Olaper is the XMLA OLAP interface to your SQL database. It allows to run multi-dimensional (MDX) queries on your database - be it MySQL, Oracle, Vertica or other. You then can use specialized OLAP tools, like Saiku to see your data in different dimensions and perform deep analysis.
Olaper is installed as Java servlet in the J2EE container, like Jetty or Tomcat. Then it should be configured according to the schema of your database.
-
Olaper builds multi-dimensional cubes from relational tables
-
Olaper exposes XMLA interface, which is a standard way to execute MDX queries remotely, over HTTP or HTTPs protocols. Actually it means that you expose your database in a Web service for analysis, that can then be used by many parties and tools in a variety of ways
-
Olaper is a ROLAP - type engine. Together with high-performance databases, like HP Vertica, it allows to run real-time queries over data. Olaper does not use any caching, so the data you get will always be up-to-date.
-
Olaper automatically uses aggregates (Oracle "materialized views" or Vertica's "projections") if possible on per-query basis. It allows to run queries faster even on large amount of data, pre-aggregating it on database side.
-
Olaper have separated configuration for "cubes" and "tables". Cubes is OLAP world, and tables is SQL world. It allows to define a logical cube schema and run it against your database.
-
Olaper uses JDBC drivers and standard SQL to connect to databases.
-
Download a servlet container server ( for example, Jetty ) and install it, or use your favorite one.
-
Place file olaper.war from the latest release ( https://github.com/Wondersoft/olaper/releases ) and place it in webapps folder in container
-
Create a directory /etc/olaper and copy files from https://github.com/Wondersoft/olaper/tree/master/example directory: cubes.json and tables.json
-
Depending on what database you use, download JDBC driver JAR and place it in your server in lib ( or lib/ext ) directory. It may depend on the server you use, but basically the JDBC JAR must appear in the classpath when your server starts.
After installation, you should configure files cubes.json and tables.json for your particular database. Then you may connect to server using XMLA URL, like http://localhost:8180/olaper/xmla.
To test and try olaper, you can use the demo configuration with the pre-configured database.
Demo is available as Docker image: https://github.com/ivansabik/docker-olaper
Otherwise, to configure the demo configuration manually, use following steps:
- To setup the database you will need MySQL server installation. Log into MySQL console and create a database:
mysql> create database foodmart default character set utf8 default collate utf8_general_ci;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0,01 sec)
mysql> create user 'foodmart'@'localhost' identified by 'foodmart';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0,11 sec)
mysql> grant ALL privileges on foodmart.* to 'foodmart'@'localhost' identified by 'foodmart' with grant option;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0,00 sec)
- checkout the project https://github.com/OSBI/foodmart-data and populate data in database:
$ cd data/
$ unzip DataScript.zip
Archive: DataScript.zip
inflating: FoodMartCreateData.sql
$ ls
DataScript.zip FoodMartCreateData.sql
$ cd ..
$ sh FoodMartLoader.sh --db mysql
-
Download MySQL JDBC driver JAR and place it in your server in lib ( or lib/ext ) directory of your web server.
