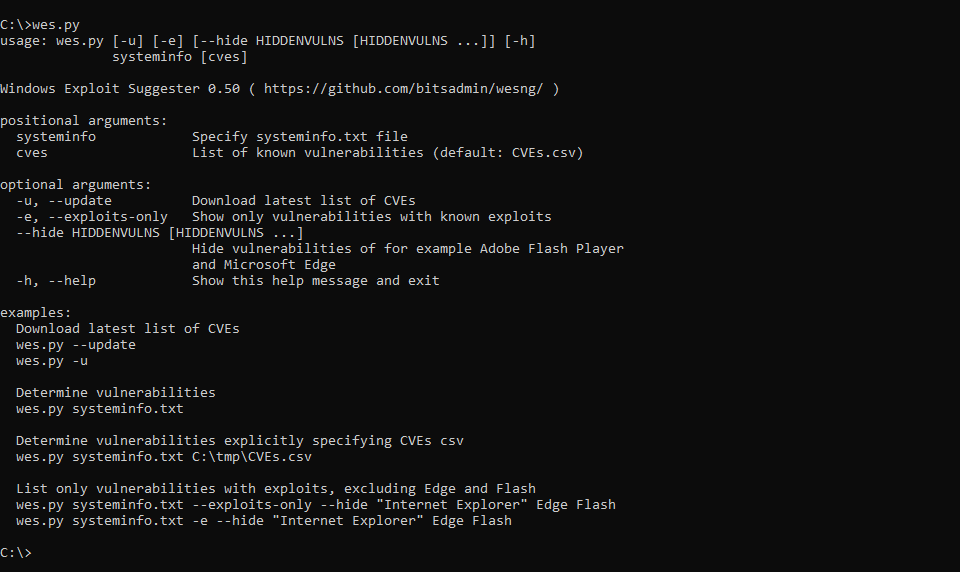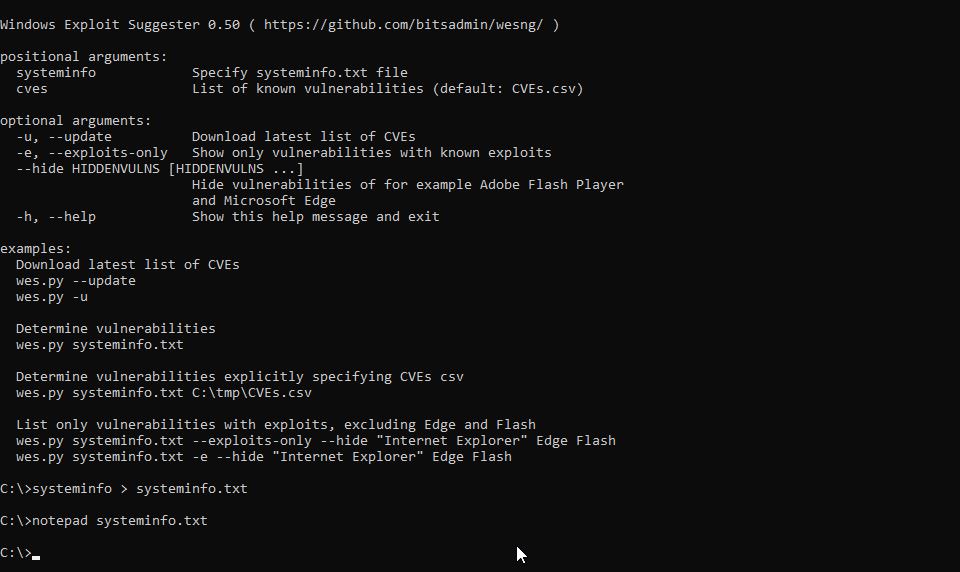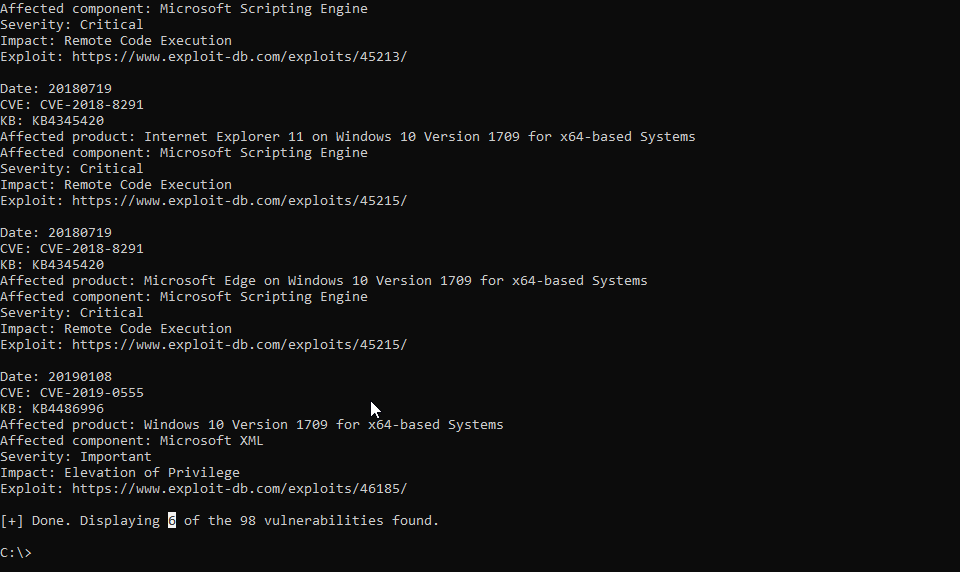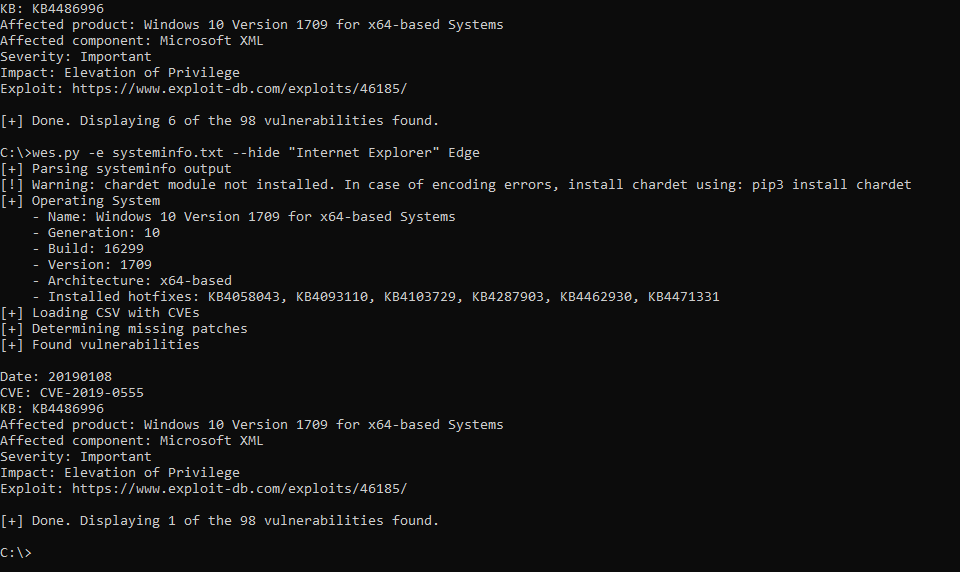
WES-NG is a tool based on the output of Windows' systeminfo utility which provides the list of vulnerabilities the OS is vulnerable to, including any exploits for these vulnerabilities. Every Windows OS between Windows XP and Windows 10, including their Windows Server counterparts, is supported.
- Obtain the latest database of vulnerabilities by executing the command
wes.py --update. - Use Windows' built-in
systeminfo.exetool to obtain the system information of the local system, or from a remote system usingsysteminfo.exe /S MyRemoteHost, and redirect this to a file:systeminfo > systeminfo.txt - Execute WES-NG with the systeminfo.txt output file as the parameter:
wes.py systeminfo.txt. WES-NG then uses the database to determine which patches are applicable to the system and to which vulnerabilities are currently exposed, including exploits if available. - As the data provided by Microsoft is frequently incomplete and false positives are reported by wes.py, make sure to check the Eliminating false positives page at the Wiki on how to deal with this. For an overview of all available parameters, check CMDLINE.md.
This GitHub repository regularly updates the database of vulnerabilities, so running wes.py with the --update parameter gets the latest version.
If manual generation of the .csv file with hotfix information is required, use the scripts from the /collector folder to compile the database. Read the comments at the top of each script and execute them in the order as they are listed below. Executing these scripts will produce CVEs.csv.
The WES-NG collector pulls information from various sources:
- Microsoft Security Bulletin Data: KBs for older systems [1]
