Angular 8 has arrived and with it a bunch of workflow and a new set of powerful features that Angular developers will appreciate like the core framework, Angular Material library, and the Command Line Interface. They have enabled major launch partner as Angular Console for running Angular projects, #angular/fire for integrating Firebase with Angular, StackBlitz integrated IDE and NativeScript for building native mobile apps with Angular. let’s go over and summarize what are new features introduced in Angular 8 as well as how upgrading your Angular 7 apps to Angular 8.
Spring Boot is Spring's convention-over-configuration solution for creating stand-alone, production-grade Spring-based Applications that you can "just run". It is preconfigured with the Spring team's "opinionated view" of the best configuration and use of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need very little Spring configuration.- It is very easy to develop Spring Based applications with Java or Groovy.
- It reduces lots of development time and increases productivity.
- It avoids writing lots of boilerplate Code, Annotations and XML Configuration.
- It is very easy to integrate Spring Boot Application with its Spring Ecosystem like Spring JDBC, Spring ORM, Spring Data, Spring Security etc.
- It follows “Opinionated Defaults Configuration” Approach to reduce Developer effort
- It provides Embedded HTTP servers like Tomcat, Jetty etc. to develop and test our web applications very easily.
- It provides CLI (Command Line Interface) tool to develop and test Spring Boot(Java or Groovy) Applications from command prompt very easily and quickly.
- It provides lots of plugins to develop and test Spring Boot Applications very easily using Build Tools like Maven and Gradle
- It provides lots of plugins to work with embedded and in-memory Databases very easily.
The main goal of Spring Boot Framework is to reduce Development, Unit Test and Integration Test time and to ease the development of Production ready web applications very easily compared to existing Spring Framework, which really takes more time.
- To avoid XML Configuration completely
- To avoid defining more Annotation Configuration(It combined some existing Spring Framework Annotations to a simple and single Annotation)
- To avoid writing lots of import statements
- To provide some defaults to quick start new projects within no time.
- To provide Opinionated Development approach.
By providing or avoiding these things, Spring Boot Framework reduces Development time, Developer Effort and increases productivity.
MongoDB is a cross-platform document-oriented database program. Classified as a NoSQL database program, MongoDB uses JSON-like documents with schema. MongoDB is developed by MongoDB Inc. and licensed under the Server Side Public License (SSPL).- First and foremost, it is very easy to install and setup the MongoDB.
- The very basic feature of MongoDB is that it is a schema-less database. No schema migrations anymore. Since MongoDB is schema-free, your code defines your schema.
- The ability to derive a document-based data model is one of the most attractive advantages of MongoDB. Because, the way it stores the data in the form of BSON (Binary JSON), ruby hashes etc, helps to store the data in a very rich way while being capable of holding arrays and other documents.
- The document query language supported by MongoDB plays a vital role in supporting dynamic queries.
- Very easy to scale.
- Due to the structuring (BSON format - key value pair) way of the data in MongoDB, no complex joins are needed.
- Performance tuning is absolutely easy compared to any relational databases.
- No need of mapping the application objects to the data objects.
- Enables faster access of the data due to its nature of using the internal memory for the storage.
- Since, it is a NOSQL database, then it is obviously secure because no sql injection can be made.
- MongoDB can also be used as a file system, which helps in easier way of load balancing.
- MongoDB supports, the search by regex and fields as well.
- MongoDB can be run as windows service as well.
- Good amount of documentation is available.
- MongoDB does not require a VM to be run.
- MongoDB follows regular release cycle of its newer versions.
- The support for Sharding is one of its key feature. Sharding is the process of storing the data in different machines and MongoDB's ability to process the data, as and when the size of the data grows. This results in the horizontal scaling. With sharding, more amount of data can be written and read back as and when there is an increase in the data growth.
The term representational state transfer was introduced and defined in 2000 by Roy Fielding in his doctoral dissertation. Fielding's dissertation explained the REST principles that were known as the "HTTP object model" beginning in 1994, and were used in designing the HTTP 1.1 and Uniform Resource Identifiers (URI) standards. The term is intended to evoke an image of how a well-designed Web application behaves: it is a network of Web resources (a virtual state-machine) where the user progresses through the application by selecting resource identifiers such as http://www.example.com/articles/21 and resource operations such as GET or POST (application state transitions), resulting in the next resource's representation (the next application state) being transferred to the end user for their use.
