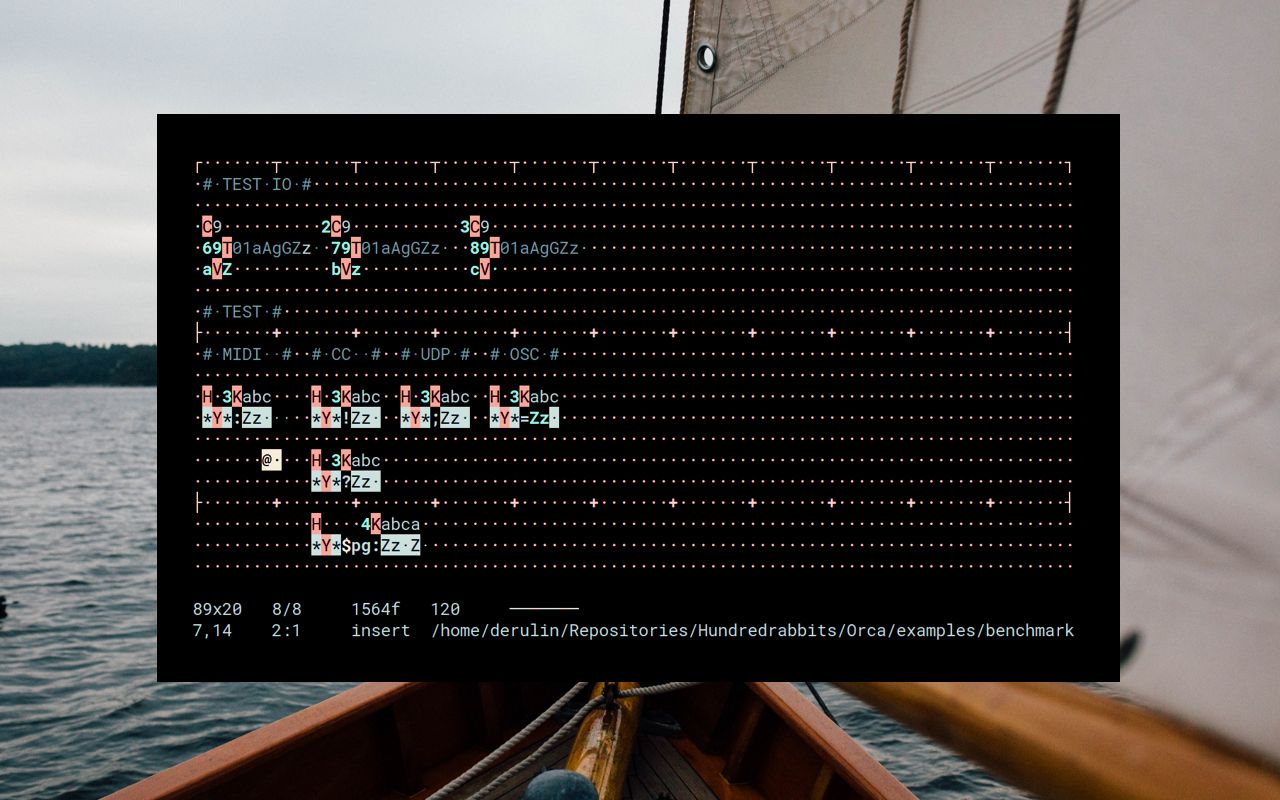
Orca is an esoteric programming language designed to quickly create procedural sequencers, in which every letter of the alphabet is an operation, where lowercase letters operate on bang, uppercase letters operate each frame.
This application is not a synthesizer, but a flexible livecoding environment capable of sending MIDI, OSC & UDP to your audio/visual interfaces, like Ableton, Renoise, VCV Rack or SuperCollider.
If you need help, visit the chatroom or the forum.
This is the C implementation of the ORCΛ language and tools. The livecoding environment for this C version runs in a terminal. It's designed to be power efficient. It can handle large files, even if your terminal is small.
sudo apt-get install git libncurses5-dev libncursesw5-dev libportmidi-dev
git clone https://github.com/hundredrabbits/Orca-c.git
cd Orca-c
make # Compile orca
build/orca # Run orcaTo choose your MIDI output device, press F1 (or Ctrl+D) to open the main menu, and then select MIDI Output...
