"Data structures" course at FCIS - ASU
(4th semester)
Why we need Data structure ?🤔
Data structures make it easy for users to access and work with the data they need in appropriate ways. Most importantly, data structures frame the organization of information so that machines and humans can better understand it.
There are two categories of data structures :
- Linear data structures
- Stack
- Queue
- Lists
- Non linear data structures
- Trees
- Graphs
📌Both will be discussed
List Of Implemented Algorithms:
- Stack
- Queue
- Array list
- Linked list
- Binary search tree
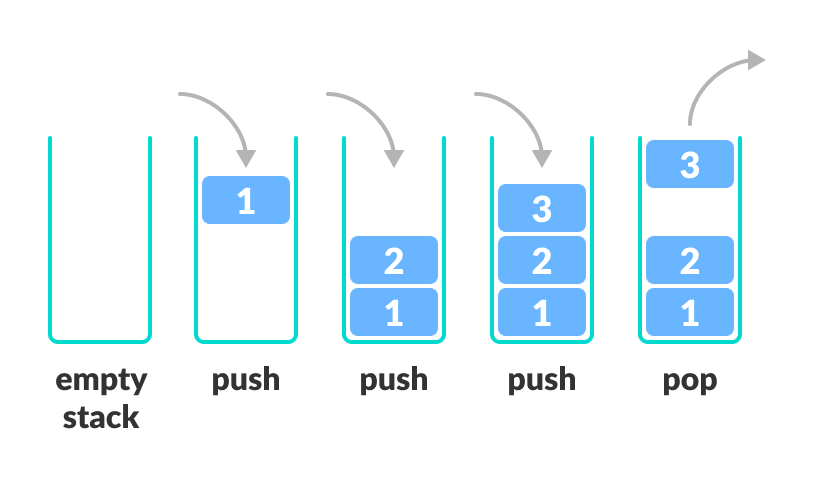
1️⃣Stack
What is Stack ?
The stack data structure is a linear data structure that accompanies a principle known as LIFO (Last In First Out) . Real-life examples of a stack are a deck of cards, piles of books, piles of money, and many more.
When we use Stack ?
Stack data structures are useful when the order of actions is important. They ensure that a system does not move onto a new action before completing those before. Here are some common examples where a stack is used:
- Reversing
- Undo/redo operations
- Backtracking
What is the complexity when using Stack ?
For the array-based implementation of a stack, the push and pop operations take constant time, i.e. O(1) , and it requires O(N) operations to display all elements of the Stack as we need to pop all elements in the stack .
Implementation of Stack can be done by using :
- Array (used in the repo)
- Linked list
Operations need to be implemented to create a stack :
- lenght : return number of elements in the stack
- Push : Add an element to the top of a stack
- Pop : Remove an element from the top of a stack
- Top : return the top element
- Empty : Check if the stack is empty
- Expand : increase the size of the array if Stack is full
STL used for Stack
Stack <int> S;
S.empty(); //return weather stack is empty or not
S.push(value); //Add an element to the top of a stack
S.pop(); //Remove an element from the top of a stack
S.size(); //return the size of the stack
S.top(); //return the top element
Problems to solve on stack
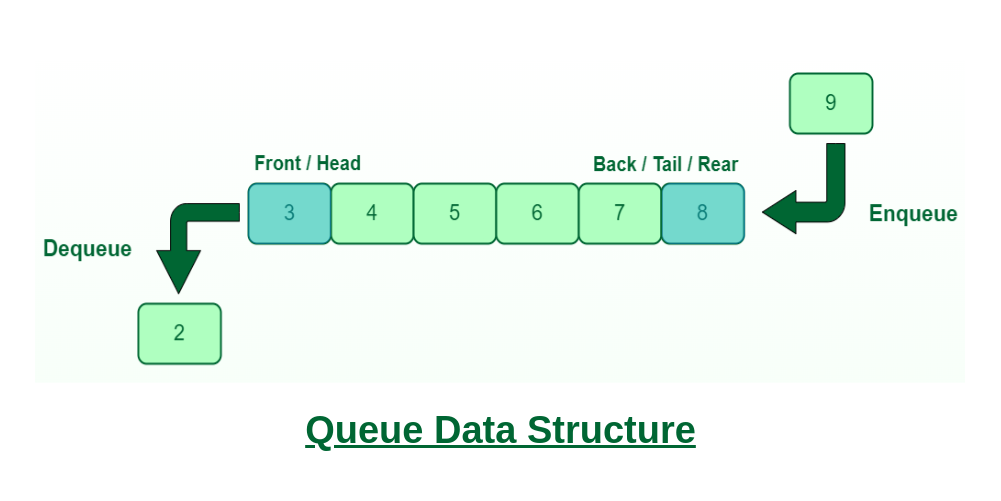
2️⃣Queue
What is Queue ?
