MNIST ("Modified National Institute of Standards and Technology") is the de facto “Hello World” dataset of computer vision. Since its release in 1999, this classic dataset of handwritten images has served as the basis for benchmarking classification algorithms. As new machine learning techniques emerge, MNIST remains a reliable resource for researchers and learners alike.
In this, we aim to correctly identify digits from a dataset of tens of thousands of handwritten images.
- 940MX GPU with CUDA 10.1
- 8GB RAM at 2133 Hz.
- i5 @2.4 Ghz with 4 cores.
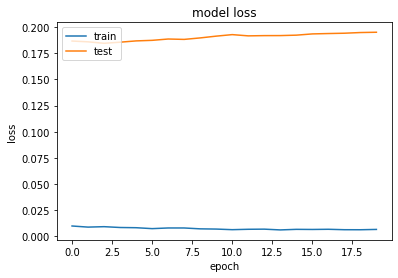
The process is divided into 3 parts.
- Add Gaussian noise to dataset.
- Create Autoencoder to denoise the image.
- Create a Dense layer model to identify Digits.
- It helps to prevent GAN attacks.
- It can be used for dimensionality reduction.
-
- How to add gaussian noise
- Here is the link to my the code. Link
-
- Encoder - Input image => CONV => RELU => BN => CONV => RELU => BN => Flatten => Dense
- Decoder - Output Encoder image => CONV_TRANSPOSE => RELU => BN => CONV_TRANSPOSE => RELU => BN => CONV_TRANSPOSE => Sigmoid
- Autoencoder - Encoder + Decoder
-
- Dense => Dropout => Dense => Dropout => Dense => Dropout => Dense => Dense
- Output one hot encoded numbers between 0-9
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
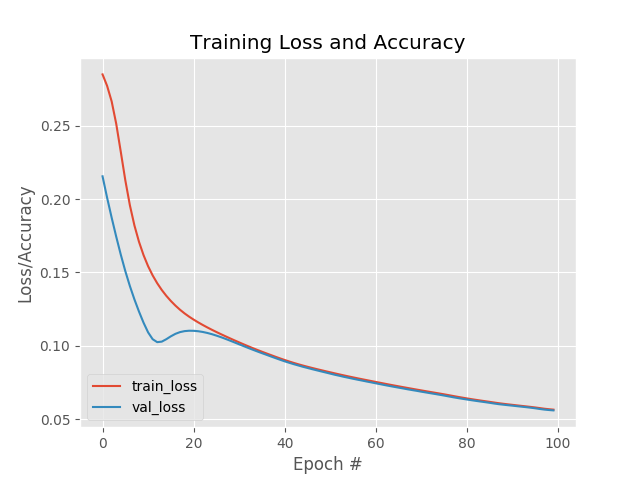
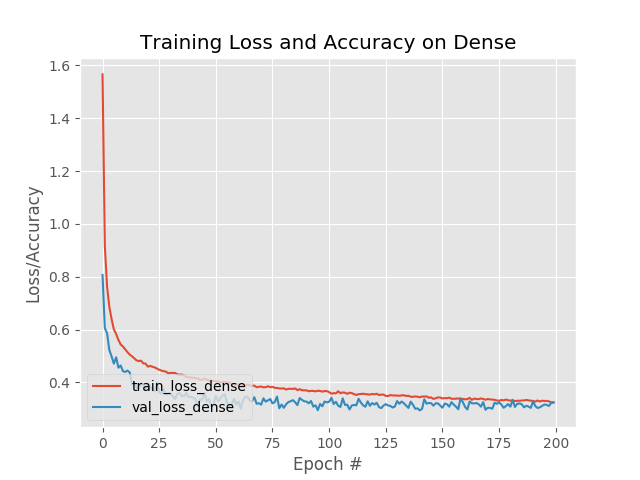
| Epochs(Autoencoder) | 100 |
| Epochs(Dense) | 200 |
| Optimizer(Autoencoder) | Adam |
| Optimizer(Dense) | Adam |
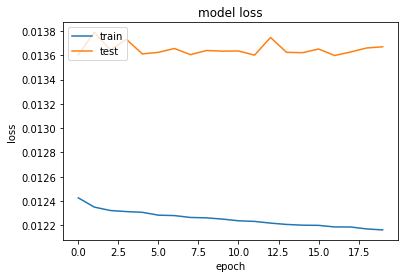
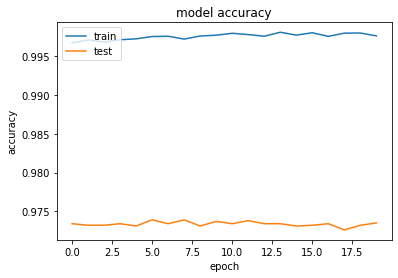
| Property | Training | Testing |
|---|---|---|
| No. of Images | 60,000 | 10,000 |
| Time (Autoencoder) | 2 hrs | 23 mins |
| Time (Digit Prediction) | 20 mins | 4 mins |