Source code for IJCAI 2020 paper "A Relation-Specific Attention Network for Joint Entity and Relation Extraction"
- Pytorch (1.0.1)
- nltk
- numpy
- six
├── config.py
├── data
├── DataLoader.py
├── data_prepare.py
├── eval_utils.py
├── misc
│ ├── init.py
│ ├── LossWrapper.py
│ └── utils.py
├── model
│ ├── init.py
│ └── Rel_based_labeling.py
├── networks
│ ├── decoder.py
│ ├── embedding.py
│ ├── encoder.py
│ └── init.py
├── Test.py
└── train.py
data/multiNYT/util.py
Process raw data to obtain word dict (word.npy),relation dict(rel2id.json),label dict(label2id.json) and so on.
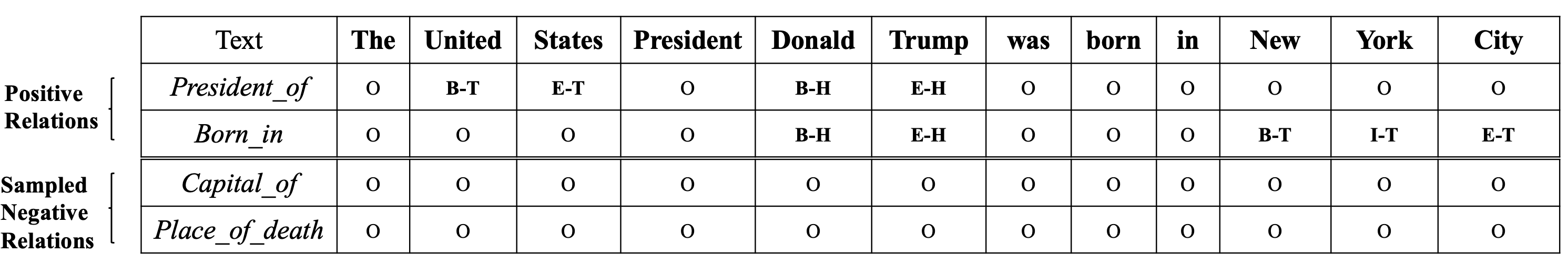
Labels:["S-H", "S-T", "B-H", "B-T", "I-H", "I-T", "E-H", "E-T", "O", "X"]
Tag H and T stand for head and tail respectively, tag O stands for irrelevant tokens in the sentence, and tag X is padding signal.
data_prepare.py
Convert the original input data into the form of model input and save as .pkl files.
-
Construct ground truth tag sequences
We will construct different tag sequences for different relations, and align head and tail entities of the triplets in the original sentence.
-
Relational negative sampling
We use relational negative sampling mechanism for efficiency. We treat the relations that are described in the current sentence as positive relations, and the rest are negative ones. We randomly select
$n_{neg}$ relations from the negatives of each sentence (corresponding to parameter--neg_numinconfig.py), whose ground truth tag sequences contain only O and X labels.
See the example below.
DataLoader.py
Construct dataloader from .pkl files stored in the previous step. Note that our batch_size refers to the number of sentences, one sentence corresponds to
-
python data_prepare.py -
Train
python train.py --checkpoint_path [ckpt_path] --gpu 3 --use_pos -
Test
python Test.py --load_from [ckpt_path] --gpu 0 --use_pos