- MSRC: The Microsoft Security Update API of the Microsoft Security Response Center (MSRC): Standard source of information for modern Microsoft Updates [2]
- NIST National Vulnerability Database (NVD): Complement vulnerabilities with Exploit-DB links [3] These are combined into a single .csv file which is compressed and hosted in this GitHub repository.
I developed WES-NG because while GDSSecurity's Windows-Exploit-Suggester worked excellently for operating systems in the Windows XP and Windows Vista era, GDSSecurity's Windows-Exploit-Suggester does not work for operating systems like Windows 10 and vulnerabilities published in recent years. This is because Microsoft replaced the Microsoft Security Bulletin Data Excel file [1] on which GDSSecurity's Windows-Exploit-Suggester is fully dependent, by the MSRC API [2]. The Microsoft Security Bulletin Data Excel file has not been updated since Q1 2017, so later operating systems and vulnerabilities cannot be detected. Thanks @gdssecurity, for this great tool which has served many of us for so many years!
- Bugs can be submitted via the Issues page
- For false positives in results, please read the Eliminating false positives page at the Wiki first. In case that doesn't significantly reduce the number of false positives, follow the steps at the Report false positives page on the Wiki
See CHANGELOG.md
- Add support for NoPowerShell's
Get-SystemInfocmdlet output - Add support for
wmic qfeoutput together with support for parameters to manually specify the operating system - Add support for alternative output formats of
systeminfo(csv, table) - More testing on the returned false positive vulnerabilities - see also the wiki
- Add support for Itanium architecuture
[1] https://www.microsoft.com/download/details.aspx?id=36982
[2] https://portal.msrc.microsoft.com/en-us/developer
[3] https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/data-feeds
Authored by Arris Huijgen (@bitsadmin - https://github.com/bitsadmin/)