-
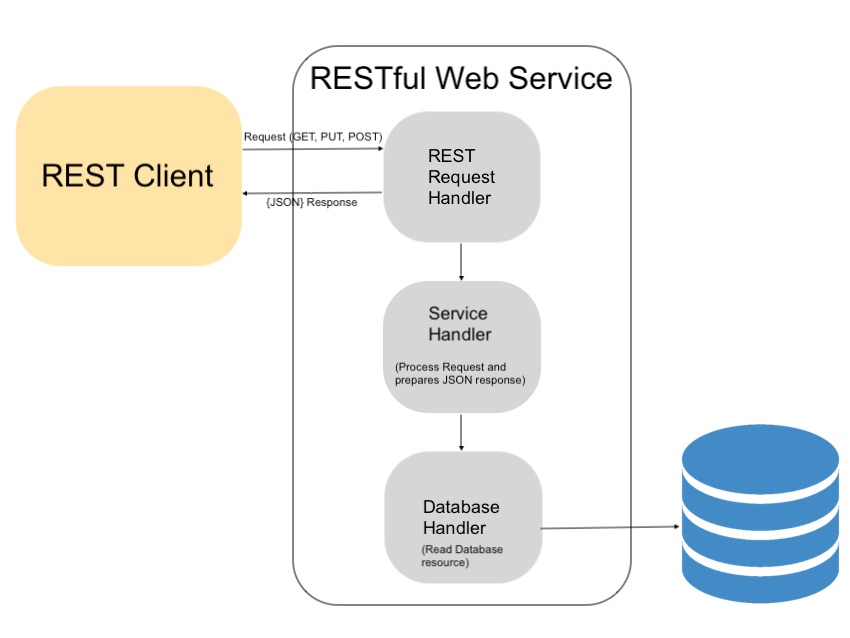
Resource identification through URI : A RESTful web service exposes a set of resources that identify the targets of the interaction with its clients. Resources are identified by URIs, which provide a global addressing space for resource and service discovery. See The @Path Annotation and URI Path Templates for more information.
-
Uniform interface : Resources are manipulated using a fixed set of four create, read, update, delete operations: PUT, GET, POST, and DELETE. PUT creates a new resource, which can be then deleted by using DELETE. GET retrieves the current state of a resource in some representation. POST transfers a new state onto a resource. See Responding to HTTP Methods and Requests for more information.
-
Self-descriptive messages : Resources are decoupled from their representation so that their content can be accessed in a variety of formats, such as HTML, XML, plain text, PDF, JPEG, JSON, and others. Metadata about the resource is available and used, for example, to control caching, detect transmission errors, negotiate the appropriate representation format, and perform authentication or access control. See Responding to HTTP Methods and Requests and Using Entity Providers to Map HTTP Response and Request Entity Bodies for more information.
-
Stateful interactions through hyperlinks : Every interaction with a resource is stateless; that is, request messages are self-contained. Stateful interactions are based on the concept of explicit state transfer. Several techniques exist to exchange state, such as URI rewriting, cookies, and hidden form fields. State can be embedded in response messages to point to valid future states of the interaction. See Using Entity Providers to Map HTTP Response and Request Entity Bodies and “Building URIs” in the JAX-RS Overview document for more information.
Maven is a build automation tool used primarily for Java projects.
Maven addresses two aspects of building software: first, it describes how software is built, and second, it describes its dependencies. Unlike earlier tools like Apache Ant, it uses conventions for the build procedure, and only exceptions need to be written down. An XML file describes the software project being built, its dependencies on other external modules and components, the build order, directories, and required plug-ins. It comes with pre-defined targets for performing certain well-defined tasks such as compilation of code and its packaging.
Maven dynamically downloads Java libraries and Maven plug-ins from one or more repositories such as the Maven 2 Central Repository, and stores them in a local cache. This local cache of downloaded artifacts can also be updated with artifacts created by local projects. Public repositories can also be updated.
- Eases the building process for any project.
- It maintains a uniformity along the entire build process.
- It’s very important to understand the project that we are working on. It provides Comprehensive information about the project.
- To ensure quality in a project, it’s necessary to develop it in the best possible manner and It provides the guidelines to do just that.
- Often in a project, it’s required to migrate to new features and with Maven, the migration is simplified.