web_api_base is a npm packaged that allows to create web-apis like MVC of .NET
npm install web_api_baseFirst of all we need implement the abstract class Application. After that, we need to create some controllers and they must inherit the abstract class ControllerBase.
We can create a controller using the create-controller command :
npx create-controllerimport { ControllerBase, Route, GET } from "web_api_base";
@Route()
export default class SampleController extends ControllerBase
{
@GET()
public Hello() : ActionResult
{
return this.OK({message: "Hello Word!"})
}
}We can create a app using the create-application command :
npx create-application import SampleController from "./controllers/SampleController ";
import { ControllerBase, Application, IApplicationConfiguration, DependecyService } from "web_api_base";
export default class App extends Application
{
public override Configure(appConfig: IApplicationConfiguration): void
{
//allow CORS
this.UseCors();
//if the controlles follow the naming rules, the method UseControllers will automatically append them
this.UseControllersAsync();
}
}import Application from './Application';
new Application().StartAsync();Consider this abstraction of a service and some imnplementations
export abstract class SampleServiceAbstract
{
abstract DoSomething() : void;
}
export class SampleService extends SampleServiceAbstract
{
public DoSomething(): void {
console.log("Doing in SampleServices");
}
}
export class GenericService<T>
{
public SomeGenericResult<T>(obj : T) {
console.log("typeof obj: " + typeof obj);
}
}We can use the DI service like this
import { ControllerBase, Route, GET, Inject } from "web_api_base";
import {SampleServiceAbstract, GenericService } from '../services/SampleService.ts';
@Route()
export default class SampleController extends ControllerBase
{
@Inject() // say to DI that this property will be inject on the instance
public SomeDepency : SampleServiceAbstract;
@Inject() // say to DI that this property will be inject on the instance
//the type argument do not exists on runtime, on .js result files. The DI system will work fine and we
//will still have the type check on development time
public SomeGenericDepency : GenericService<string> ;
constructor(someDependecy : SampleServiceAbstract, someGenericDepency: GenericService<string>)
{
super();
this.SomeDepency = someDependecy ;
this.SomeGenericDepency = someGenericDepency;
this.SomeGenericDepency.SomeGenericresult("Test") // typeof obj: string
//this.SomeGenericDepency.SomeGenericresult(10) // compiler error
}
@GET()
public Hello() : ActionResult
{
return this.OK({message: "Hello Word!"})
}
}And we can register our dependecies in Application ConfigureAsync method
import { Application, IApplicationConfiguration} from "web_api_base";
import { SampleService, SampleServiceAbstract, GenericService } from './service/SampleService';
export default class App extends Application
{
constructor()
{
super();
}
public override async ConfigureAsync(appConfig: IApplicationConfiguration): Promise<void>
{
this.UseCors();
//DI AddScoped, AddTransient and AddSingleton
appConfig.AddScoped(SampleServiceAbstract, SampleService);
appConfig.AddScoped(GenericService) // will register for all generic type arguments
//will register only for GenericService<User>. We need use @InjectTypeArgument(User) on dependecy
//to work fine
//appConfig.AddGenericScoped(GenericService, User)
//will register only for GenericService<User>. We need use @InjectTypeArgument(User) on dependecy
//to work fine
//appConfig.AddGenericScoped(GenericService, undefined, undefined, typeArgument =>
//{
// here we can determine how to create the instance. We have access of type argument on typeArgument
// argument. After this function execution, the instance will pass for DI pipeline to get all
// dependecies
//})
this.UseControllers();
}
}Create a GET endpoint
Create a PUT endpoint
Create a POST endpoint
Create a DELETE endpoint
All instances of Controller was the default HTTP response status code response method implementeds
Send status 200 and a optional body
Send status 201 and a optional body
Send status 202 and a optional body
Send status 204 and a optional body
Send status 400 and a optional body
Send status 401 and a optional body
Send status 403 and a optional body
Send status 404 and a optional body
Send status 500 and a optional body
Send a status code and a optional body
Append a delegate to execute before the controller´s action
@Route("/status")
@UseBefore(async context =>
{
if(context.Request.headers["token"] != "we have access to request object")
{
context.Response.json({Message : "we have access to response object"});
return;
}
else
return await context.Next(); // call next function in the pipeline
})
export default class StatusController extends ControllerBase
{Append a delegate to execute after the controller´s action
@Route("/status")
@UseAfter(async actionResult =>
{
if(actionResult.Exception) // if a exception was launched
{
actionResult.Response.status(500); // we can access the original request
actionResult.Response.json({Error : actionResult.Exception.Message});
return;
}
actionResult.Response.status(200); // we can access the original response
actionResult.Response.json(actionResult.Result); // we can acess the return of controller´s action
})
export default class StatusController extends ControllerBase
{Define that the request must have some header
@Route("/status")
@UseHeader('api_token')
export default class StatusController extends ControllerBase
{Extract a method parameter type instance from body of request
{
"Name": "Adriano Marino Balera",
"Email": "adriano@gmail.com",
"Age" : 30
} @POST()
public async InsertAsync(@FromBody()user : User) : Promise<User>
{
return await this._service.AddAsync(user);
}In the example above, the model binding system will cast the body in a intance of type User.
