X2C provides a meta-language for turning xml-formatted data into cypher commands ready to be imported into your Neo4j database.
Sample usage of this tool can be seen here:
If this is useful to you, feel free to drop a message in the issues or at my email. I'd be glad to know about your project !
- Handles simple and complex scenarios
- Syntax and XML Processing debugging
- Variables, scopes, ...
- User functions
- Type chaining
- Auto variable definition with "id" type
- Readability: Modular definitions, Comments, ...
- More !
- Download X2C
- Install dependency:
pip install xmltodict - Create schema and python module
- Run module
- Import generated *.cql in Neo4j using
neo4j-shell -file <file>
<root> ::= <mode> | <mode> <root>
<mode> ::= <type_mode> | <structure_mode> | <schema_mode> | <comment>
<type_mode> ::= "types:" NEWLINE [INDENT <type_list> DEDENT]
<structure_mode> ::= "structures:" NEWLINE [INDENT <node_rel_list> DEDENT]
<schema_mode> ::= "schema:" NEWLINE [INDENT <node_rel_list> DEDENT]
<comment> ::= [WHITESPACE] "#" <sequences-of-characters>
<type_list> ::= <type> NEWLINE | <type> NEWLINE <type_list>
<node_rel_list> ::= <node_rel> NEWLINE | <node_rel> NEWLINE <node_rel_list> | <node> NEWLINE INDENT <node_rel_list> DEDENT
<node_rel> ::= <node> | <relationship>
<type> ::= <id> ":" <path> "->" <return_type>
<node> ::= ["?"] [<id>] ":" [<id>] "(" [<property_list>] ")" ["[]"] ["->" <return_type> "(" [<property_list>] ")"] [<option_list>]
<relationship> ::= <id> "(" [<property_list>] ")-[" <id> "(" [<property_list>] ")]->" <id> "(" [<property_list>] ")"
<property_list> ::= <property> | <property> "," <property_list>
<property> ::= ["?" | "!"] [<lname>] ":" [<path>] ":" <return-type> [" as " <id>]
<path> ::= <aflid> | <aflid> ":" <path>
<option_list> ::= <option> | <option> <option_list>
<aflid> ::= <name> | <variable> | <literal> | <function> | <attribute> | <array>
<lid> ::= <name> | <variable> | <literal>
<id> ::= <name> | <variable>
<function> ::= "#{" <name> ["," <property_list>] "}"
<variable> ::= "${" <name> "}"
<attribute> ::= "@" <name>
<option> ::= "@MERGE" | "@CREATE"
<literal> ::= '"' <sequence-of-character> '"'
<array> ::= "[" <number> "]"
<return_type> ::= "str" | "int" | "float" | "boolean" | "id" | "idem"
<name> ::= <id_char> | <id_char> <name>
<id_char> ::= 'a' | .. | 'z' | 'A' | .. | 'Z' | '0' | .. | '9' | '_'
songs.xml:
<songs>
<song tags="rock alternative">
<title>Comfortably numb</title>
<artist>Pink Floyd</artist>
</song>
<song tags="trip-hop alternative">
<title>Again</title>
<artist>Archive</artist>
</song>
<song tags="trip-hop alternative">
<title>Collapse / Collide</title>
<artist>Archive</artist>
</song>
</songs>songs.schema:
structures:
:songs()
Song:song(id:->id, title:title->string, :#{parseTags, tags:@tags->string}->idem as Tags)[]
Artist:artist(id:->id, name:_->string)
Artist(id:${ArtistId}->id)-[AUTHORED()]->Song(id:${SongId}->id)
Tag:${Tags}(id:->id, name:_->string)[]@MERGE
Song(id:${SongId}->id)-[HAS_TAG()]->Tag(id:${TagId}->id)
schema:
:songs()->songs()
songs-commented.schema:
# Re-usable nodes definitions
"""structures:"""
# Opens the "songs" XML node.
# The left side of ":" is empty, this statement won't produce any node.
""" :songs()"""
