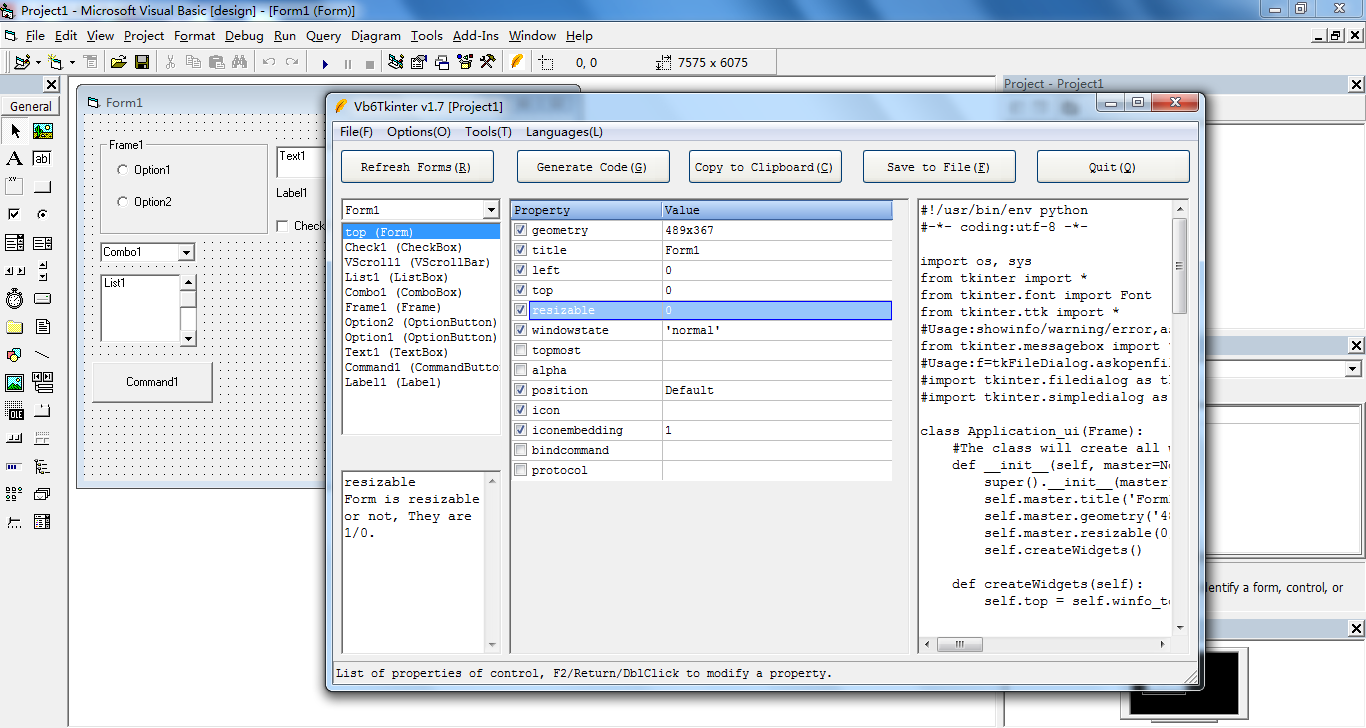
The program is an addin for VB6, It allows you design your GUI layout of Tkinter (standard GUI library of Python) in VB6 Integrated Development Environment. The addin will generate python code of GUI framework for you. the only thing you need to do is that add your logical code in Callback of GUI framework.
This tool supports the majority of TKinter widgets, making it suitable for most GUI requirements. (List of widgets can be found in the section "List of VB Controls Supported" below).
Suitable for those who have learned TKinter and prefer not to manually write GUI code, without relying on third-party tools or frameworks like wxPython/PyQt.
Ideal for small program development with relatively simple UI; for complex interfaces, frameworks like wxPython/PyQt are more suitable.
As TKinter is part of the Python standard library, programs developed with TKinter can be considered "green software" or "portable software", They don't require the installation of third-party frameworks like wxPython/PyQt on the target machine. as long as Python is present, the program can run. Even when packaged into executables using tools like pyinstaller/cx_freeze, the final files remain relatively small.
If software logic is not overly complex, typically handled with a single .py file.
(If you don't want a command prompt window to pop up during direct interpretation of the .py file, change the extension to .pyw)
There are two methods, choose either:
-
Integrated Installation:
Download the pre-integrated and pre-patched VB6 nano installer at https://github.com/cdhigh/Vb6Tkinter/releases, Double-click to execute the installation, Do not need the operations in the following section. -
Standalone Installation:
2.1. Download the addin from https://github.com/cdhigh/Vb6Tkinter/releases extract it to a directory. 2.2. Install VB6 independently, either the complete version or a lite/nano version.
