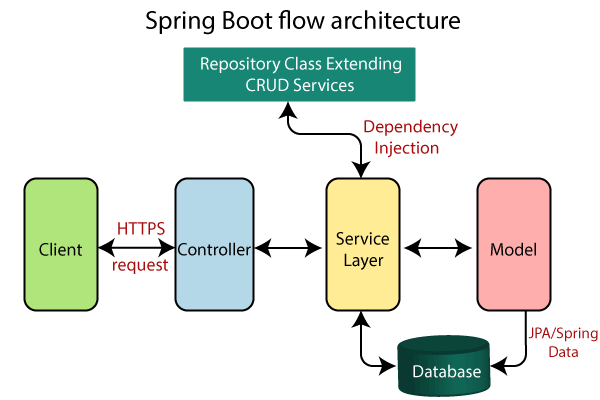
A Java Spring Boot backend app that performs CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations is a web application that allows you to create, read, update, and delete data from a database. The app is built using the Spring Boot framework, which provides a set of tools and libraries for building scalable and robust web applications.
The CRUD operations are implemented using RESTful APIs, which provide a standard way of accessing and manipulating resources over the internet. The app exposes endpoints for each CRUD operation, and these endpoints are mapped to specific HTTP methods (POST, GET, PUT, DELETE) based on the operation being performed.
Assuming we have a Student class with id, name, and email properties, and we want to add a new student to our database using a POST request:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/students")
public class StudentController {
private final StudentRepository studentRepository;
public StudentController(StudentRepository studentRepository) {
this.studentRepository = studentRepository;
}
@PostMapping
public ResponseEntity<?> createStudent(@RequestBody Student student) {
if (student.getName() == null || student.getEmail() == null) {
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("Name and email are required.");
}
Optional<Student> existingStudent = studentRepository.findByEmail(student.getEmail());
if (existingStudent.isPresent()) {
return ResponseEntity.badRequest().body("A student with this email already exists.");
}
Student savedStudent = studentRepository.save(student);
return ResponseEntity.ok(savedStudent);
}
}In this example, the @PostMapping annotation is used to map the createStudent() method to a POST request to the /students endpoint. The @RequestBody annotation is used to deserialize the request body, which should contain a JSON representation of the Student object.
The StudentRepository is an interface that extends JpaRepository and provides CRUD methods for the Student entity.
When a new student is added, the save() method of the StudentRepository is called to persist the student to the database. The saved student is returned in the response body along with an HTTP status code of 200 (OK).
It's a good practice to declare the studentRepository field as final because it indicates that the reference to the repository cannot be changed once it has been initialized. This can help prevent bugs and make code more maintainable.
The app connects to a database using an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) tool, such as Hibernate or MyBatis, which allows it to interact with the database using Java objects. The data is stored in a relational database, such as MySQL or PostgreSQL, and is accessed using SQL queries.
Overall, a Java Spring Boot backend app that performs CRUD operations is a powerful tool for building data-driven web applications that can scale to handle large volumes of data and user