Deploys a self-contained WVD environment with a hosted domain controller.
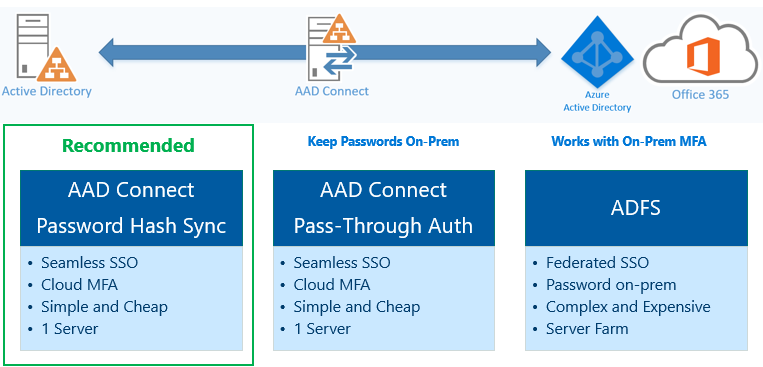
You can configure the environment with AD as either the source or target for identities.
This is the simplest scenario to cater for.
- Use the hosted domain the authoritive domain, or
- Connect it to your existing AD as a resource domain with an external trust.
- Password hash synchronization is not required for either of these scenarios.
When choosing to use the domain at the authoritive source for identities one must install and configure AADConnect.
In this scenario one would use an external HR system (Workday, etc.) as the identity source and OKTA for provisioning & entitlement.
Password synchronization is required for this scenario.
- Add the managed domain as a directory to OKTA (ensuring it's NOT configured as a profile source)
- Provision user accounts to the managed domain as usual.
- Use the Office 365 connector to provision those same users to AAD
- Use push groups to grant access to to the WVD service
- Assign access to the WVD application group to the push group created by OKTA
- Run the script 'deploy_infra.sh' to deploy.
- There are some variables which you can change to modify the name of the managed domain, etc.
Configure the managed domain per your chosen architecture
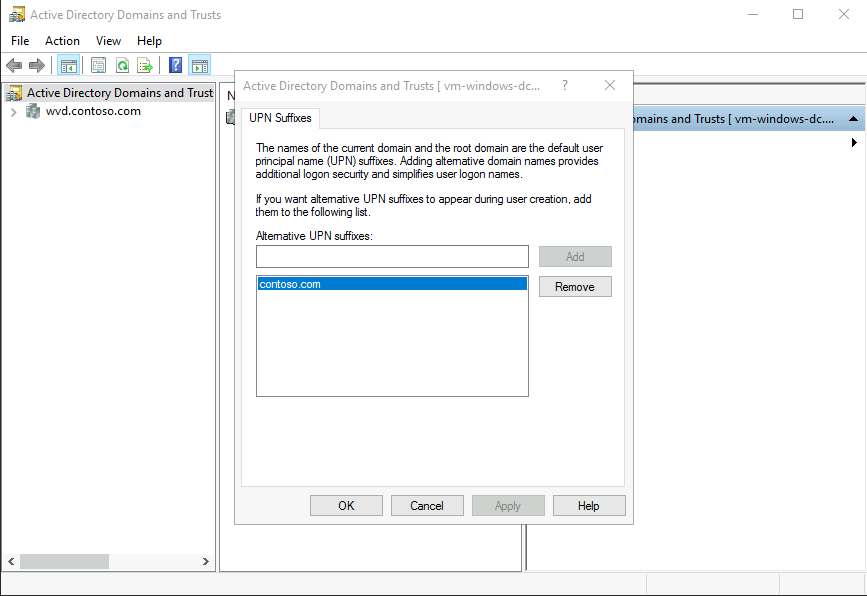
If the managed domain is going to be used as the authoritive source for identities a UPN suffix must be added to the domain which matches the vanity domain configured in Azure Active Directory. Use the Active Directory Domains and Trusts MMC add this UPN suffix to the domain.
If one wishes to secure traffic to the domain controller subnet (NSG or Azure Firewall) these are the ports required for the WVD clients to join the domain:
- TCP In: 53, 88, 135, 139, 389, 445, 636, 3268, 3269, 49152-65535
- UDP In: 53, 123, 137, 138, 389, 123, 49152-65536
- ICMP In: used for slow link detection when applying GPOs at logon