2.2.1. In Windows 7 and newer, please install VB6 SP6 version and overwrite VB6.EXE using Vb6_SP6_Fix_for_Win7.zip.
2.2.2. In Windows 10 and newer, please apply VB6_AppCompat.
2.3. Register the addin using the provided registration tool "Setup for Vb6Tkinter.exe" or manually:
2.3.1. Runregsvr32 /s directory\Vb6Tkinter.dll.
2.3.2. Add a line in the [Add-Ins32] section of C:\Windows\VBADDIN.INI:
Vb6Tkinter.Connect=3 -
Once the addin have been installed and registered, future updates can be done by simply downloading the new versions of Vb6Tkinter.dll/Vb6Tkinter.lng and overwriting the existing files.
-
Open VB6 and create a new standard EXE project. Design your GUI layout on the form. This task should be easy even for those without experience in VB6. Don't forget to set the corresponding control properties. If you prefer a non-resizable window, consider changing the VB6 form's "BorderStyle" property to "Fixed Single" or "Fixed Dialog".
-
If the addin is registered properly, you should now see a new icon (an orange-red feather) on the VB toolbar. If not, navigate to "Add-Ins" | "Add-In Manager" and launch Vb6Tkinter from there. The Vb6Tkinter icon and menu should appear accordingly.
-
After launching Vb6Tkinter, click the "Refresh Forms" button to display all forms and controls in the current project.
-
Review each control's properties, checking the desired options. If needed, double-click on a property in the list to modify its value. Typically, there's no need for additional modifications to control properties. Vb6Tkinter try it's best to translate VB control properties into Tkinter properties, covering aspects like font, color, initial value, appearance, and state. It even includes settings for buttons and menu shortcuts. If certain properties lack a direct correspondence, adjustments may be necessary within the Vb6Tkinter interface.
-
Click the "Generate Code" button to produce code in the code preview window. You can either double-click on the code preview window to view it in detail or make direct modifications to the code.
-
Once confirmed, copy the code to the clipboard or save it to a file. Layouts can utilize percentage-based (relative) or absolute coordinate-based (pixel) positioning. The advantage of percentage positioning is that controls can adjust relative to changes in the main interface size. For a fixed layout, opt for absolute coordinate positioning. Note: If altering a previously designed UI, consider outputting only the ui class to avoid affecting existing external logic code.
-
In the case of multiple GUI dialog/form application, add forms within the VB project. This allows you to select which form to generate code.
-
Regarding structured code, if you need to reference and modify other widgets values in Python, use the global dictionary gComps. This dictionary stores all GUI elements and some corresponding control variables. Access widgets directly using code like gComps["Text1Var"].set("new Text"). For object-oriented code, access widgets directly in the derived class Application using self.widgetName.
-
GUI frameworks typically segregate UI and logic code into different files. In logic code files, import the UI file to ensure UI modifications don't impact the logic. While many prefer this separation, for simpler programs, I've chosen to keep both the UI class and logic code class in the same file. After modifying the interface, overwrite the corresponding Application_ui class to implement interface changes. If new event callback functions are added, remember to include them in the subclass Application.
-
Form
The VB6 window (Form) corresponds to Tkinter's Frame, serving as the main interface presentation. For a more polished appearance, it's recommended to set the VB6 Form's BorderStyle property to "Fixed Single" or "Fixed Dialog." -
Label
Label in VB and Python is essentially the same. Line breaks can be achieved by inserting "\n" in the text, and with ttk enabled(default), the wraplength property becomes available. -
TextBox
Python offers two types of text boxes: Entry and Text. If VB's TextBox has property MultiLine=False, it generates an Entry; otherwise, it produces a Text. -
Frame
Corresponding to Python's LabelFrame widget, the Frame acts as a container for other controls or visually classifies interface elements.
A LabelFrame will be placed if the property "Caption" is not empty, otherwise, will be a Frame. -
CommandButton Corresponding to Python's Button with minimal differences. For concise code, setting the Cancel property to True for the form's exit button generates the Tkinter destroy callback, eliminating the need for a separate callback function. In VB, prefixing a letter with "&" directly binds a shortcut key 'Alt + corresponding letter'(forexample &A). Vb6Tkinter supports this, automatically generating the associated event binding code. The same approach applies to other controls with a "Caption" property, such as CheckBox.
-
CheckBox The CheckBox corresponds to Python's Checkbutton.
