After this learning unit, you will be able to:
- Implement basic authorization, using Express, BCrypt, Mongo, and Mongoose.
- Implement basic authentication, using Express, BCrypt, Mongo, and Mongoose.
- Handle server-side errors.
- Validate fields on the client side.
- Create a protected route.
- Fork this repo
- Clone this repo into your
~/code/labs/folder
Upon completion, run the following commands:
$ git add .
$ git commit -m "done"
$ git push origin masterNavigate to your repo and create a Pull Request -from your master branch to the original repository master branch.
In the Pull Request name, add your Campus city, your name, and your last name separated by a dash.
Please, push every file needed to make your app properly to Github before creating the pull request.
In this Pair Programming exercise, we are going to create a project where we will have all the basic authorization and authentication processes and features that you would in a real application.
Go ahead and generate a new project using Ironhack Generator.
We have to create the signup of the application, that allow our users to register. The users have to provide the following information:
- Username: Must be unique in our application, and will identify each user.
- Password: Must be encrypted, using
bcrypt.
To complete this first iteration, you have to create the database model with mongoose, the routes, and the views.
Remember that you have to handle validation errors when a user signs up:
- The fields can't be empty.
- The username can't be repeated.
Once the user has signed up, he has to be able to log in the application. You have to create the view and add the correct functionality in the controller to let them log in the application.
Once the user has logged in, you have to create a session with express-session and mongo-connect.
Again, we have to check out that the fields are correctly filled before try to authenticate him.
At this point, we have implemented basic authentication features. Now, we have to create some routes that are protected, meaning that users can't visit these routes unless they're authenticated.
Let's create two different routes protected by authentication:
/main- Add a funny picture of a cat and a link back to the home page/private- Add your favoritegifand an<h1>denoting the page as private.
Create the views and add the middleware configuration to avoid accessing these routes without being authenticated.
Let's add validations to our forms. Remember we have two different forms: sign up and login.
Remember, when a user signs up or logs in, both the username and password fields must be filled in.
Check out the documentation at MDN. See if you can find a constraint that requires the user to fill a field prior to submission.
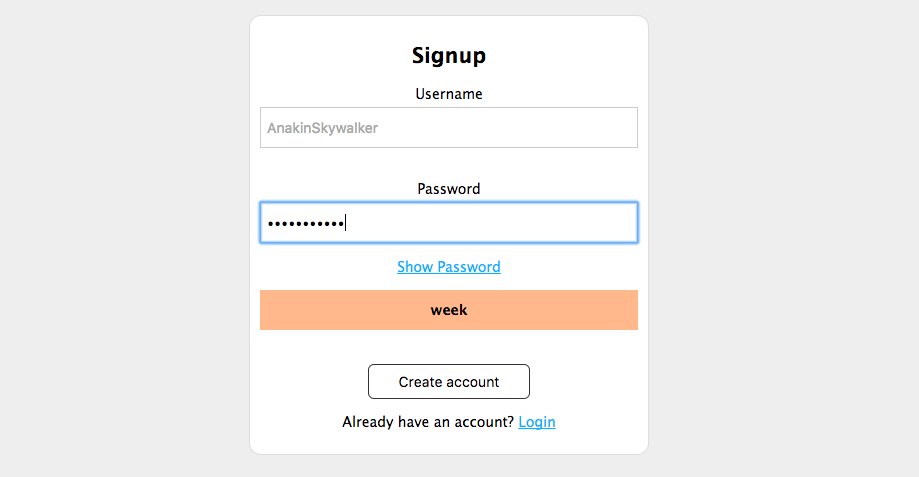
Finally, we will add a jQuery plugin to measure the password strength when we sign up in the application. We recommend you to use the Strength.js library, but feel free to look for another one.
Once finished, the result should be something like this:
This is a very common and helpful feature for users, as many do not know anything about password strength.
Once you are done with this exercise, you will have an excellent boilerplate that will include the basics of authorization and authentication.