A Queue is defined as a linear data structure that is open at both ends and the operations are performed in First In First Out (FIFO) order.
When we use Queue ?
The basic appeal of a queue is that is a data structure that guarantees order and it guarantees a fair order. The first element that entered the Queue is the first element to be dequeued .
What is the complexity when using Queue ?
For the array-based implementation of a Queue , the enqueue and dequeue operations take constant time, i.e. O(1) .
Implementation of Queue can be done by using :
- Array (used in the repo)
- Linked list
- Stack
Operations need to be implemented to create a queue :
- enqueue : Add element to the back
- dequeue : Remove an element from the front
- frontf : Return the front element
- backf : Return the back element
- lenthf : return no. of elements in the queue
- isempty : return true if queue is empty
- isfull : return true if the queue is full
STL used for Queue
queue Q;
deque Q;
Functionality
Q.empty();
Q.empty();
Returns whether the queue is empty
Q.pop();
Q.pop_front();
Removes the element at the front of the queue
Q.push();
Q.push_back();
Adds an element to the end of the queue
Q.size();
Q.size();
Returns the number of elements in the queue
Q.front();
Q.front();
Returns the front element
Q.back();
Q.back();
Returns the back element.
--
Q.pop_back();
Remove last element
--
Q.push_front();
Adds an element at the start
Problems to solve on Queue
3️⃣Array list
What is Arraylist ?
They are resizable arrays, also called dynamic arrays, are data structures that store elements in sequential order and whose size can be increased or decreased by adding or removing elements.
When we use Array list ?
ArrayLists are a type of collection that can be used to store various types of data. This means two different classes like string and integer can be stored together in a single collection. There are both advantages and disadvantages to ArrayLists.
What is the complexity when using arraylist ?
Operation
Time complexity
Insert at last index
O(1)
Insert at given index
O(N)
Search by value
O(N)
Get by index
O(1)
Remove by value
O(N)
Remove by index
O(N)
Operations need to be implemented to create a queue :
- Length : returns number of elements
- Append : Add an element at the end
- Expand : insert an element at last position in the arraylist
- At : returns the element at specified position
- DeleteAt : remove an element at specific position
- InsertAt : add an element at specific position
STL used for Arraylist
vector<int> V;
V.at(index); //returns the element at the specified position.
V.capacity(); //returns the size of the storage space currently allocated for the vector.
V.clear(); //Removes all elements from the vector
V.empty(); //Returns whether the vector is empty.
V.push_back(value); //Adds a new element at the end of the vector (increases size).
V.pop_back(); //Removes the last element in the vector (reduces size);
V.size(); // Returns the number of elements in the vector.
Problems to solve on Vector
4️⃣Linkedlist
What is Linkedlist ?
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers
When we use Linkedlist ?
- Linked Lists are used when the number of elements is not known in advance i.e. size is not known as linked lists support dynamic memory allocation.
- Linked Lists can be used for the manipulation of polynomials.
- Linked lists are used for performing arithmetic operations on long integers.
There are four key types of linked lists:
- Singly linked lists (our focus)
- Doubly linked lists
- Circular linked lists
- Circular doubly linked lists
What is the complexity when using Linkedlist ?
Operation
Time complexity
Insert at last index
O(1)
Insert at given index
O(N)
Search by value
O(N)
Get by index
O(N)
Remove by value
O(N)
Remove by index
O(N)
Operations need to be implemented to create a Singly Linkedlist :
- Length : returns number of elements.
- Append : Add an element at the end.
- At : returns the element at specified position.
- InsertAt : add an element at specific position.