-
OptionButton The OptionButton corresponds to Python's Radiobutton. The grouping method for Radiobuttons in tkinter differs slightly from VB (grouping implies mutual exclusivity; selecting one automatically deselects others). In VB, placing several OptionButtons within a Frame automatically groups them, a feature supported by Vb6Tkinter. For manual handling, set the variable property of Radiobuttons in the same group to the same variable. Ensure that the value property of each Radiobutton is unique (default is the control name). Setting different values (e.g., 1/2/3 or "man"/"woman") ensures that when a Radiobutton is selected, the variable is set to the corresponding value. Reading the variable indicates the selected Radiobutton, and vice versa, setting the variable selects the corresponding Radiobutton.
-
ComboBox
There is no direct equivalent for ComboBox in Tkinter legacy. The closest match is OptionMenu, behaving similarly to a VB ComboBox with Style=2 (Dropdown List)—a list where you can only choose from provided values and cannot input directly. Hence, it's advisable to list all dropdown values in VB's ComboBox. If TTK theme extension library support is enabled (default enabled), it directly corresponds to TTK's Combobox with a similar appearance and behavior. -
ListBox
The ListBox corresponds to Python's Listbox, behaving similarly, and allowing the setting of an initial list during design. If scrolling is required, create a scrollbar at an appropriate position. If the scrollbar is close to the right or bottom of the ListBox, and the length (horizontal scrollbar) or height (vertical scrollbar) is roughly similar, the scrollbar and ListBox are automatically bound. If not automatically bound, you can select its xscrollcommand or yscrollcommand properties in the Addin interface to correspond to the set method of the respective scrollbar. -
HScrollBar, VScrollBar
Scrollbars in Python are Scrollbar, with orientation controlled by the orient property. -
PictureBox
Roughly corresponds to Canvas in Python, serving as a container for other controls or as a drawing container. If scrolling is needed, create a scrollbar at an appropriate position. If the scrollbar is close to the right or bottom of the PictureBox, and the length (horizontal scrollbar) or height (vertical scrollbar) is roughly similar, the scrollbar and PictureBox are automatically bound. If not automatically bound, you can choose its xscrollcommand and yscrollcommand properties in the Addin interface to correspond to the set method of the respective scrollbar. -
Menu
You can use VB's menu editor to design menus in Python. In VB, setting the menu title to "-" creates a separator. You can also add Alt shortcuts to normal menu titles using the format (&+letter). Apart from Alt shortcuts, choosing a shortcut key for the menu in the VB menu editor will display the shortcut key information directly after the menu title and automatically bind the corresponding command. -
Line
This can be used to organize complex interfaces and supports only horizontal or vertical lines.
Adding the component 'Microsoft Windows Common Controls 6.0' to toolbox of VB IDE to support the following controls.
-
Slider
Similar to Python's Scale, it corresponds to the Slider control in VB. To use, add it from the 'Control Toolbox' in VB by right-clicking, selecting 'Components,' and choosing "Microsoft Windows Common Controls 6.0." -
ProgressBar
Corresponds to Python's Progressbar. Enable TTK theme extension (default) and add it from the 'Control Toolbox' in VB by right-clicking, selecting 'Components,' and choosing "Microsoft Windows Common Controls 6.0." -
TreeView
Corresponds to Python's Treeview, a tree-like display control. You can choose whether to display header rows. Enable TTK theme extension (default) and add it from the 'Control Toolbox' in VB by right-clicking, selecting 'Components,' and choosing "Microsoft Windows Common Controls 6.0." If scrolling is required, create a scrollbar at an appropriate position. If the scrollbar is close to the right or bottom of the TreeView, and the length (horizontal scrollbar) or height (vertical scrollbar) is roughly similar, the scrollbar and TreeView are automatically bound. If not, you can select its xscrollcommand and yscrollcommand properties in the Addin interface to correspond to the set method of the respective scrollbar. -
TabStrip
The TabStrip control, corresponding to Python's Notebook, requires TTK theme extension (default). To layout controls within each page: -
Each tab corresponds to a Frame or PictureBox, named: TabStrip's name +
__Tab(double underscore) + a number starting from 1 (e.g., if the TabStrip's name is TabStrip1, you can create a PictureBox namedTabStrip1__Tab1). -
Place other controls you need within the PictureBox/Frame. After generating the code, this container is automatically added to the corresponding tab. Vb6Tkinter handles this behind the scenes. Tab pages' PictureBox/Frame can be placed outside the visible range of the form. Once you've designed the corresponding tab, resize the form in the IDE to your desired size. Note: - If using relative coordinates, make sure the PictureBox or Frame container's size matches or is close to the size inside the TabStrip. Otherwise, the controls inside the tab may stretch or shrink to fit the available space, leading to an odd appearance. If using absolute coordinates, the PictureBox/Frame doesn't need to be the same size as the TabStrip, and the controls inside will be placed with the top-left corner of the TabStrip as the origin, maintaining the same proportions as designed. Therefore, it's recommended to use absolute coordinates if you have a TabStrip control.
