Backtracking is an algorithmic-technique for solving problems recursively by trying to build a solution incrementally, one piece at a time, removing those solutions that fail to satisfy the constraints of the problem at any point of time (by time, here, is referred to the time elapsed till reaching any level of the search tree).
Basic idea: FIND ALL POSIBLE COMBINATIONS. When an element its found we "backtrack" erasing that element and continuing analizing other cases. Like every recursive algorithm it counts with two elements
- Base case
- Recursive case
Essentially, the idea is to find the best possible match at any given time, which is why this type of algorithm is said to be an in-depth search. During the search, if a wrong alternative is found, the search goes back to the previous step and takes the next alternative. When the possibilities have been finished, the previous choice is returned and the next option is taken (child [if we refer to a tree]). If there are no more alternatives the search fails. In this way, an implicit tree is created, in which each node is a state of the solution (partial solution in the case of interior nodes or total solution in the case of leaf nodes).
Basically we do three things:
- Choice
- Constrains
- Goal
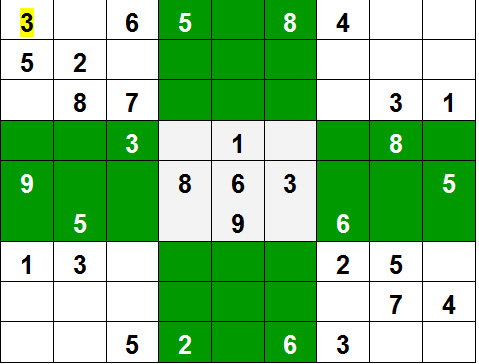
For example, consider the SudoKo solving Problem, we try filling digits one by one. Whenever we find that current digit cannot lead to a solution, we remove it (backtrack) and try next digit. This is better than naive approach (generating all possible combinations of digits and then trying every combination one by one) as it drops a set of permutations whenever it backtracks.
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
ArrayList<Integer> combinations = new ArrayList<>();
upToNumberCombinations(10, numbers, 0, combinations, 0);
}
public static void upToNumberCombinations(int number, int[] numbers, int sum, ArrayList<Integer> combinations, int pos) {
if (sum == number) {
System.out.println(combinations.toString());
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
if (pos < numbers.length) {
// ADD
combinations.add(numbers[pos]);
sum = sum + numbers[pos];
//RECURSIVE
upToNumberCombinations(number, numbers, sum, combinations, pos + 1);
// ERASE
sum = sum - numbers[pos];
combinations.remove(combinations.lastIndexOf(numbers[pos]));
pos++;
}else {
break;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 4;
ArrayList<Integer> numeros = new ArrayList<>();
combinacionesSuma(4, numeros,0);
}
public static void combinacionesSuma(int numero, ArrayList<Integer> numeros, int suma){
if(suma == numero){ // Base Case
System.out.println(numeros);
}else { // Recursive Case
for (int i = 1; i<=numero; i++){
suma += i;
if (suma <= numero){
numeros.add(i);
combinacionesSuma(numero,numeros,suma);
numeros.remove(numeros.indexOf(i));
}
suma -= i;
}
}
}
public static int solution(String S) {
List<String> allIpAddresses = new ArrayList<>();
int[] path = new int[4];
snapshotIp(allIpAddresses, S, 0, path, 0);
return allIpAddresses.size();
}
private static void snapshotIp(List<String> allIpAddresses, String s, int builderIndex, int[] path, int segment) {
if (segment==4 && builderIndex == s.length()){
allIpAddresses.add(path[0]+ "." + path[1] + "." + path[2]+ "." + path[3]);
return;
}else if ((segment==4 || builderIndex == s.length())){
return;
}
for (int len = 1; len <=3 && builderIndex + len <= s.length(); len++){
String snapshot = s.substring(builderIndex, builderIndex+len);
int value = Integer.parseInt(snapshot);
if (value>255 || len>=2 && s.charAt(builderIndex)=='0'){
break;
}
path[segment] = value;
snapshotIp(allIpAddresses,s,builderIndex + len, path, segment+1);
path[segment] = -1;
}
}