This fork of RNNLG adds Python3 compatibility and various bits of formatting and documentation updated.
The original RNNLG is an open source benchmark toolkit for Natural Language Generation (NLG) in spoken dialogue system application domains. It is released by Tsung-Hsien (Shawn) Wen from Cambridge Dialogue Systems Group under Apache License 2.0.
Naturally, this version with updates from David M. Howcroft, are released under the Apache License 2.0 as well.
If you want an overview of the methods used in this codebase, check out Shawn's tutorial from INLG 2016 (PDF).
The original repo requires:
* Theano 0.8.2 and accompanying packages such as numpy, scipy ...
* NLTK 3.0.0
Note, however, that I use Theano 1.0 (and pygpu 0.7.6) for my own development, as noted in the Pipfile.
The Pipfile included in this repo also lists further packages which I am using in my development environment. If you are using Pipenv and use this list of dependencies, you may want to check if everything listed is necessary for your setup.
Each example in the file is represented as a 3-element list:
* [MR/Dialogue Act, Human Authored Response, HDC baseline]
For more detail of how the datasets were collected, please refer to Wen et al, 2015b and Wen et al, 2016.
The toolkit encloses the following four benchmark datasets:
* data/original/restaurant/ : San Francisco restaurant search
* data/original/hotel/ : San Francisco hotel search
* data/original/laptop/ : Laptop sale/search
* data/original/tv/ : Television sale/search
and the counterfeited datasets produced in Wen et al, 2016:
* data/counterfeit/r2h/ : Restaurant to hotel counterfeited dataset
* data/counterfeit/h2r/ : Hotel to restaurant counterfeited dataset
* data/counterfeit/l2t/ : Laptop to TV counterfeited dataset
* data/counterfeit/t2l/ : TV to laptop counterfeited dataset
* data/counterfeit/r+h2l+t/ : Restaurant/hotel to laptop/TV ...
* data/counterfeit/l+t2r+h/ : Laptop/TV to restaurant/hotel ...
as well as some union of domains:
* data/union/r+h/
* data/union/l+t/
* data/union/r+h+l/
* data/union/r+h+l+t/
I am working on using RNNLG with the E2E Challenge dataset, so you may see files related to this added to the repo.
The toolkit is implmented in Python. The training of the neural networks is implemented in Theano library, while the decoding is implemented in Numpy for runtime efficiency.
Note that, since 2017, Theano is no longer developed or maintained, so you may want to reimplement these models in a different NN framework.
The toolkit supports several RNN-based generators as well as several baselines:
* Model
- (knn) kNN generator:
k-nearest neighbor example-based generator, based on MR similarty.
- (ngram) Class-based Ngram generator [Oh & Rudnicky, 2000]:
Class-based language model generator by utterance class partitions.
- (hlstm) Heuristic Gated LSTM [Wen et al, 2015a]:
An MR-conditioned LSTM generator with heuristic gates.
- (sclstm) Semantically Conditioned LSTM [Wen et al, 2015b]:
An MR-conditioned LSTM generator with learned gates.
- (encdec) Attentive Encoder-Decoder LSTM [Wen et al, 2015c]:
An encoder-decoder LSTM with slot-value level attention.
* Training Strategy
- (ml) Maximum Likehood Training, using token cross-entropy
- (dt) Discriminative Training (or Expected BLEU training) [Wen et al, 2016]
* Decoding Strategy
- (beam) Beam search
- (sample) Random sampling
Below are configuration parameters explained by sections:
* [learn]
- lr : learning rate of SGD.
- lr_decay : learning rate decay.
- lr_divide : the maximum number of times when validation gets worse.
for early stopping.
- beta : regularisation parameter.
- random_seed : random seed.
- min_impr : the relative minimal improvement allowed.
- debug : debug flag
- llogp : log prob in the last epoch
* [train_mode]
- mode : training mode, currently only support 'all'
- obj : training objective, 'ml' or 'dt'
- gamma : hyperparameter for DT training
- batch : batch size
* [generator]
- type : the model type, [hlstm|sclstm|encdec]
- hidden : hidden layer size
* [data]
- domain : application domain
- train/valid/test: dataset operated on
- vocab : vocabulary
- percentage : the percentage of train/valid considered
- wvec : pretrained word vectors
- model : the produced model path
* [gen]
- topk : the N-best list returned
- overgen : number of over-generation
- beamwidth : the beam width used to decode utterances
- detectpairs : the mapping file for calculating the slot error rate
- verbose : verbose level of the model, not supported yet
- decode : decoding strategy, 'beam' or 'sample'
Below are knn/ngram specific parameters:
* [ngram]
- ngram : the N of ngram
- rho : number of slots considered to partition the dataset
To run ML training:
python main.py -config config/sclstm.cfg -mode train
To run generation:
python main.py -config config/sclstm.cfg -mode test
To run ngram/knn baselines:
python main.py -config config/ngram.cfg -mode ngram
python main.py -config config/knn.cfg -mode knn
To run training/adaptation/DT training/fine-tuning on an existing model
python main.py -config config/sclstm-DT.cfg -mode adapt
Note : before you run anything, make sure the config vars are properly set.
