The APM Server receives data from the Elastic APM agents and stores the data into Elasticsearch. The APM Server and the APM agents are currently experimental and under heavy development which might result in breaking changes. If you are trying out APM and have feedback or problems, please post them on the Discuss forum.
Read our announcement blog post.
To run Elastic APM for your own applications you need the following setup:
- Install & run Elasticsearch and Kibana
- Install, build and run the APM Server
- Install the Node.js or Python APM Agent. The agents are libraries in your application that run inside of your application process.
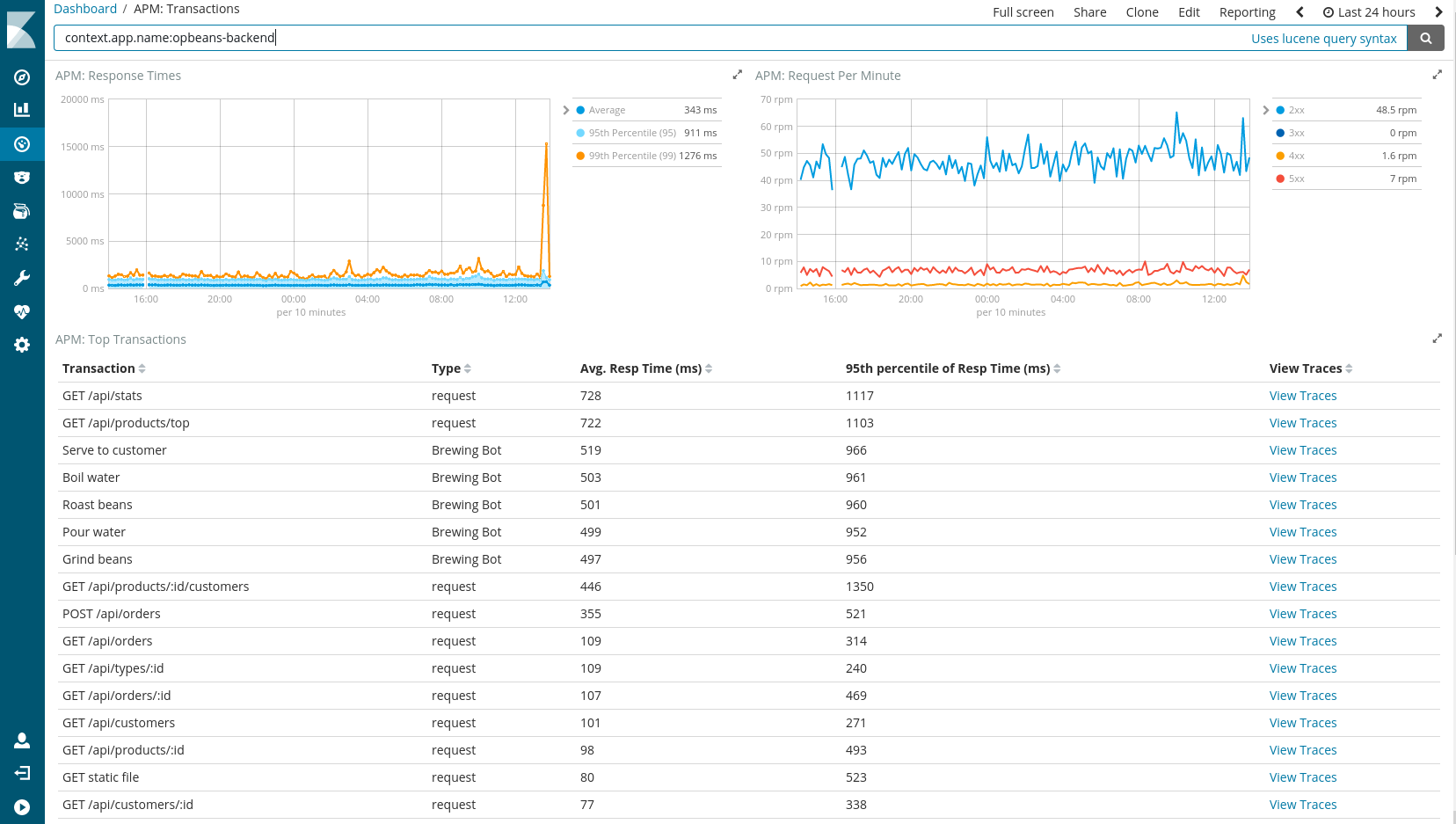
- Load UI dashboards into Kibana. The dashboards will give you an overview of application response times, requests per minutes, error occurrences and more.
By default the agents send data to localhost, the APM Server listens on localhost and sends data to Elasticsearch on localhost. If your setups involves multiple hosts, you need to adjust the configuration options accordingly.
The current UI consists of pre-built, customizable Kibana dashboards. The dashboards are shipped with the APM Server. For now, the dashboards have to be loaded manually with the following command:
curl --user elastic:changeme -XPOST http://localhost:5601/api/kibana/dashboards/import -H 'Content-type:application/json' -H 'kbn-xsrf:true' -d @./_meta/kibana/default/dashboard/apm-dashboards.json
Here's a screenshot of one of the dashboards:
- Golang 1.8.3
- Fork the repo with the Github interface and clone it:
cd ${GOPATH}/src/github.com/elastic/
git clone git@github.com:[USER]/apm-server.git
Note that it should be cloned from the fork (replace [USER] with your Github user), not from origin.
- Add the upstream remote:
git remote add elastic git@github.com:elastic/apm-server.git
To build the binary for APM Server run the command below. This will generate a binary in the same directory with the name apm-server.
make
To run APM Server with debugging output enabled, run:
./apm-server -c apm-server.yml -e -d "*"
For Testing check out the testing guide
Each beat has a template for the mapping in elasticsearch and a documentation for the fields
which is automatically generated based on etc/fields.yml.
To generate etc/apm-server.template.json and etc/apm-server.asciidoc
make update
To clean APM Server source code, run the following commands:
make fmt
To clean up the build directory and generated artifacts, run:
make clean
For further development, check out the beat developer guide.
The beat frameworks provides tools to crosscompile and package your beat for different platforms. This requires docker and vendoring as described above. To build packages of your beat, run the following command:
make package
This will fetch and create all images required for the build process. The hole process to finish can take several minutes.
The apm-server has two types of dependencies:
- Golang packages managed with
govendor - Beats framework managed with
cd _beats && sh update.sh
It is recommended to keep the version of the beats framework and libbeat in sync. To make an update of both, run make update-beats.
For details on govendor check the docs here.
To update beats to the most recent version from your go path for example use: govendor fetch github.com/elastic/beats/....
Govendor will automatically pick the files needed.
To update the beats framework run make update-beats. This will fetch the most recent version of beats from master and copy
the files which are needed for the framework part to the _beats directory. These are files like libbeat config files and
scripts which are used for testing or packaging.
To update the dependency to a specific commit or branch run command as following:
BEATS_VERSION=f240148065af94d55c5149e444482b9635801f27 make update-beats
The Documentation for the Intake-API and Elasticsearch can be found in docs/data.
make help