我以前在nodemcu上实现过哈,还写了博客)端口随便,但是最好不要小于1024因为这些都已经被系统程序占用了,就像前面维基百科说的,TCP和UDP的端口号都是53(TCP端口和UDP端口是两个东西)。这里客户端向已知IP和端口号的服务端请求连接成功后,就可以通过流来发送数据了。
服务端用需要newServerSocket serSocket;然后就可以通过acceptSocket = serSocket.accept();得到用来进行数据传输的套接字。在通过
inputStreamServer = acceptSocket.getInputStream();
outputStreamServer = acceptSocket.getOutputStream();
分别得到用来接收和发送数据的流。
客户端的话,只有一个Socket,就是通过它来获得用来发送和接收的流的
cliSocket =new Socket(serverIP,port);
outputStreamClient = cliSocket.getOutputStream();
inputStreamClient = cliSocket.getInputStream();
完结,(╹▽╹)