We can extract some part of body using named FromBody args: @FromBody('user'). The model binding system will use the 'user' property of body json.
{
"user" :
{
"Name": "Adriano Marino Balera",
"Email": "adriano@gmail.com",
"Age" : 30
}
}Extract the method parameter from query string of request
@GET()
public async GetByIdAsync(@FromQuery()id : number) : Promise<OKResult<User>>
{
return this.OK(await this._service.GetByIdAsync(id));
} In the example above, the model binding system will get the first query argument of request. We can also determine the name of parameter: @FromQuery('id').
Extract a method File(web_api_base) type parameter from multipart/form-data request
@POST()
public async InsertAsync(@FromFiles()file: File) : Promise<User>
{
return await this._service.MoveFiles(file, newPath);
}import { ControllerBase, Route, POST, PUT, DELETE, GET, Inject, Validate, FromBody, FromQuery } from "web_api_base";
import AbstractUserService from "../core/abstractions/AbstractUserService";
import User from "../core/entities/User";
@Validate()
@Route('/v1/users/')
export default class UserController extends ControllerBase
{
@Inject()
private _service : AbstractUserService;
constructor(service : AbstractUserService)
{
super();
this._service = service;
}
@GET("list")
public async GetAllAsync() : Promise<OKResult<User[]>>
{
return this.OK(await this._service.GetAllAsync());
}
@GET("permissions")
public async GetAllPermissionsAsync() : Promise<OKResult<Permission>>
{
return this.OK(await this._service.GetAllPermissions());
}
@GET()
public async GetByIdAsync(@FromQuery("id")id : number) : Promise<OKResult<User>>
{
return this.OK(await this._service.GetByIdAsync(id));
}
@POST()
public async InsertAsync(@FromBody()user : User) : Promise<CreatedResult<User>>
{
return this.Created(await this._service.AddAsync(user));
}
@PUT()
public async UpdateAsync(@FromBody()user : User, ) : Promise<ActionResult>
{
if(user.Id == undefined || user.Id <= 0)
return this.BadRequest({ Message : "The ID must be greater than 0"});
return this.OK(await this._service.UpdateAsync(user));
}
@DELETE()
public async DeleteAsync(@FromQuery()id : number) : Promise<ActionResult>
{
let del = await this._service.GetByIdAsync(id);
if(!del)
return this.NotFound();
return this.OK(await this._service.DeleteAsync(del));
}
}Say that all arguments from model bind will be validated before injected on the controller action. This decorator must be used in the controller declaration.
