SURE-GB: Identifying Stereotypical, Under-REpresentational, and Algorithmic Gender Bias in Machine Translation
SURE-GB aims to build an automated service that identifies occupation-related under-representational, stereotypical, and algorithmic gender bias in machine translation, targeting English and French and lower resource languages, i.e., Greek. The proposed method involves creating a curated knowledge graph that a) encodes standardised knowledge and data for occupations (based on data and hierarchies from EU-LFS, the ESS, and the International Classification of Occupations-ISCO), b) incorporates statistics for occupation-related gendered language usage derived from linguistic corpora. Our goal is to develop a ready-to-use machine learning toolkit, that utilises the above knowledge to detect and categorise gender biases for: a) providing actionable recommendations for improvement, b) establishing guidelines for unbiased language translation, and c) raising awareness of gender biases in machine translation systems.
Script name: occ_models.py
This script provides functionality to extract and identify occupations mentioned in a given text using two methods:
- Local Model (HF_Model) – Uses a Hugging Face model to find occupations in the input text.
- AWS Model (find_occupations_aws) – Leverages an AWS Bedrock model to achieve the same.
Both methods analyze the input text and return any detected occupation titles along with brief definitions. The script is useful for tasks where you need to extract profession-related information from raw text.
transformersboto3
Install via:
pip install transformers boto3-
Local Model:
from occ_models import HF_Model model = HF_Model(hf_path) model.find_occupations(text)
-
AWS Model:
from occ_models import find_occupations_aws find_occupations_aws(text, hf_path, aws_model_id)
For the aws the hf path is required to ensure proper tokenization.
Make sure to set your AWS credentials in the environment before using the AWS model:
os.environ['aws_access_key_id'] = 'your_access_key'
os.environ['aws_secret_access_key'] = 'your_secret_key'The Knowledge class is designed to facilitate the handling of occupational definitions and their retrieval from a dataset based on the International Standard Classification of Occupations (ISCO-08). It primarily interacts with a CSV file containing occupational data and provides methods to search for and retrieve occupation descriptions.
-
__init__(self, filename, column):- Initializes the class by reading a CSV file (specified by
filename) that contains occupational information, using a specified column to retrieve the text data. - The CSV file is loaded into a pandas DataFrame, and the values from the selected
columnare used to create a searchable index via theSearchclass for efficient retrieval of occupation descriptions.
- Initializes the class by reading a CSV file (specified by
-
connect(self, descr, top_k=5):- Searches the indexed occupational descriptions for the input
descr(a description), returning the topkresults (default is 5). - Utilizes the
Searchclass to perform the search and returns the most relevant occupational matches.
- Searches the indexed occupational descriptions for the input
-
describe_occ(self, index):- Given an index (row number), this method retrieves and formats the detailed information of an occupation from the CSV file.
- The details include the occupational level, ISCO 08 code, English title, and definition, formatted as a multi-line string.
-
describe_occ_dict(self, index):- Similar to
describe_occ(), but instead of returning a formatted string, it returns the occupation details in a dictionary format. - The dictionary contains keys such as
"level","title EN","definition", and"ISCO 08 Code"for easy access and further manipulation.
- Similar to
This class allows for efficient search and retrieval of occupational definitions, making it useful for tasks such as analyzing occupation data or mapping occupations to gender biases in various studies.