# Let's break down this statement.
# "song:song"
# - Defines a node labeled "Song",
# - Maps it with the "song" XML node.
# "id:->id"
# - Adds an "id" attribute.
# - Its path is empty (":{path}->").
# - Its return type is "id", which is a special type.
# - When no path is defined, this acts similar to "serial" or "auto_increment" in SQL databases.
# "title:title->string" adds a "title" attribute.
# - Its path "title" maps the homonymous XML node <title>.
# - Return type is "string", which will convert the content of <title> accordingly.
# ":#{parseTags, tags:@tags->string}->idem as Tags"
# - Calls function "parseTags", which splits space-separated
# tags in a list.
# - Parameter 'tags' is passed with content of attribute 'tags' (@tags), which itself is a string
# - Return type of function is left untouched using 'idem'.
# - No identifier is specified before the first ":", this statement won't add a new attribute.
# - Final result is put in a variable named "Tags"
# "[]" declares this node as a collection, X2C will iterate over its elements
""" Song:song(id:->id, title:title->string, :#{parseTags, tags:@tags->string}->idem as Tags)[]"""
# Defines a node labeled "Artist", mapped to XML node "artist".
# "id"
# - Attribute is auto-generated.
# "name:_->string"
# - Adds a "name" attribute using current node content ('_')
# - Of type string.
""" Artist:artist(id:->id, name:_->string)"""
# Defines a relationship "AUTHORED"
# - Between node "Artist" with id "${ArtistId}",
# - And node "Song" with id "${SongId}".
# - These variables were automatically mapped using type "id" in their respective nodes.
""" Artist(id:${ArtistId}->id)-[AUTHORED()]->Song(id:${SongId}->id)"""
# Tag:${Tags}
# - Defines a node labeled "Tag"
# - Mapped to our previously generated list of tags.
# "name"
# - Attribute uses the immediate value ('_') of each item in the tag collection.
# "@MERGE"
# - Option will generate "MERGE" commands instead of default "CREATE" ones
""" Tag:${Tags}(id:->id, name:_->string)[]@MERGE"""
# Defines a relationship "HAS_TAG" between Song and Tag nodes.
""" Song(id:${SongId}->id)-[HAS_TAG()]->Tag(id:${TagId}->id)"""
# Main content -- what actually gets processed
"""schema:"""
# Use previously-defined nodes.
# In this simple example, the node definition could be written directly in schema, this is meant only for illustrative purposes.
""" :songs()->songs()"""songs.py:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# Xml : dictionary mapping
import xmltodict
# X2C
import CypherWriter
import Xml2Cypher
def parseTags(params):
return params['tags'].split(' ')
def main():
x2c = Xml2Cypher.parse('songs.schema')
nodeWriter = CypherWriter.CypherWriter('songs-nodes.cql')
rsWriter = CypherWriter.CypherWriter('songs-relationships.cql')
# CAPEC XML definitions
capecXMLFile = 'songs.xml'
capecXMLEncoding = 'utf8'
# Load XML file into a dictionary object
with open(capecXMLFile, encoding=capecXMLEncoding) as fd:
root = xmltodict.parse(fd.read())
x2c.apply(root, nodeWriter, rsWriter, { 'parseTags': parseTags })
nodeWriter.close()
rsWriter.close()
main()songs-nodes.cql:
CREATE (:Song{id: 1, title: "Comfortably numb"});
CREATE (:Artist{id: 1, name: "Pink Floyd"});
MERGE (:Tag{id: 1, name: "rock"});
MERGE (:Tag{id: 2, name: "alternative"});
[...]songs-relationships.cql:
MATCH (Artist28c7f06b05f12aacda482ab8357af7ba:Artist{id: 1})
MATCH (Song28c7f06b05f12aacda482ab8357af7ba:Song{id: 1})
CREATE (Artist28c7f06b05f12aacda482ab8357af7ba)-[:AUTHORED]->(Song28c7f06b05f12aacda482ab8357af7ba);
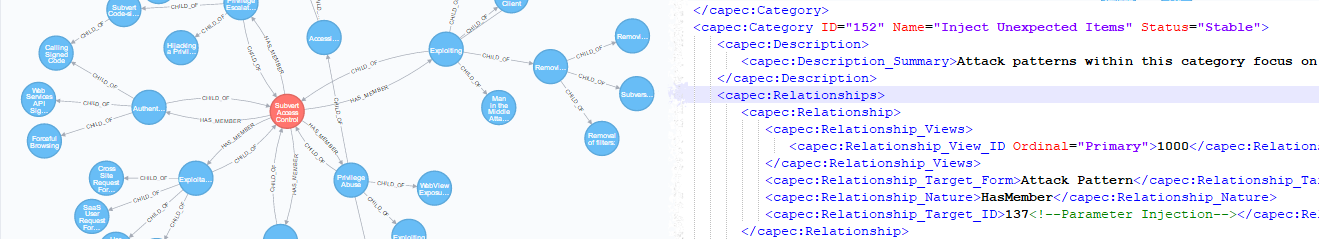
[...]For a more complex example, have a look at CAPEC graph
X2C is bundled with augmented debug and processing information which helps identifying and fixing schema (or code !) issues.
MIT
- Index creation (@INDEX option)
- Improve parser for edge cases
- Clean embedded functions call -- these were added as late-citizens and are only parsed at runtime
- Optimizations