-
CommonDialog
This control is also supported. If your VB form contains this control, you can import the filedialog, simpledialog, and colorchooser modules in Python. These modules provide simple file selection, input box, and color selection dialog functions. Add the "Microsoft Common Dialog Control 6.0" from the 'Control Toolbox' in VB by right-clicking, selecting 'Components,' and choosing "Microsoft Windows Common Controls 6.0."
-
Since tkinter lacks a Statusbar control, I have implemented a simple Statusbar using a Label. After adding a Statusbar to the VB form, the corresponding implementation code will be inserted. (VB needs to add the "Microsoft Windows Common Controls 6.0" component to have a Statusbar).
-
As tkinter widgets do not have a Tooltip property, I have implemented a basic Tooltip class to add Tooltip functionality to tkinter controls. Setting the ToolTipText property of VB controls will automatically create a Tooltip class for the corresponding widget. ToolTipText supports automatic line breaks, and if manual control is needed, '\n' can be used.
-
The application hides the counterintuitive TK control setting and retrieving mechanism for displaying values (requires the use of control variable textvariable). For Entry/Label/Button/Checkbutton/Radiobutton controls, more intuitive
setText()andtext()methods have been added for directly setting and retrieving the displayed text values of the controls. (Checkbutton/Radiobutton are not added by default. If needed, you can check the textvariable in Vb6Tkinter, as these two controls rarely require runtime modification of text). -
Similar to the third point,
setValue()andvalue()methods have been added for Checkbutton/Radiobutton, with parameters 1/0.self.Text1.setText('new text') print(self.Text1.text()) print(self.Check1.value()) self.Option1.setValue(1) print(self.Option1.value())
- One of the features I love most about the VB IDE's form designer is the "Format" menu. By selecting multiple controls, you can easily set their size, alignment, and relative positions using this menu. Leveraging this functionality in UI design is not only effortless but also results in a more aesthetically pleasing UI.
- Align: Left, top, etc.
- Make same size: width, height, both the same.
- Horizontal Spacing: Equal, increase, decrease, etc.
- Vertical Spacing: Equal, increase, decrease, etc.
- Center in Form: Horizontally, vertically.
-
The addin does not support the use of control arrays. While the UI can display them, subsequent controls with the same name will overwrite the previously defined ones, making it impossible to interact with these controls in the code.
-
It is recommended to keep the default value (vbTwips) for the ScaleMode property of VB forms. If you need to set it to another value, avoid placing Frame controls inside other Frame controls, as this may lead to layout errors for the controls within.
-
For a Simplified Chinese addin interface, the Vb6Tkinter.lng file should be in the same directory as Vb6Tkinter.dll.
-
GUI design often requires multiple iterations. If certain properties deviate from the default values generated by Vb6Tkinter, there's a risk of forgetting to update them during subsequent modifications, potentially causing GUI errors. To address this, you can update the corresponding control's
Tagproperty using one of the following formats:
p@property1@property2@propertyNp@property1=value1@property2=value2@propertyN=valueN
In this notation, you can omit the value of any property. When a value is omitted, the corresponding property is automatically selected without altering its value.
- The addin offers additional convenient features scattered throughout its version changelog. Here, we won't list them all, but those interested can explore them as needed.
The standard built-in ttk themes extension provides native style on different operating systems. It is recommended for use, but be aware of the following ttk bugs:
- Setting the background color for TTK's Entry and Combobox controls is ineffective (you can set it without errors, but the interface remains unchanged).
- Individually setting the font for LabelFrame and Notebook controls has no effect, but you can use ttk's global font attributes to change it, for example:
self.style.configure('.', font=('Arial', 12)).
- v1.9
- Supported I18N feature (gettext)
- v1.8.1
- Frame of VB will be translated to LabelFrame or Frame of tkinter automatically.
- v1.8
- Generate oop code only.
- Add an interpretation of property (MultiSelect -> selectmode) of ListBox.
- v1.7.2
- bugfix: Cannot preview structured code.
- v1.7.1
- The 'Change' event of the Combobox is mapped to 'ComboboxSelected'.
- The 'Change' event of the multi-line Text is mapped to 'Modified'.
- Bugfix: a minor bug in the base64 encoding where the padding = at the end was removed, causing some decoding libraries to throw errors.
