A header-only C++ library which allows the numerical optimisation of any given problem, function, program or you-name-it
without knowing the "function" of the problem simply by smartly testing certain values
- you only have to include a single header file
cppOpt.h - using heuristic algorithms http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heuristic
- using Catch as testing framework https://github.com/philsquared/Catch
Bascially the entire structure of the library has been changed. The performance has been optimised as well, so a switch to the new version might be worth it.
Otherwise simply stick to earlier versions of cppOpt.
optimise any given problem by providing an std::function
auto toOptimize = [](OptCalculation<double>& optCalculation) {
optCalculation.result = YOUR CODE COMES HERE
};for optimising x^2 you could write:
auto toOptimize = [](OptCalculation<double>& optCalculation) {
optCalculation.result = pow(optCalculation.get_parameter("X"), 2);
};you can even run other programs:
auto toOptimize = [](OptCalculation<double>& optCalculation) {
std::string parameter1 = optCalculation.get_parameter("X").to_string();
std::string parameter2 = optCalculation.get_parameter("Y").to_string();
system(( "someExecuteable -p1 " + parameter1 + " -p2 " + parameter2).c_str() );
optCalculation.result = parse_generated_output_file();
}OptBoundaries<T> optBoundaries;
optBoundaries.add_boundary({-5.0, 5.0, "X"});
optBoundaries.add_boundary({-50.0, 55.0, "Y"});
optBoundaries.add_boundary({33.0, 3.0, "potatoe"});enum class OptTarget {
MINIMIZE,
MAXIMIZE,
APPROACH,
DIVERGE
};use any of these:
<float>
<double>
<long double>// the bool flag decides whether multithreading is active
OptCoordinator<double, false> coordinator(
maxCalculations,
toOptimize,
optTarget,
targetValue);coordinator.add_child(make_unique<OptSimulatedAnnealing<double>>(...))
coordinator.add_child(make_unique<OptThresholdAccepting<double>(...))
coordinator.add_child(make_unique<OptGreatDeluge<double>(...))
coordinator.add_child(make_unique<OptEvolutionary<double>(...))you can add any number of child algorithms and run these in parallel. Just make sure your calculation callback is thread-safe.
coordinator.run_optimisation(); // if single threaded
coordinator.run_optimisation(NUMBER_OF_THREADS); // if multi threadedyou can also define when to abort the optimisation, in case the value is good enough
coordinator.enable_early_abort(13.37);add logging by via your calculate function
auto toOptimize = [](OptCalculation<double>& optCalculation) {
optCalculation.result = YOUR CODE COMES HERE
//also log the result
cout << optCalculation.to_string_values() << " =>\t" << optCalculation.result << endl;
};2.162039 4.674414 => 4.67441
-0.185813 0.034526 => 0.0345263
-1.505135 2.265430 => 2.26543
-4.193620 17.586445 => 17.5864
-2.887129 8.335513 => 8.33551
-0.469162 0.220113 => 0.220113
-3.301420 10.899376 => 10.8994
-2.083137 4.339458 => 4.33946
2.035803 4.144495 => 4.1445
2.998251 8.989506 => 8.98951
0.830960 0.690495 => 0.690495
you can retrieve the best value once the optimisation is done
OptCalculation<double> best = coordinator.get_best_calculation();
cout << best.to_string_header() << endl;
cout << best.to_string_values() << endl;Please refer to the examples/ folder for well documented and currently compiling usage examples.