@Validate()
@Route('v1/users/')
export default class UserController extends ControllerBaseDetermine whether a property of a class is required
Determine the maximun value of a number property
Determine the minimun value of a number property
Determine the maximun number of characters of a string
Determine the minumun number of characters of a string
Determine the pattern expression to validate the string property
Determine the delegate used to validate the property
import {Required, MaxLenght, MinLenght, Rule, Max, Min, Regex} from 'web_api_base';
export default class ValidatedObject
{
@Max(10)
public MaxValue : number;
@Min(10)
public MinValue : number;
@Min(10)
@Max(20)
public Range: number;
@Regex(/^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/)
public RegExp : string;
@Required()
public Required : string;
@MaxLenght(20)
public MaxLenght : string;
@MinLenght(10)
public MinLenght : string;
@Rule<string[]>(p => p.length > 5)
public Permissions : string[];
constructor()
{
this.MaxValue = -1;
this.MinValue = -1;
this.Range = -1;
this.Required = "";
this.MaxLenght = "";
this.MinLenght = "";
this.RegExp = "";
this.Permissions = [];
}
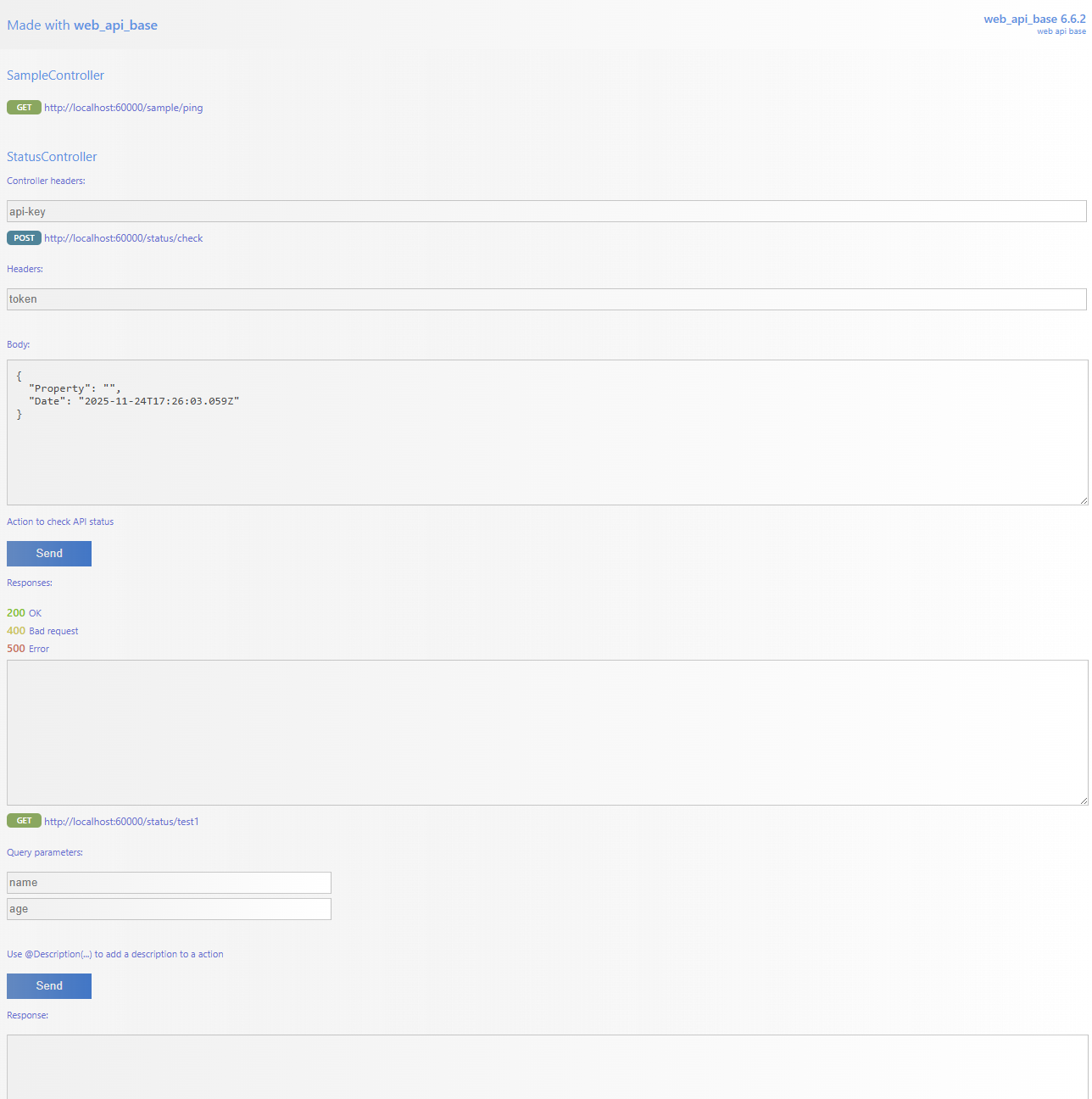
}We can create a API playground(host/playground) using the Aplication.CreateDocumentation method inside the Application.ConfigureAsync
public override async ConfigureAsync(appConfig: IApplicationConfiguration): Promise<void>
{
this.UseCors();
await this.UseControllersAsync();
appConfig.AddScoped(SampleServiceAbstract, AnotherService);
if(Application.DEBUG)
this.CreateDocumentation();
} We have some decorators to add a more information to our auto-generated documentation
Add a header field to a controller. All requests will have this header on it
Add a header field to a controller´s action
Add a description text on a action
Add a json template as a placeholder of body field. We can use if we want manually define the json, because, the framework can create the json template base on the argument type of action method
Explain all the possibles rsponses of a controller´s action. We can use this decorator many times we need to explain all possible resposes
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Please make sure to update tests as appropriate.