-
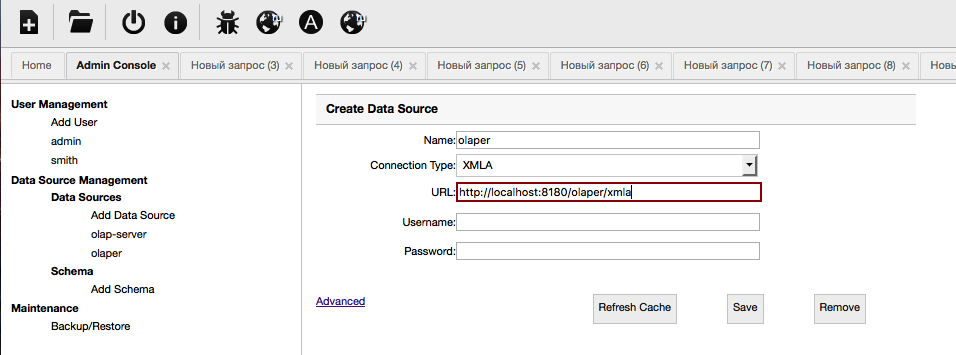
Start the server and try to connect to Olaper URL http://localhost:8080/olaper/xmla ( the port number may differ depending on your server configuration! ). You should then get something like this:
HTTP ERROR 405
Problem accessing /olaper/xmla. Reason:
HTTP method GET is not supported by this URL
- Run OLAP tool and configure it to the Olaper URL. For saiku, it may look like this:
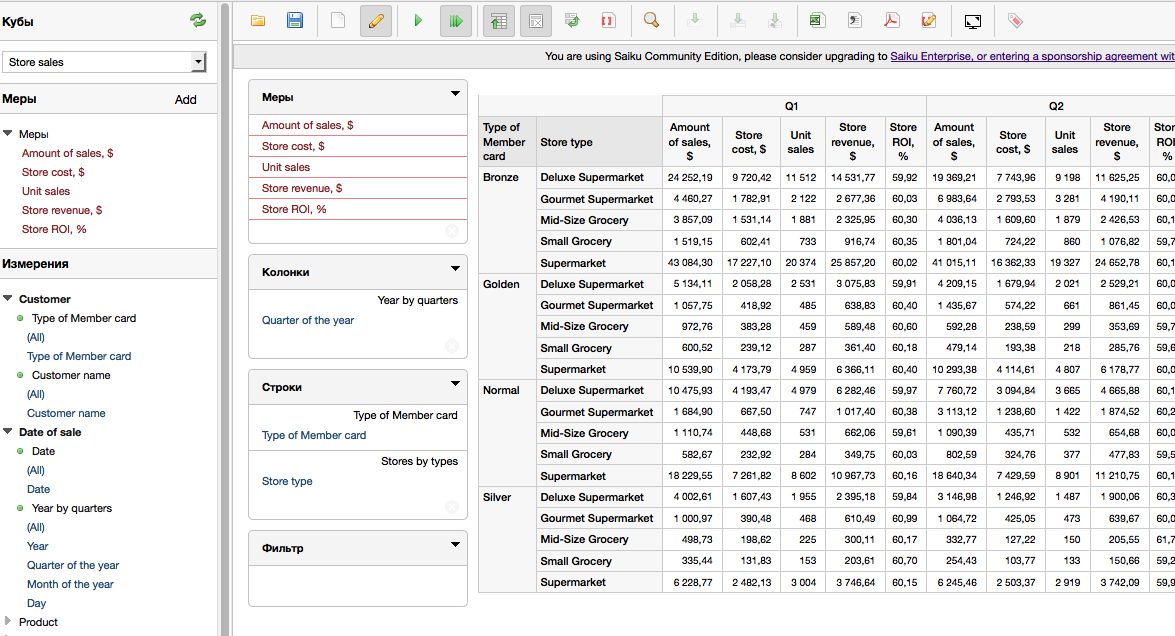
- After that, you can run queries on the cube Foodmart:
Have fun!
Configuration for olaper is stored in 2 files: cubes.json and tables.json. The path to the configuration is defined in web.xml file and can be changed, so that you can deploy multiple olaper's on same machine.
By default, olaper looks for the file /etc/olaper/cubes.json. If the file not found in file system, it is searched in the classpath.
Olaper has separate configuration for OLAP meta-data and physical structure of database:
- cubes.json defines what queries you may generate with OLAP tools. It describes "logical" structure of your storage from the end user point of view.
- tables.json defines how the logical storage mapped to physical database and how to access it.
cubes.json file is JSON with the following structure:
{
"name": "Provider=Mondrian;DataSource=Foodmart;",
"caption": "Foodmart DWH",
"catalogs": [
{
"name": "Foodmart",
"physical_schema": "/etc/olaper/tables.json",
"dimensions": [...]
"cubes": [...]
}
]
}It describes the datasource, containing catalogs. Datasource and catalog names are identification properties, used to connect to the data using OLAP tools. Important note: as olaper uses mondrian XMLA server as a frontend, it is required to use Provider=Monrian as the first part of the name.
Catalog contains dimensions and cubes.
Catalog has a link to the physical schema ( tables.json ). Relative paths are not supported, you should define the full path here.
Dimension has the following structure:
{
"name": "Date",
"caption": "Date of sale",
"attributes": [
{
"name": "Year",
"caption": "Year",
"auto_hierarchy": false
}, ...
],
"hierarchies": [
{
"name": "Year by quarters",
"caption": "Year by quarters",
"levels": [
"Year",
"Quarter",
"Month of the year",
"Day of month"
]
}
]
}Dimension structure defines attributes and hierarchies.
Hierarchies are built from attributes, the "auto_hierarchy" controls if the single attribute should automatically form an hierarchy or not.
Names of attribute and hierarchy are names, used in MDX queries. Captions is what the tool will show to end user.
Apparently, dimension may contain 1..many of attributes, forming 0...many hierarchies.
Cube is a logical unity of dimensions and measures. It is defined as:
{
"name": "Store sales",
"caption": "Store sales",
"dimensions": [
"Date", ...
],
"measures": [
{
"name": "Store sales",
"caption": "Amount of sales, $",
"datatype": "Double",
"format": "#,##0.00"
}, ...
]
}Cube has a name, used in MDX queries and caption, displayed by the tool to end user.
Dimensions is the list of dimensions of the cube.
Measures is the list of measure definition - name, caption, the datatype and format ( optional ). All measures are considered numeric - Double or Integer.
- Fork it ( https://github.com/Wondersoft/olaper/fork )
- Create your feature branch (
git checkout -b my-new-feature) - Commit your changes (
git commit -am 'Add some feature') - Push to the branch (
git push origin my-new-feature) - Create a new Pull Request