- DeleteAt : remove an element at specific position
STL used for Linkedlist
list<int> L;
L.push_back(value); //Inserts a new element at the end of the list.
L.pop_back(); //Delete the element at the end of the list.
L.push_front(); //Inserts a new element at the beginning of the list.
L.pop_front(); //Delete the element at the beginning of the list.
L.empty() //Returns whether the list container is empty .
L.clear() //Removes all elements from the list container.
Problems to solve on List
5️⃣Binary Search Tree(BST)
What is Binary search tree (BST) ?
Binary Search Tree is a node-based binary tree data structure which has the following properties:
-
he left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the node’s key.
-
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
-
The left and right subtree each must also be a binary search tree.
**Types of BST : **
▶️ Full Binary Tree : a Binary Tree in which every node has 0 or 2 children .
▶️ Complete Binary Tree : has all levels completely filled with nodes except the last level and in the last level, all the nodes are as left side as possible.
▶️ Perfect Binary Tree : a Binary Tree in which all internal nodes have 2 children, and all the leaf nodes are at the same depth or same level.
▶️ Balanced Binary Tree : a Binary tree in which height of the left and the right sub-trees of every node may differ by at most 1.
▶️ Degenerate Binary Tree : a Binary Tree where every parent node has only one child node.
▶️ A skewed binary tree : a type of binary tree in which all the nodes have only either one child or no child.
When we use Binary Search Tree ?
a binary search tree is a data structure that allows for fast insertion, removal, and lookup of items while offering an efficient way to iterate them in sorted
order, For these reasons, we use binary search trees when we need efficient ways to access or modify a collection while maintaining the order of its elements.
What is the complexity when using Binary Search Tree ?
Operation
Time complexity (Average Complexity)
Access an element
θ(log(N))
Search for an element
θ(log(N))
Insert an element
θ(log(N))
Delete an element
θ(log(N))
And the worst case is O(N)
Operations need to be implemented to create a Binary Search Tree :
- Contains: returns true if “value” exists in the tree.
- Insert: adds a value to the tree.
- FindNode: Retrurn the address of a certain element in the tree if exist .
- Traverse: (display) displays all nodes in the tree .
- Inorder : Left, Root, Right (Ascending order)
- preOrder : Root, Left, Right
- postOrder : Left, Right, Root
STL used for BST
SET OR MAP (BOTH ARE BST STLs)
set <int> S;
//Some functions in Set
S.insert(val); //insert an element in the tree
S.begin(); //Returns an iterator to the first element in the set.
S.end(); //Returns an iterator to the theoretical element that follows the last element in the set.
S.size(); //Returns the number of elements in the set.
S.empty(); //Returns whether the set is empty.
S.clear(); //Removes all the elements from the set.
S.cbegin(); //Returns a constant iterator pointing to the first element in the container.
map<int> M;
//Some functions in Map
M.begin(); // Returns an iterator to the first element in the map.
M.size(); // Returns the number of elements in the map.
M.clear(); // Removes all the elements from the map.
M.count(); // Returns the number of matches to element with key-value ‘g’ in the map. –> O(log n).
Set vs Maps :
Set
Map
Set is used to store all the unique elements.
map is used to store all the unique elements.
set<data_type>name_of_set;
map<data_type , data_type>name_of_map;
It stores the elements in increasing order
It stores the elements in key , value pairs.
Set is implemented using Binary search tree.
Map is implemented using Balance Binary tree.
Sets are traversed using the iterators.
It is defined in #include header file.
Problems to solve on Binary Search Tree
Why we need Data structure ?🤔
Data structures make it easy for users to access and work with the data they need in appropriate ways. Most importantly, data structures frame the organization of information so that machines and humans can better understand it.
There are two categories of data structures :
- Linear data structures
- Stack
- Queue
- Lists
- Non linear data structures
- Trees
- Graphs
📌Both will be discussed
List Of Implemented Algorithms:
- Stack
- Queue
- Array list
- Linked list
- Binary search tree
1️⃣Stack
What is Stack ?
The stack data structure is a linear data structure that accompanies a principle known as LIFO (Last In First Out) . Real-life examples of a stack are a deck of cards, piles of books, piles of money, and many more.
When we use Stack ?
