FedSepsis: A Federated Multi-Modal Deep Learning-Based Internet of Medical Things Application for Early Detection of Sepsis from Electronic Health Records Using Raspberry Pi and Jetson Nano Devices, Mahbub Ul Alam, Rahim Rahmani. Sensors 23, no. 2: 970, https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020970. (presentation slides)
-
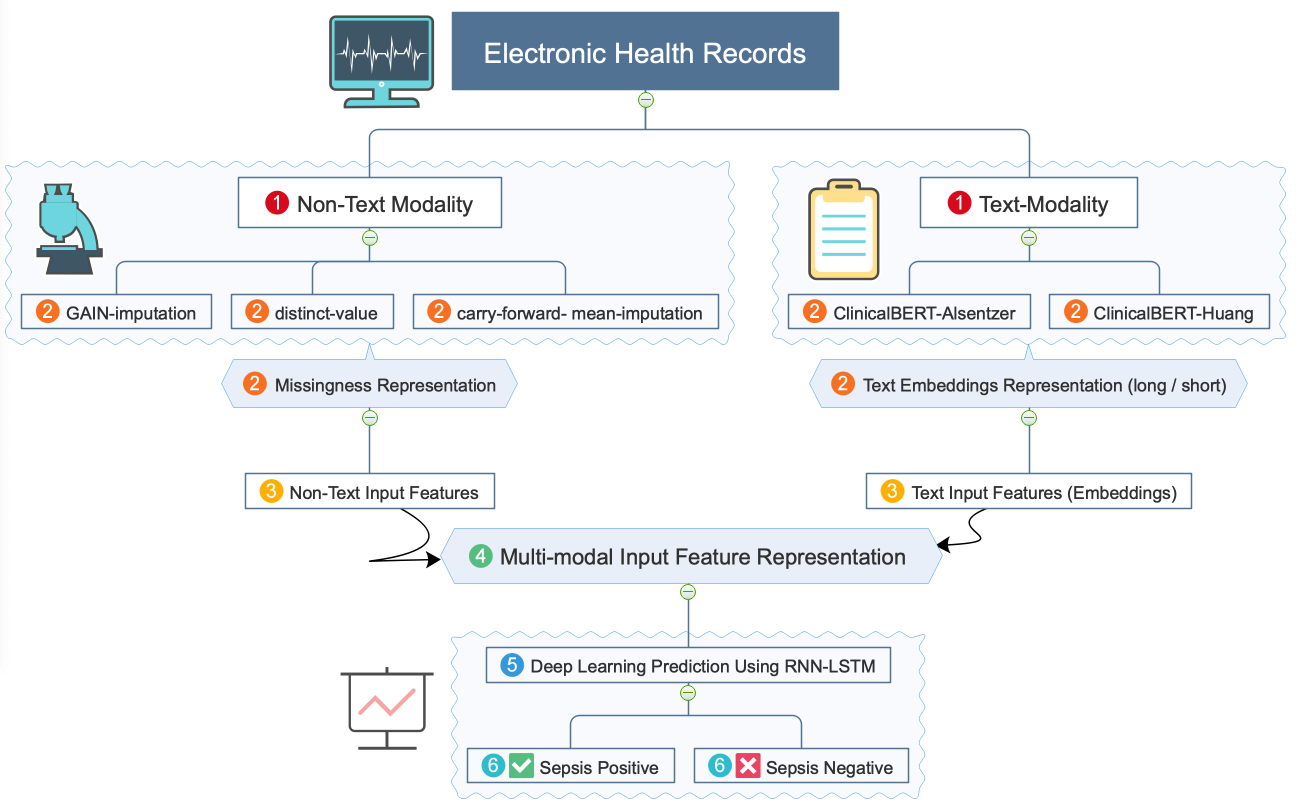
FedSepsis utilizes federated learning, a distributed machine learning approach to ensure security and privacy.
-
It uses multi-modality, that is, analyzing the data using different associated forms or modalities to ensure better performance and to mimic the real-world diagnosis process.
-
It uses a cutting-edge technique to handle missing non-text data. Missingness is a crucial issue in electronic health records.
-
It uses cutting-edge ClinicalBERT models to generate improved features from text data.
-
FedSepsis is practical and ensures that low-cost and low-capacity device usage is possible to ensure practicality and usability for wider stakeholders. We thoroughly investigated the system-level aspects of low-end devices such as Raspberry Pi and Jetson Nano.
-
The data and code are publicly available so that everybody can benefit from them.
-
FedSepsis suggests that incorporating such a concept with low-end computational devices could benefit all medical sector stakeholders and should be explored further.
The concept of the Internet of Medical Things brings a promising option to utilize various electronic health records stored in different medical devices and servers to create practical but secure clinical decision support systems. To achieve such a system, we need to focus on several aspects, most notably the usability aspect of deploying it using low-end devices. This study introduces one such application, namely FedSepsis, for the early detection of sepsis using electronic health records. We incorporate several cutting-edge deep learning techniques for the prediction and natural-language processing tasks. We also explore the multimodality aspect for the better use of electronic health records. A secure distributed machine learning mechanism is essential to building such a practical internet of medical things application. To address this, we analyze two federated learning techniques. Moreover, we use two different kinds of low-computational edge devices, namely Raspberry Pi and Jetson Nano, to address the challenges of using such a system in a practical setting and report the comparisons. We report several critical system-level information about the devices, namely CPU utilization, disk utilization, process CPU threads in use, process memory in use (non-swap), process memory available (non-swap), system memory utilization, temperature, and network traffic. We publish the prediction results with the evaluation metrics area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, the area under the precision–recall curve, and the earliness to predict sepsis in hours. Our results show that the performance is satisfactory, and with a moderate amount of devices, the federated learning setting results are similar to the single server-centric setting. Multimodality provides the best results compared to any single modality in the input features obtained from the electronic health records. Generative adversarial neural networks provide a clear superiority in handling the sparsity of electronic health records. Multimodality with the generative adversarial neural networks provides the best result: the area under the precision–recall curve is 96.55%, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve is 99.35%, and earliness is 4.56 h. FedSepsis suggests that incorporating such a concept together with low-end computational devices could be beneficial for all the medical sector stakeholders and should be explored further.
Please acknowledge the following work in papers or derivative software:
Alam MU, Rahmani R. FedSepsis: A Federated Multi-Modal Deep Learning-Based Internet of Medical Things Application for Early Detection of Sepsis from Electronic Health Records Using Raspberry Pi and Jetson Nano Devices. Sensors. 2023; 23(2):970. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23020970
@Article{s23020970,
AUTHOR = {Alam, Mahbub Ul and Rahmani, Rahim},
TITLE = {FedSepsis: A Federated Multi-Modal Deep Learning-Based Internet of Medical Things Application for Early Detection of Sepsis from Electronic Health Records Using Raspberry Pi and Jetson Nano Devices},
JOURNAL = {Sensors},
VOLUME = {23},
YEAR = {2023},
NUMBER = {2},
ARTICLE-NUMBER = {970},
URL = {https://www.mdpi.com/1424-8220/23/2/970},
ISSN = {1424-8220},
DOI = {10.3390/s23020970}
}