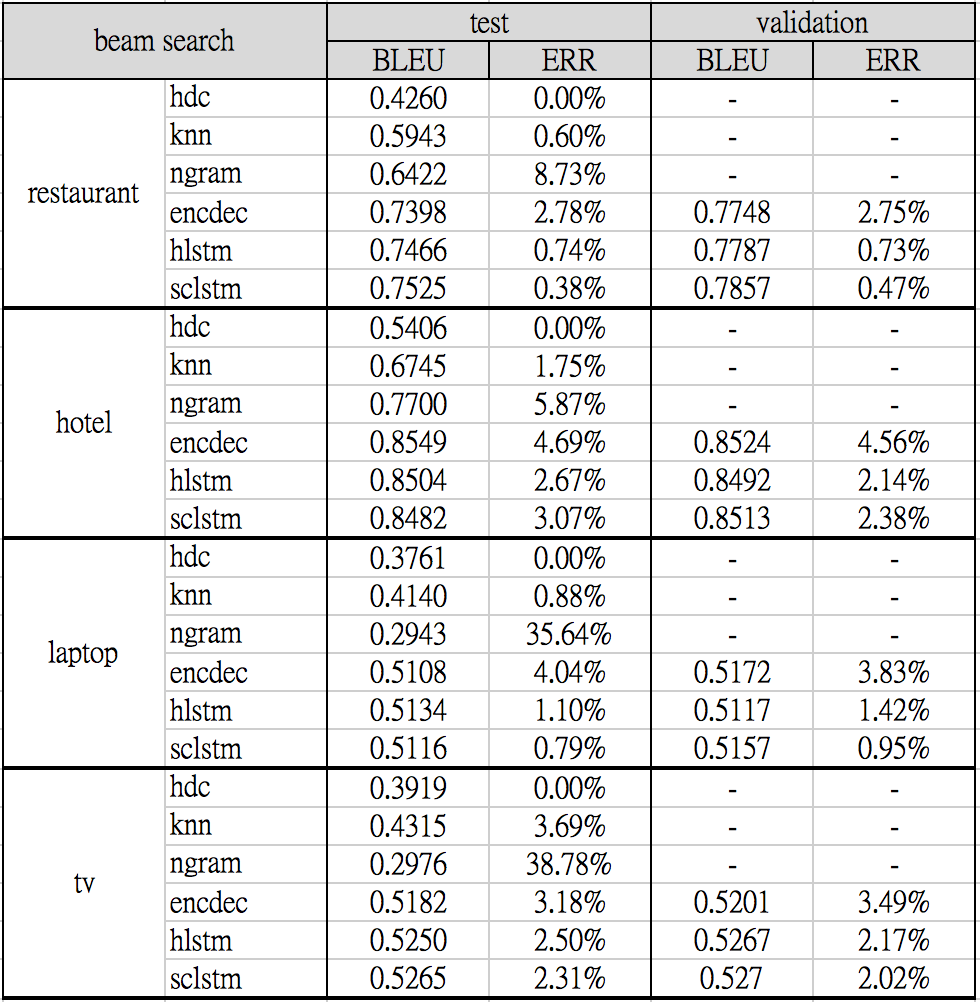
The following benchmark results were produced by training each neural network model on 5 different random seeds (1-5) and selected models with the best validation BLEU score. Both the testing and validating set performance are shown:
The original repo suggested contacting Shawn directly at his Cambridge email address with bug reports, but for this fork I am happy to accept issues and pull requests on GitHub.
This work was the byproduct of academic research. Depending on which models you use, you should cite or link to the following publications when using one of the models.
[Wen et al, 2016]:
@inproceedings{wenmultinlg16,
Author = {Wen, Tsung-Hsien and Ga{\v{s}}i\'c, Milica and Mrk{\v{s}}i\'c, Nikola and M. Rojas-Barahona, Lina and Su, Pei-Hao and Vandyke, David and Young, Steve},
title={Multi-domain Neural Network Language Generation for Spoken Dialogue Systems},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL)},
year={2016},
month={June},
publisher={Association for Computational Linguistics},
location={San Diego, USA}
}
[Wen et al, 2015a]:
@INPROCEEDINGS{
thwsjy15,
Author = {Wen, Tsung-Hsien and Ga{\v{s}}i\'c, Milica and Kim, Dongho and Mrk{\v{s}}i\'c, Nikola and Su, Pei-Hao and Vandyke, David and Young, Steve},
Title = {{Stochastic Language Generation in Dialogue using Recurrent Neural Networks with Convolutional Sentence Reranking}},
Year = {2015},
month={September},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 16th Annual Meeting of the Special Interest Group on Discourse and Dialogue (SIGDIAL)},
publisher={Association for Computational Linguistics},
location={Prague, Czech Republic}
}
[Wen et al, 2015b]:
@inproceedings{wensclstm15,
Author = {Wen, Tsung-Hsien and Ga{\v{s}}i\'c, Milica and Mrk{\v{s}}i\'c, Nikola and Su, Pei-Hao and Vandyke, David and Young, Steve},
title={Semantically Conditioned LSTM-based Natural Language Generation for Spoken Dialogue Systems},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 2015 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP)},
year={2015},
month={September},
publisher={Association for Computational Linguistics},
location={Lisbon, Portugal}
}
[Wen et al, 2015c]:
@article{wenmlsds16,
Author = {Wen, Tsung-Hsien and Ga{\v{s}}i\'c, Milica and Mrk{\v{s}}i\'c, Nikola and M. Rojas-Barahona, Lina and Su, Pei-Hao and Vandyke, David and Young, Steve},
title={Toward Multi-domain Language Generation using Recurrent Neural Networks},
journal={NIPS Workshop on Machine Learning for Spoken Language Understanding and Interaction},
year={2015},
month={Dec},
location={Montreal, Canada}
}
Of course, if you use this codebase for your own system rather than the original repo, it makes sense to link to this repository in your papers or websites.