Stack data structures are useful when the order of actions is important. They ensure that a system does not move onto a new action before completing those before. Here are some common examples where a stack is used:
- Reversing
- Undo/redo operations
- Backtracking
What is the complexity when using Stack ?
For the array-based implementation of a stack, the push and pop operations take constant time, i.e. O(1) , and it requires O(N) operations to display all elements of the Stack as we need to pop all elements in the stack .
Implementation of Stack can be done by using :
- Array (used in the repo)
- Linked list
Operations need to be implemented to create a stack :
- lenght : return number of elements in the stack
- Push : Add an element to the top of a stack
- Pop : Remove an element from the top of a stack
- Top : return the top element
- Empty : Check if the stack is empty
- Expand : increase the size of the array if Stack is full
STL used for Stack
Stack <int> S;
S.empty(); //return weather stack is empty or not
S.push(value); //Add an element to the top of a stack
S.pop(); //Remove an element from the top of a stack
S.size(); //return the size of the stack
S.top(); //return the top elementProblems to solve on stack
2️⃣Queue
What is Queue ?
A Queue is defined as a linear data structure that is open at both ends and the operations are performed in First In First Out (FIFO) order.
When we use Queue ?
The basic appeal of a queue is that is a data structure that guarantees order and it guarantees a fair order. The first element that entered the Queue is the first element to be dequeued .
What is the complexity when using Queue ?
For the array-based implementation of a Queue , the enqueue and dequeue operations take constant time, i.e. O(1) .
Implementation of Queue can be done by using :
- Array (used in the repo)
- Linked list
- Stack
Operations need to be implemented to create a queue :
- enqueue : Add element to the back
- dequeue : Remove an element from the front
- frontf : Return the front element
- backf : Return the back element
- lenthf : return no. of elements in the queue
- isempty : return true if queue is empty
- isfull : return true if the queue is full
STL used for Queue
| queue Q; | deque Q; | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Q.empty(); | Q.empty(); | Returns whether the queue is empty |
| Q.pop(); | Q.pop_front(); | Removes the element at the front of the queue |
| Q.push(); | Q.push_back(); | Adds an element to the end of the queue |
| Q.size(); | Q.size(); | Returns the number of elements in the queue |
| Q.front(); | Q.front(); | Returns the front element |
| Q.back(); | Q.back(); | Returns the back element. |
| -- | Q.pop_back(); | Remove last element |
| -- | Q.push_front(); | Adds an element at the start |
Problems to solve on Queue
3️⃣Array list
What is Arraylist ?
They are resizable arrays, also called dynamic arrays, are data structures that store elements in sequential order and whose size can be increased or decreased by adding or removing elements.
When we use Array list ?
ArrayLists are a type of collection that can be used to store various types of data. This means two different classes like string and integer can be stored together in a single collection. There are both advantages and disadvantages to ArrayLists.
What is the complexity when using arraylist ?
| Operation | Time complexity |
|---|---|
| Insert at last index | O(1) |
| Insert at given index | O(N) |
| Search by value | O(N) |
| Get by index | O(1) |
| Remove by value | O(N) |
| Remove by index | O(N) |
Operations need to be implemented to create a queue :
- Length : returns number of elements
- Append : Add an element at the end
- Expand : insert an element at last position in the arraylist
- At : returns the element at specified position
- DeleteAt : remove an element at specific position
- InsertAt : add an element at specific position
STL used for Arraylist
vector<int> V;
V.at(index); //returns the element at the specified position.
V.capacity(); //returns the size of the storage space currently allocated for the vector.
V.clear(); //Removes all elements from the vector
V.empty(); //Returns whether the vector is empty.
V.push_back(value); //Adds a new element at the end of the vector (increases size).
V.pop_back(); //Removes the last element in the vector (reduces size);
V.size(); // Returns the number of elements in the vector.Problems to solve on Vector
4️⃣Linkedlist
What is Linkedlist ?
A linked list is a linear data structure, in which the elements are not stored at contiguous memory locations. The elements in a linked list are linked using pointers
When we use Linkedlist ?
- Linked Lists are used when the number of elements is not known in advance i.e. size is not known as linked lists support dynamic memory allocation.
- Linked Lists can be used for the manipulation of polynomials.
