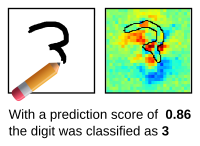
The Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP) algorithm explains a classifer's prediction specific to a given data point by attributing relevance scores to important components of the input by using the topology of the learned model itself.
The LRP Toolbox provides simple and accessible stand-alone implementations of LRP for artificial neural networks supporting Matlab and python. The Toolbox realizes LRP functionality for the Caffe Deep Learning Framework as an extension of Caffe source code published in 10/2015.
The implementations for Matlab and python are intended as a sandbox or playground to familiarize the user to the LRP algorithm and thus are implemented with readability and transparency in mind. Models and data can be imported and exported using raw text formats, Matlab's .mat files and the .npy format for python/numpy/cupy.
To try out either the python-based MNIST demo, or the Caffe based ImageNet demo in your browser, click on the respective panels:
Clone or download it from github!
After having obtained the toolbox code, data and models of choice, simply move into the subpackage folder of you choice -- matlab, python or caffe-master-lrp -- and execute the installation script (written for Ubuntu 14.04 or newer).
<obtain the toolbox>
cd lrp_toolbox/$yourChoice
bash install.sh
Make sure to at least skim through the installation scripts! For more details and instructions please refer to the manual.
We highly recommend building LRP for Caffe via the singularity image definition (You might regret doing something else outside of Ubuntu 14.04 LTS or Ubuntu 16.04 LTS...). In this case, we also recommend to only download the content of the singularity folder. Call
cd <toolbox_location>/singularity
singularity build --fakeroot --force caffe-lrp-cpu-u16.04.sif caffe-lrp-cpu-u16.04.def
and the go have a coffee. The resulting caffe-lrp-cpu-u16.04.sif is an (executable) Singularity image which allows you to process LRP (and other methods) for Caffe Models with
[singularity run] ./caffe-lrp-cpu-u16.04.sif -c CONFIGPATH -f FILELISTPATH -p OUTPUTPATH
Have a look at the manual for details.
When using (any part) of this toolbox, please cite our paper
@article{JMLR:v17:15-618,
author = {Sebastian Lapuschkin and Alexander Binder and Gr{{\'e}}goire Montavon and Klaus-Robert M{{{\"u}}}ller and Wojciech Samek},
title = {The LRP Toolbox for Artificial Neural Networks},
journal = {Journal of Machine Learning Research},
year = {2016},
volume = {17},
number = {114},
pages = {1-5},
url = {http://jmlr.org/papers/v17/15-618.html}
}
For further research and projects involving LRP, visit heatmapping.org
Also, consider paying https://github.com/albermax/innvestigate a visit! Next to LRP, iNNvestigate efficiently implements a hand full of additional DNN analysis methods and can boast with a >500-fold increase in computation speed when compared with our CPU-bound Caffe implementation!
- a slightly updated singularity image
.def-file - formula 11 now implements the vanilla backprop gradient
- formula 99 is now the only variant implementing Sensitivity Analysis
- update to python 3
- updated treatment of softmax and target class
- lrp_aware option for efficient calculation of multiple backward passes (at the cost of a more expensive forward pass)
- custom colormaps in render.py
- gpu support when cupy is installed. this is an optional feature. without the cupy package, the python code will execute using the cpu/numpy.
- updated the installation config
- new recommended formula types 100, 102, 104
- support for Guided Backprop via formula type 166
- new python wrapper to use lrp in pycaffe
- pycaffe demo file
- bugfixes
- singularity image definition for building a hassle-free OS-agnostic command line executable
- Convnets with Sum- and Maxpooling are now supported, including demo code.
- LRP-parameters can now be set for each layer individually
- w² and flat weight decomposition implemented.
- Minimal output versions implemented.
- Matthew Zeiler et al.'s Deconvolution, Karen Simonyan et al.'s Sensitivity Maps, and aspects of Grégoire Montavon et al.'s Deep Taylor Decomposition are implemented, alongside the flat weight decomposition for uniformly projecting relevance scores to a neuron's receptive field have been implemented.
- Various optimizations, refactoring, bits and pieces here and there.