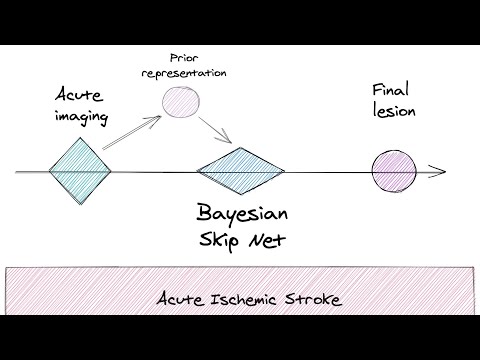
Perfusion CT is widely used in acute ischemic stroke to determine eligibility for acute treatment, by defining an ischemic core and penumbra. In this work presented at the Brain Lesion Workshop at MICCAI 2020, we used a novel way of building on prior information for the automatic prediction and segmentation of stroke lesions. We reformulate the task to identify differences from a prior segmentation by extending a three-dimensional Attention Gated Unet with a skip connection allowing only an unchanged prior to bypass most of the network. We show that this technique improves results obtained by a baseline Attention Gated Unet on both the Geneva Stroke Dataset and the ISLES 2018 dataset.
Please cite as: Klug, J. et al. Bayesian Skip Net: Building on Prior Information for the Prediction and Segmentation of Stroke Lesions. in Brainlesion: Glioma, Multiple Sclerosis, Stroke and Traumatic Brain Injuries (eds. Crimi, A. & Bakas, S.) 168–180 (Springer International Publishing, 2021). doi:10.1007/978-3-030-72084-1_16.
Click on the image below:
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Environment must use python 3.7 (for torch and CUDA compatibility)
- The main file for training can be found under
train_segmentation.py. It takes a config file as argument, examples can be found in the./configfolder. - A visdom server can be launched as well for visualisation:
python -m visdom.server
- "Attention U-Net: Learning Where to Look for the Pancreas", MIDL'18, Amsterdam, original paper
- Clinical implications: https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/2762679
- Active development repo: https://github.com/JulianKlug/PerfusionCT-Net