PNICER is an astronomical software suite for estimating extinction for individual sources and creating extinction maps using unsupervised machine learning algorithms. If you want to know more about the technique, you are invited to study the published manuscript, which is currently available on Astro-ph. Please note that this is our first release and if you encounter problems, let us know so that we can fix issues asap.
PNICER is designed to have as few dependencies as possible and there is a good chance that you are already running Python with all necessary packages. PNICER requires numpy, scipy, astropy, matplotlib, and scikit-learn. All necessary packages will be installed or upgraded automatically with pip. Also, at the moment this package is not compatible with Windows operating systems due to parallel processing frameworks available in Python.
To install the package, download the latest release to your computer here. Unpack the archive and install with pip
pip install --user /path/to/PNICER/where the last argument points to the saved and unpacked downloaded directory. All dependencies will be installed automatically.
To test the installation, start up python (or ipython) and type
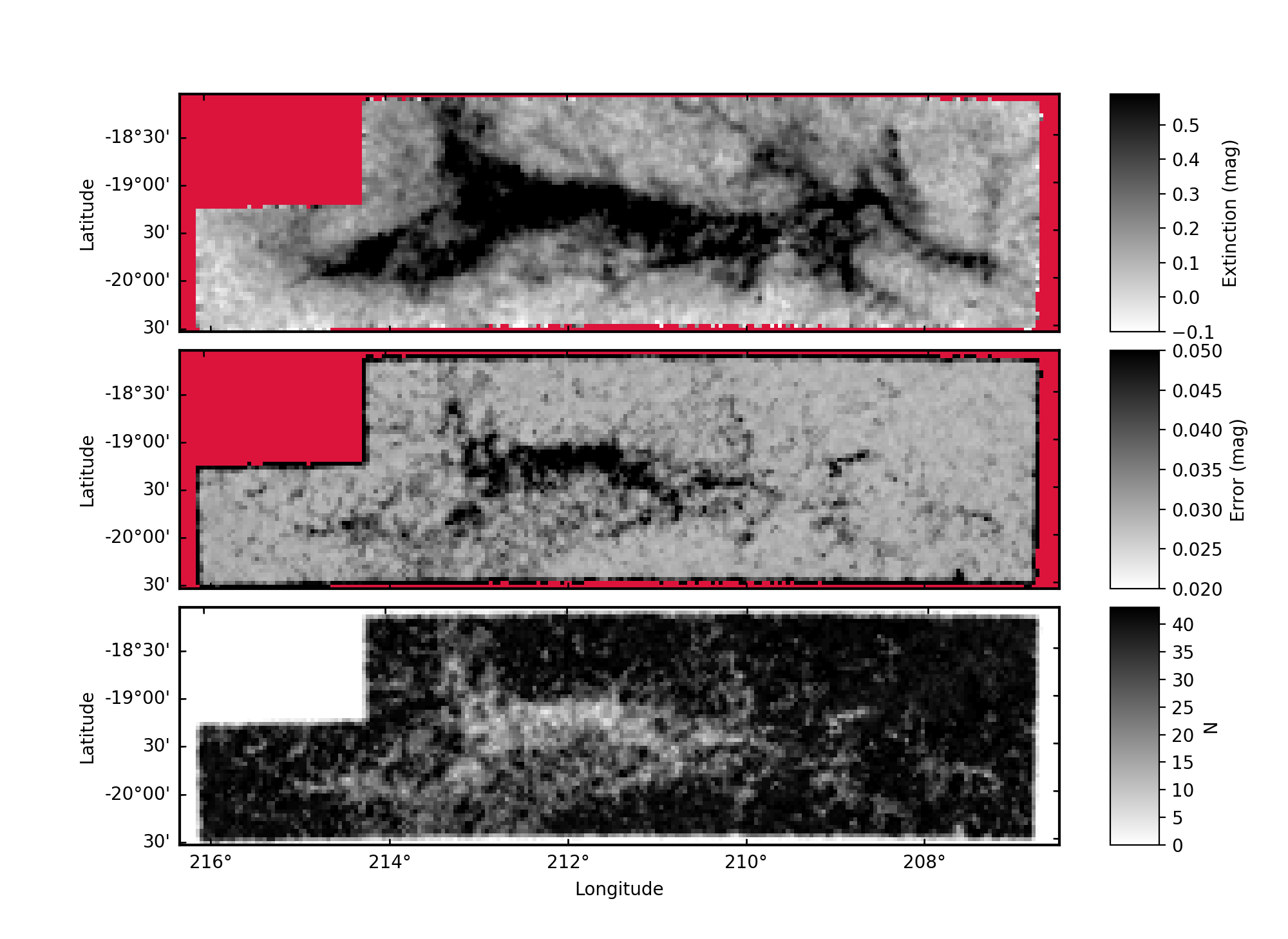
from pnicer.tests import orion
orion()which will go through all major PNICER methods. At the end you should see a plot window with an extinction map of Orion A created from 2MASS data:
For an introduction to the basic tools available in PNICER, please refer to the jupyter notebook provided with this package:
In the near future (April - May 2017) we plan to implement advanced extinction mapping tools and we will also soon provide the complete API of PNICER. If you have any questions, I am always happy to receive feedback (both positive and negative).