┌ ORCA ───────────────┐┌ PortMidi Device Selection ─────┐
│ New ││ > (*) #0 - Midi Through Port-0 │
│ Open... ││ ( ) #2 - ES1371 │
│ Save │└────────────────────────────────┘
│ Save As... │
│ │
│ Set BPM... │
│ Set Grid Size... │
│ Auto-fit Grid │
│ │
│ OSC Output... │
│ > MIDI Output... │
│ │
│ Clock & Timing... │
│ Appearance... │
│ │
│ Controls... │
│ Operators... │
│ About ORCA... │
│ │
│ Quit │
└─────────────────────┘
Core library: A C99 compiler (no VLAs required), plus enough libc for malloc, realloc, free, memcpy, memset, and memmove. (Also, #pragma once must be supported.)
Command-line interpreter: The above, plus POSIX, and enough libc for the common string operations (strlen, strcmp, etc.)
Livecoding terminal UI: The above, plus ncurses (or compatible curses library), and floating point support (for timing.) Optionally, PortMidi can be used to enable direct MIDI output.
The build script, called simply tool, is written in bash. It should work with gcc (including the musl-gcc wrapper), tcc, and clang, and will automatically detect your compiler. You can manually specify a compiler with the -c option.
Currently known to build on macOS (gcc, clang, tcc) and Linux (gcc, musl-gcc, tcc, and clang, optionally with LLD), and Windows via cygwin or WSL (gcc or clang, tcc untested).
There is a fire-and-forget make wrapper around the build script.
PortMidi is an optional dependency. It can be enabled by adding the option --portmidi when running the tool build script.
Mouse awareness can be disabled by adding the --no-mouse option.
Run ./tool help to see usage info. Examples:
./tool build -c clang-7 --portmidi orca
# Build the livecoding environment with a compiler
# named clang-7, with optimizations enabled, and
# with PortMidi enabled for MIDI output.
# Binary placed at build/orca
./tool build -d orca
# Debug build of the livecoding environment.
# Binary placed at build/debug/orca
./tool build -d cli
# Debug build of the headless CLI interpreter.
# Binary placed at build/debug/cli
./tool clean
# Same as make clean. Removes build/make release # optimized build, binary placed at build/orca
make debug # debugging build, binary placed at build/debug/orca
make clean # removes build/The make wrapper will enable --portmidi by default. If you run the tool build script on its own, --portmidi is not enabled by default.
Usage: orca [options] [file]
General options:
--undo-limit <number> Set the maximum number of undo steps.
If you plan to work with large files,
set this to a low number.
Default: 100
--initial-size <nxn> When creating a new grid file, use these
starting dimensions.
--bpm <number> Set the tempo (beats per minute).
Default: 120
--seed <number> Set the seed for the random function.
Default: 1
-h or --help Print this message and exit.
OSC/MIDI options:
--strict-timing
Reduce the timing jitter of outgoing MIDI and OSC messages.
Uses more CPU time.
--osc-midi-bidule <path>
Set MIDI to be sent via OSC formatted for Plogue Bidule.
The path argument is the path of the Plogue OSC MIDI device.
Example: /OSC_MIDI_0/MIDI
$ ./tool build --portmidi orca # compile orca using build script
$ build/orca # run orca┌ Controls ───────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Ctrl+Q Quit │
│ Arrow Keys Move Cursor │
│ Ctrl+D or F1 Open Main Menu │
│ 0-9, A-Z, a-z, Insert Character │
│ ! : % / = # * │
│ Spacebar Play/Pause │
│ Ctrl+Z or Ctrl+U Undo │
│ Ctrl+X Cut │
│ Ctrl+C Copy │
│ Ctrl+V Paste │
│ Ctrl+S Save │
│ Ctrl+F Frame Step Forward │
│ Ctrl+R Reset Frame Number │
│ Ctrl+I or Insert Append/Overwrite Mode │
│ ' (quote) Rectangle Selection Mode │
│ Shift+Arrow Keys Adjust Rectangle Selection │
│ Alt+Arrow Keys Slide Selection │
│ ` (grave) or ~ Slide Selection Mode │
│ Escape Return to Normal Mode or Deselect │
│ ( ) _ + [ ] { } Adjust Grid Size and Rulers │
│ < and > Adjust BPM │
│ ? Controls (this message) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
The CLI (cli binary) reads from a file and runs the orca simulation for 1 timestep (default) or a specified number (-t option) and writes the resulting state of the grid to stdout.
cli [-t timesteps] infileYou can also make cli read from stdin:
echo -e "...\na34\n..." | cli /dev/stdin