- Bugfix: a part of the generated status bar code was missing.
- v1.7
- Rename the add-in from TkinterDesigner to Vb6Tkinter.
- Add check update feature.
- If only Python3 code is required, generate better Python3-style code.
- By default, disable the option "Compatibile with Python 2/3 code".
- v1.6.8
- Translate the click event of Notebook widget to the <> event.
- v1.6.7
- If the form is set to the center of the screen, move the code for setting the position of the form to the beginning of the initialization function to avoid a moving process of the form at startup.
- Remove some hints in generated code.
- v1.6.6
- If a file named "icon.gif" is found in the same directory, it will be automatically set as the form icon.
- v1.6.5
- Save generated code to file directly when size is larger than 65k.
- v1.6.4
- Auto generate <> bind command for Listbox if Click method found in VB code.
- v1.6.3
- Can set 'checked' for one of Radiobuttons by default.
- v1.6.2
- Added feature of Tooltip.
- v1.6.1
- Added setValue()/value() to Checkbutton/Radiobutton.
- v1.6
- Added setText()/text() method to Entry/Label/Button/Checkbutton/Radiobutton
- v1.5.2
- value of RadioButton changed to it's name.
- v1.5.1
- bugfix: Reference of some variable before defined.
- Name of variable of RadioButton changed to 'ParentName' + 'RadioVar'.
- Save code file to disk using format utf-8 (no BOM).
- v1.5
- feature added: encode a file to Base64 string.
- v1.4.13
- Change codeline of judge of python's version for better compatibility.
- v1.4.12
- combox don't need property 'height' or 'relheight'.
- v1.4.11
- change the map of event 'xxx_MouseMove' to ' in tkinter.
- v1.4.10
- properties tag of form is working now.
- v1.4.9
- bugfix: decimal seperator from comma to point in latin language.
- v1.4.6
- Setup the coordinate of form in VB.
- set the font and color of caption of labelframe.
- v1.4.5 1.Add a property 'scrollregion' to Canvas.
- v1.4.4
- Its a minor bugfix version.
- v1.4.3
- use properties tag of widgets to save same config. format is p@property1@property2 or p@property1=value1@property2=value2
- Add a property 'startup position' to Form.
- v1.4.2
- bugfix:error when change the widget before update the configure of widget.
- add properties spacing1, spacing2, spacing3 to widget 'Text'.
- v1.4.1
- Support scrollbar bind with widgets automatic.
- Control-Variable of Checkbutton changed to IntVar.
- textvariable of Combobox selected defaultly.
- v1.4
- Can used in VB6 green and compact version.
- v1.3.3
- Add properties 'Topmost' and 'Alpha' for Form.
- v1.3.2
- Support icon file without suffix.
- Add property 'cursor'.
- v1.3.1
- Bind callback functions via analysing VB code.
- Can configure widget OptionMenu now.
- v1.3
- Add a feature the allow design all tabs of Notebook widget in VB IDE. refer to description of TabStrip.
- Can add a lambda function in callback field.
- bugfix: add a wrong 'DeletE' event when you set the shortcut is 'Delete'.
- bugfix: substitute Combobox for OptionMenu widget when ttk is disabled.
- bugfix: some text disaperence when first time of display of dropdown.
- v1.2.8
- Add a process for banding of scrollbar and listbox/canvas/text widgets.
- v1.2.7
- Add family name of font to properties of widgets. (if need)
- improve the apparence of XP-Style button.
- v1.2.6
- Add feature 'preview'.
- Delete all settings saved in register when uninstall the addin.
- Substitute a XP-Style button control for shade-button.
- v1.2.5
- Add a option 'Add a prefix u to unicode string'.
- Bugfix: can't generate code for menu.
- the mainform is resizeable now, and substitute a shade-button for standard-button.
- v1.2.4 Widget Notebook create tabs as same of TabStrip(VB)
- v1.2.3
- Add a property 'protocol' to Form.
- Delete the option 'Build file for XP style of VB6.EXE', you can do it youself by using google. the keyword is 'vb xp manifest' etc.
- v1.2.2 Provide a combobox to choose some value in it.
- v1.2 1.Supports feature multi-language. 2.Add supports of Statusbar. 3.Add properties of Form, such as icon etc.
- v1.1 1.Add supports to TTK library. 2.Add supports to widget Progressbar, Treeview, Notebook. 3.Update setup program, can uninstall the addin now.
- v1.0 First version Supports : Label, Entry, LabelFrame, Button, Checkbutton, Radiobutton, OptionMenu, Combobox, Listbox, Scrollbar, Scale, Canvas, Menu