Here’s an explanation of the code you provided, broken down to help understand the steps and how to use it:
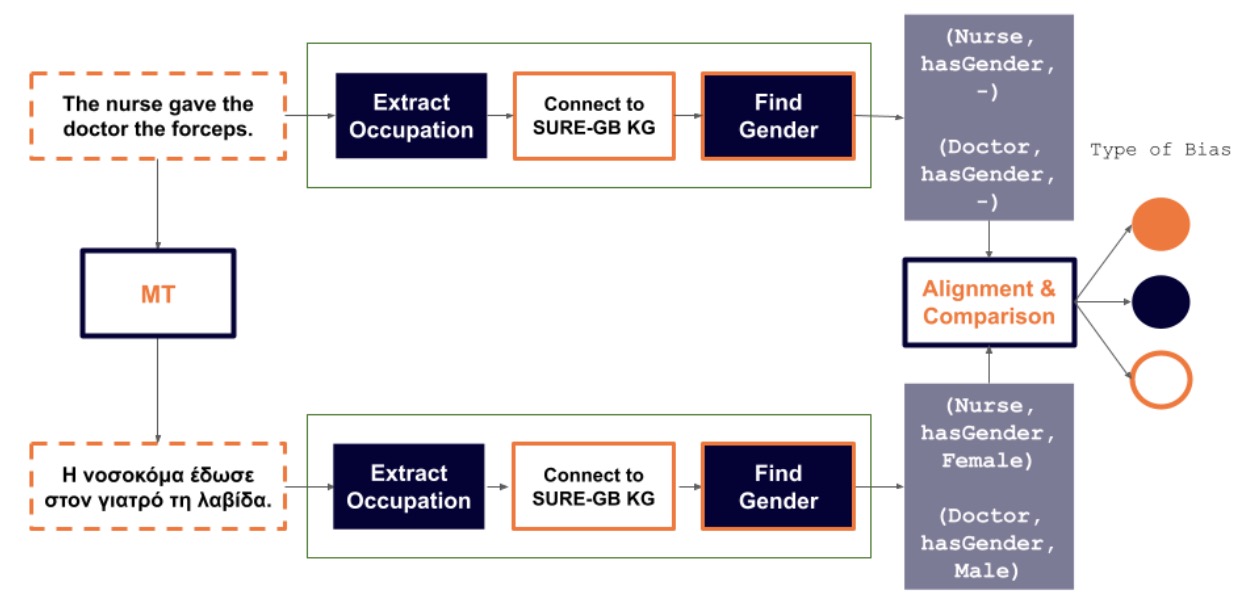
This Python script uses machine learning models and natural language processing (NLP) to:
- Extract occupations mentioned in text.
- Identify the gender associated with those occupations.
- Align corresponding words between different translations of the same text, and detect shifts in gender representation.
- HF_Model, find_occupations_aws: Used to identify occupations in the provided text.
- extract_occupations_from_resp, Knowledge: Utility functions to process LLM responses and work with an occupation database.
- gender: Module that handles gender identification.
- transformers (BERT): Tokenization and alignment of words using the BERT multilingual model.
You have three pieces of text representing the same content in three languages:
- English (source text): "A lawyer and a butcher."
- Greek (target text): "Ένας δικηγόρος και ένας χασάπης."
- French: An additional text for potential future use (commented out).
- Create Language Models: Instantiate objects for English, Greek, and French language processing using custom NLP models (
el,en, andfr). - Load Occupation Knowledge Base: The
Knowledgeobject is created using a CSV file containing occupation definitions (ISCO-08-EN.csv).
This function takes in text, the corresponding language model, and the knowledge base, and then:
- Find Occupations: Uses a function (
find_occupations_aws) to extract occupations from the text. - Match Definitions: Connects the occupations found with their definitions from the knowledge base.
- Set NLP Model for Gender Detection: Depending on the language, the appropriate NLP model is selected (English, Greek, or French).
- Identify Gender: It uses a function (
find_gender) to determine the gender for each occupation based on the text and checks for coreferences where necessary. - Compile Results: Collects the information (occupation title, probability, definition, and gender) into a structured response for each occupation.
The function align() aligns words between the source text (English) and the target text (Greek). It uses:
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) model to convert words into token embeddings.
- Softmax Layer: Applies softmax to find similarities between the source and target word tokens.
- Alignment Mapping: Creates a mapping between words in the source and target language that have a high alignment score (threshold).
- Mapping Words Between Languages: After aligning the words between the source and target texts, the function checks for potential shifts in gender representation between the two texts.
- Gender Comparison: It compares the gender assigned to the same occupation in the source and target text, and if a mismatch is found (i.e., a "gender shift"), it prints out a message indicating the detected shift.
- Extract Occupations: The script first extracts occupations from both the source and target texts using the
extract_occupations_and_gender()function. - Align Words: The
align()function aligns the source and target text words using the BERT model. - Detect Gender Shifts: Finally, the script compares the genders of aligned words and outputs any shifts in gender representation between the languages.
An example of the full pipeline is given in Example Pipeline.ipynb
Mastromichalakis, O. M., Filandrianos, G., Tsouparopoulou, E., Parsanoglou, D., Symeonaki, M., & Stamou, G. (2024). GOSt-MT: A Knowledge Graph for Occupation-related Gender Biases in Machine Translation. arXiv preprint arXiv:2409.10989.