- Linked lists are used for performing arithmetic operations on long integers.
There are four key types of linked lists:
- Singly linked lists (our focus)
- Doubly linked lists
- Circular linked lists
- Circular doubly linked lists
What is the complexity when using Linkedlist ?
| Operation | Time complexity |
|---|---|
| Insert at last index | O(1) |
| Insert at given index | O(N) |
| Search by value | O(N) |
| Get by index | O(N) |
| Remove by value | O(N) |
| Remove by index | O(N) |
Operations need to be implemented to create a Singly Linkedlist :
- Length : returns number of elements.
- Append : Add an element at the end.
- At : returns the element at specified position.
- InsertAt : add an element at specific position.
- DeleteAt : remove an element at specific position
STL used for Linkedlist
list<int> L;
L.push_back(value); //Inserts a new element at the end of the list.
L.pop_back(); //Delete the element at the end of the list.
L.push_front(); //Inserts a new element at the beginning of the list.
L.pop_front(); //Delete the element at the beginning of the list.
L.empty() //Returns whether the list container is empty .
L.clear() //Removes all elements from the list container.Problems to solve on List
5️⃣Binary Search Tree(BST)
What is Binary search tree (BST) ?
Binary Search Tree is a node-based binary tree data structure which has the following properties:
-
he left subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys lesser than the node’s key.
-
The right subtree of a node contains only nodes with keys greater than the node’s key.
-
The left and right subtree each must also be a binary search tree.
**Types of BST : **
▶️ Full Binary Tree : a Binary Tree in which every node has 0 or 2 children .▶️ Complete Binary Tree : has all levels completely filled with nodes except the last level and in the last level, all the nodes are as left side as possible.▶️ Perfect Binary Tree : a Binary Tree in which all internal nodes have 2 children, and all the leaf nodes are at the same depth or same level.▶️ Balanced Binary Tree : a Binary tree in which height of the left and the right sub-trees of every node may differ by at most 1.▶️ Degenerate Binary Tree : a Binary Tree where every parent node has only one child node.▶️ A skewed binary tree : a type of binary tree in which all the nodes have only either one child or no child.When we use Binary Search Tree ?
a binary search tree is a data structure that allows for fast insertion, removal, and lookup of items while offering an efficient way to iterate them in sorted
order, For these reasons, we use binary search trees when we need efficient ways to access or modify a collection while maintaining the order of its elements.
What is the complexity when using Binary Search Tree ?
Operation Time complexity (Average Complexity) Access an element θ(log(N))Search for an element θ(log(N))Insert an element θ(log(N))Delete an element θ(log(N))And the worst case is O(N)
Operations need to be implemented to create a Binary Search Tree :
- Contains: returns true if “value” exists in the tree.
- Insert: adds a value to the tree.
- FindNode: Retrurn the address of a certain element in the tree if exist .
- Traverse: (display) displays all nodes in the tree .
- Inorder : Left, Root, Right (Ascending order)
- preOrder : Root, Left, Right
- postOrder : Left, Right, Root
STL used for BST
SET OR MAP (BOTH ARE BST STLs)
set <int> S; //Some functions in Set S.insert(val); //insert an element in the tree S.begin(); //Returns an iterator to the first element in the set. S.end(); //Returns an iterator to the theoretical element that follows the last element in the set. S.size(); //Returns the number of elements in the set. S.empty(); //Returns whether the set is empty. S.clear(); //Removes all the elements from the set. S.cbegin(); //Returns a constant iterator pointing to the first element in the container. map<int> M; //Some functions in Map M.begin(); // Returns an iterator to the first element in the map. M.size(); // Returns the number of elements in the map. M.clear(); // Removes all the elements from the map. M.count(); // Returns the number of matches to element with key-value ‘g’ in the map. –> O(log n).
Set vs Maps :
Set Map Set is used to store all the unique elements. map is used to store all the unique elements. set<data_type>name_of_set; map<data_type , data_type>name_of_map; It stores the elements in increasing order It stores the elements in key , value pairs. Set is implemented using Binary search tree. Map is implemented using Balance Binary tree. Sets are traversed using the iterators. It is defined in #include header file. Problems to solve on Binary Search Tree