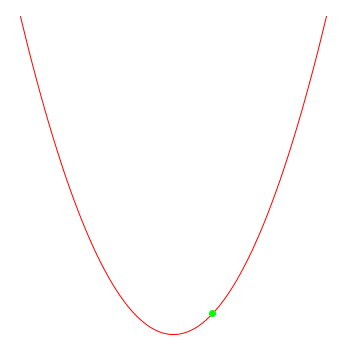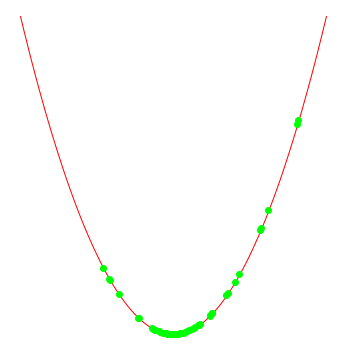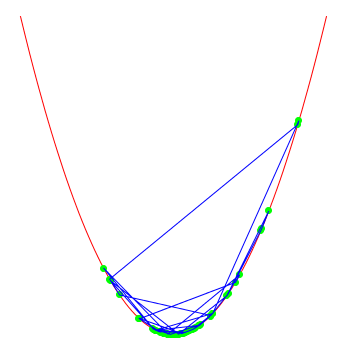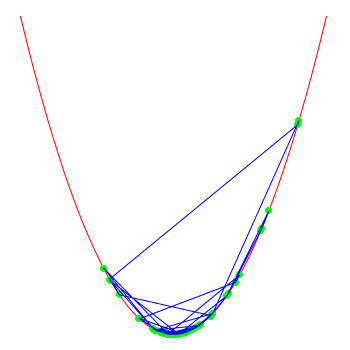
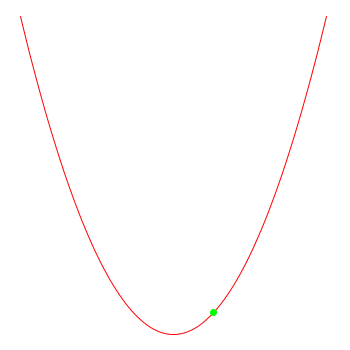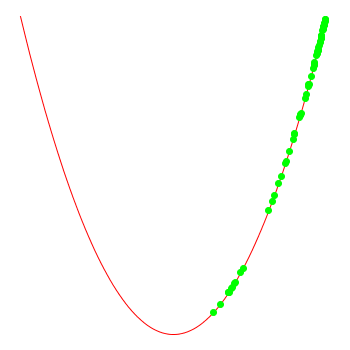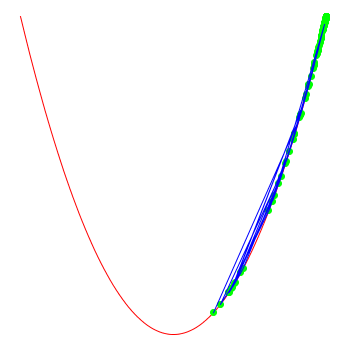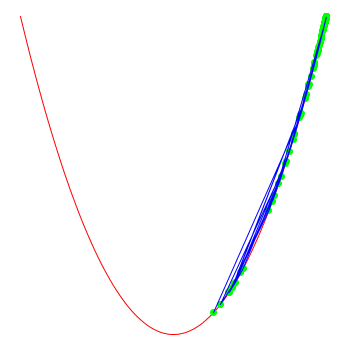
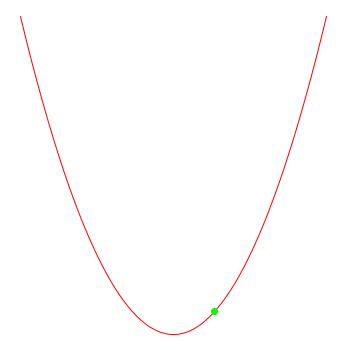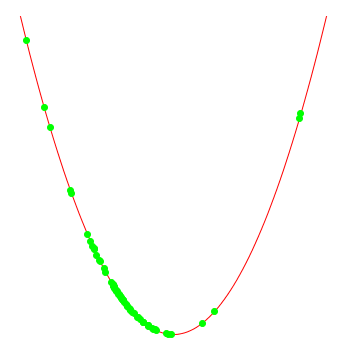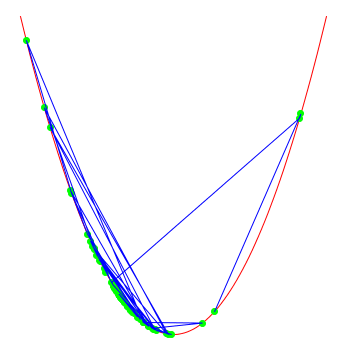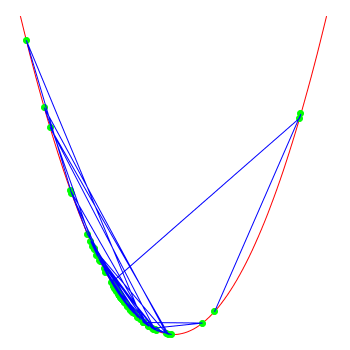
note that the optimiser doesn't "know" that the function actually is x*x
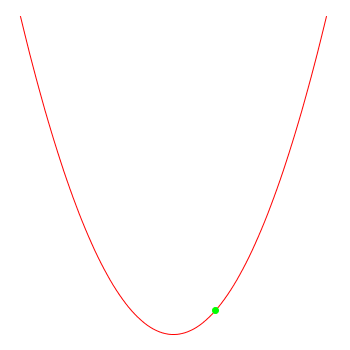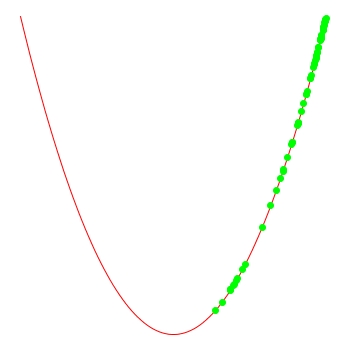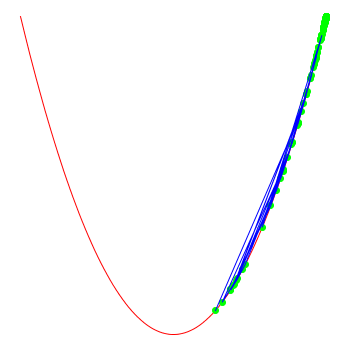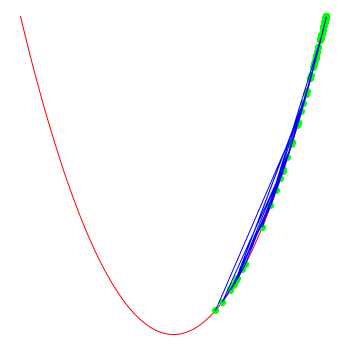
check out https://github.com/I3ck/cppOptImages for more images
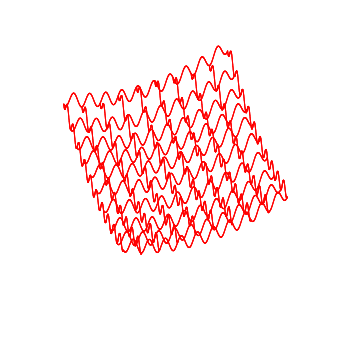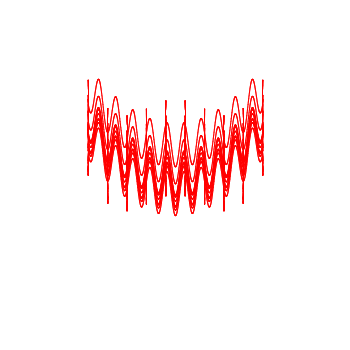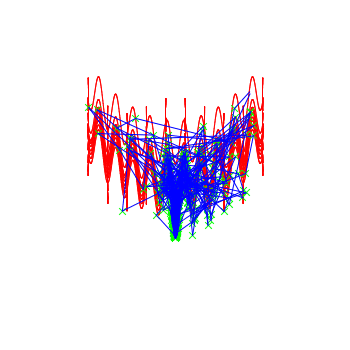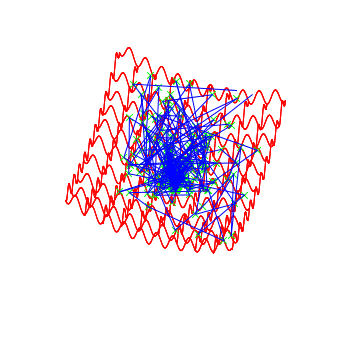
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rastrigin_function
open up inc/config.h to enable/disable DEBUG output
//#define DEBUGcmake .
make
directly include cppOpt.h which includes all required headers or choose the header files you want to use
after using cmake and make check bin/ for the test_xyz executeables
since the tests check whether the algorithms reach the wanted values, it's possible that the tests might fail in some cases (due to the random nature of the algorithms). Just restart the test in such a case.
Only if the test fails often there's an actual bug
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simulated_annealing
http://comisef.wikidot.com/concept:thresholdaccepting
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Great_Deluge_algorithm
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evolutionary_algorithm
feel free to open issues if you'd like to have new algorithms added, would like to have a new feature or found a bug